
Multipolar neuron
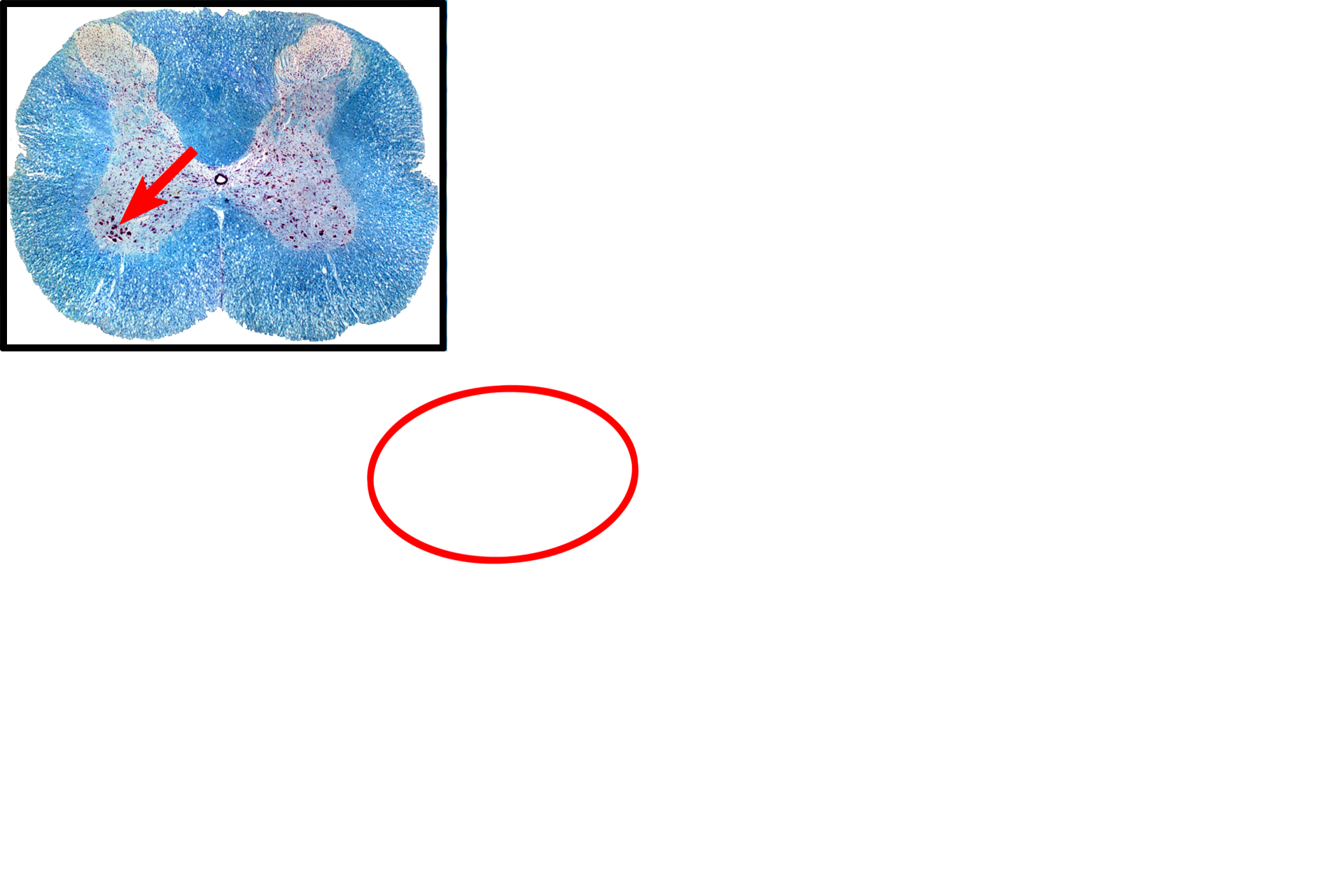
Multipolar neurons possess numerous processes which arise from a polygonal cell body. The multiple dendrites contain Nissl substance and branch at acute angles. The single axon arises from the axon hillock, a region of the cell body with reduced organelle content. Axons lack Nissl and are usually ensheathed by support cells. Kluver-Barrera stain 400x
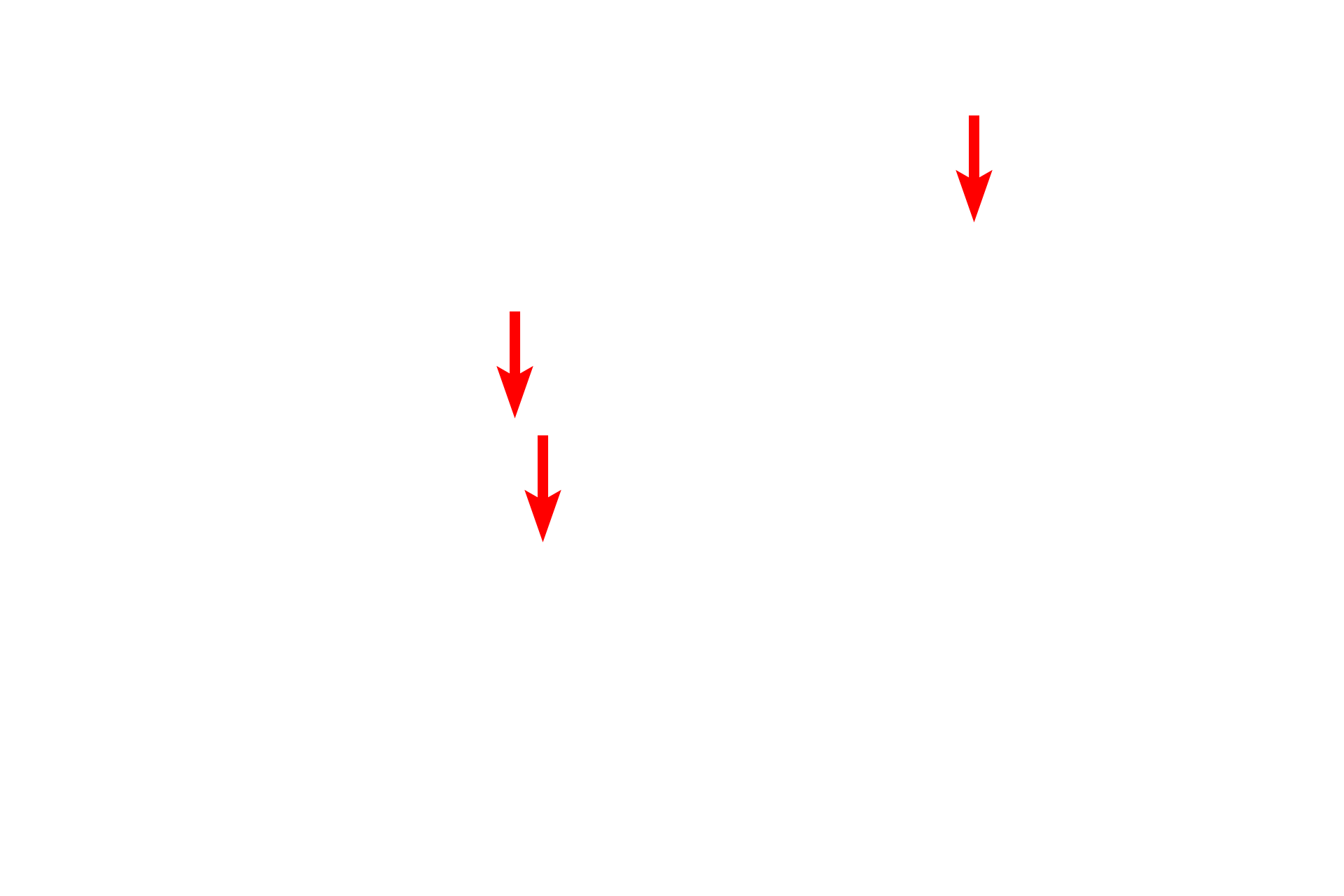
Cell body >
The cell body of a neuron houses the nucleus and is the major synthetic region of the neuron. The nucleus of most nerve cells is large and very euchromatic with a prominent nucleolus. These features reflect the intense protein synthetic activity of these cells. The inset shows a low magnification of the spinal cord and indicates the position of this neuron.

- Nucleus
The cell body of a neuron houses the nucleus and is the major synthetic region of the neuron. The nucleus of most nerve cells is large and very euchromatic with a prominent nucleolus. These features reflect the intense protein synthetic activity of these cells. The inset shows a low magnification of the spinal cord and indicates the position of this neuron.

- Nucleolus
The cell body of a neuron houses the nucleus and is the major synthetic region of the neuron. The nucleus of most nerve cells is large and very euchromatic with a prominent nucleolus. These features reflect the intense protein synthetic activity of these cells. The inset shows a low magnification of the spinal cord and indicates the position of this neuron.

- Axon hillock >
The axon hillock is a specialized region of the cell body that lack basophilia and is the site of origin for the axon.
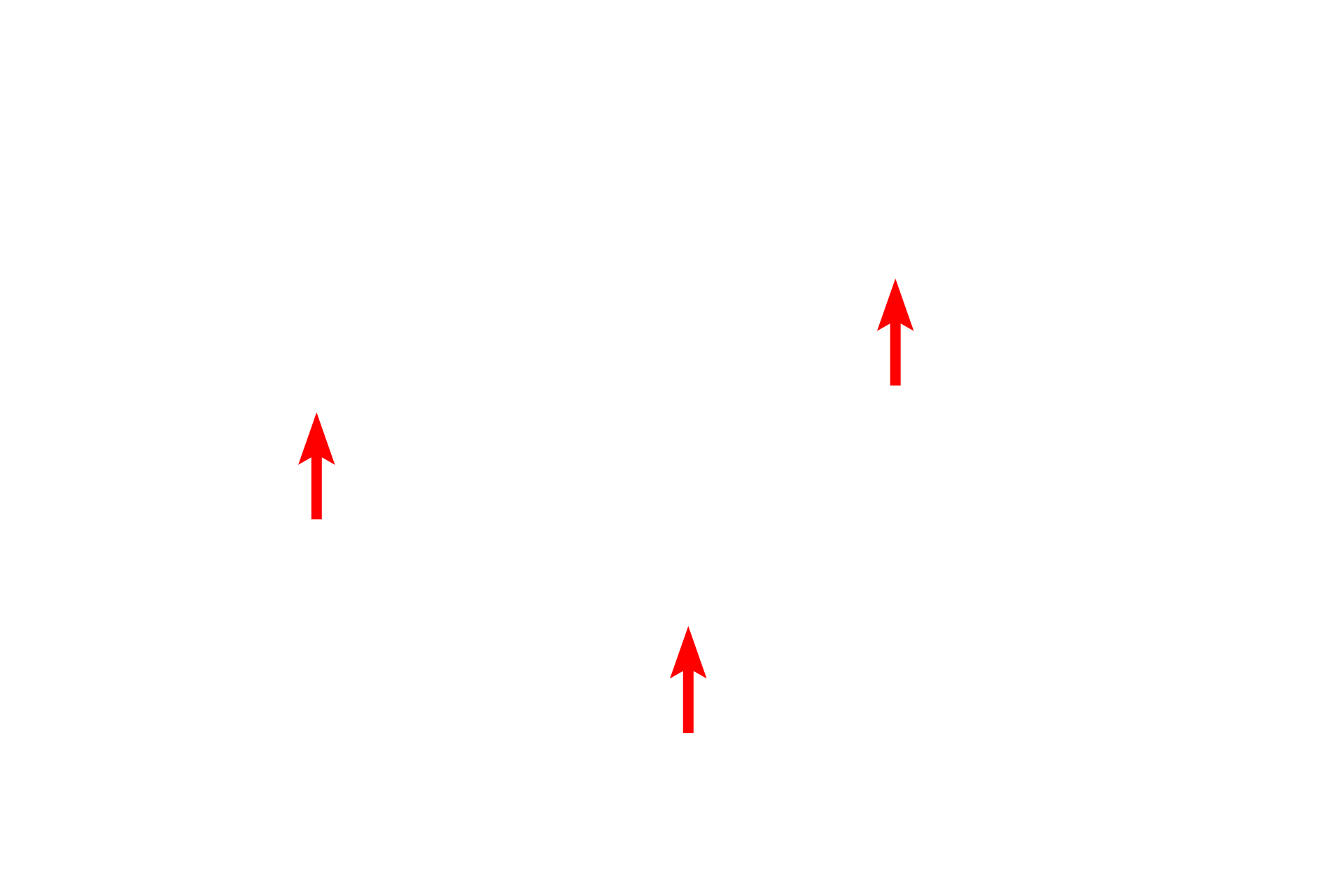
Nissl substance >
Nissl substance is an accumulation of RER and polysomes in neuronal cell bodies and dendrites. The presence of Nissl is one characteristic of dendrites which discriminates them from axons.
Dendrites >
Multiple dendrites can be seen, containing Nissl bodies, which are large accumulations of rough endoplasmic reticulum and polyribosomes. The presence of these basophilic Nissl bodies distinguishes dendrites from axons. Dendrites branch at acute angles.
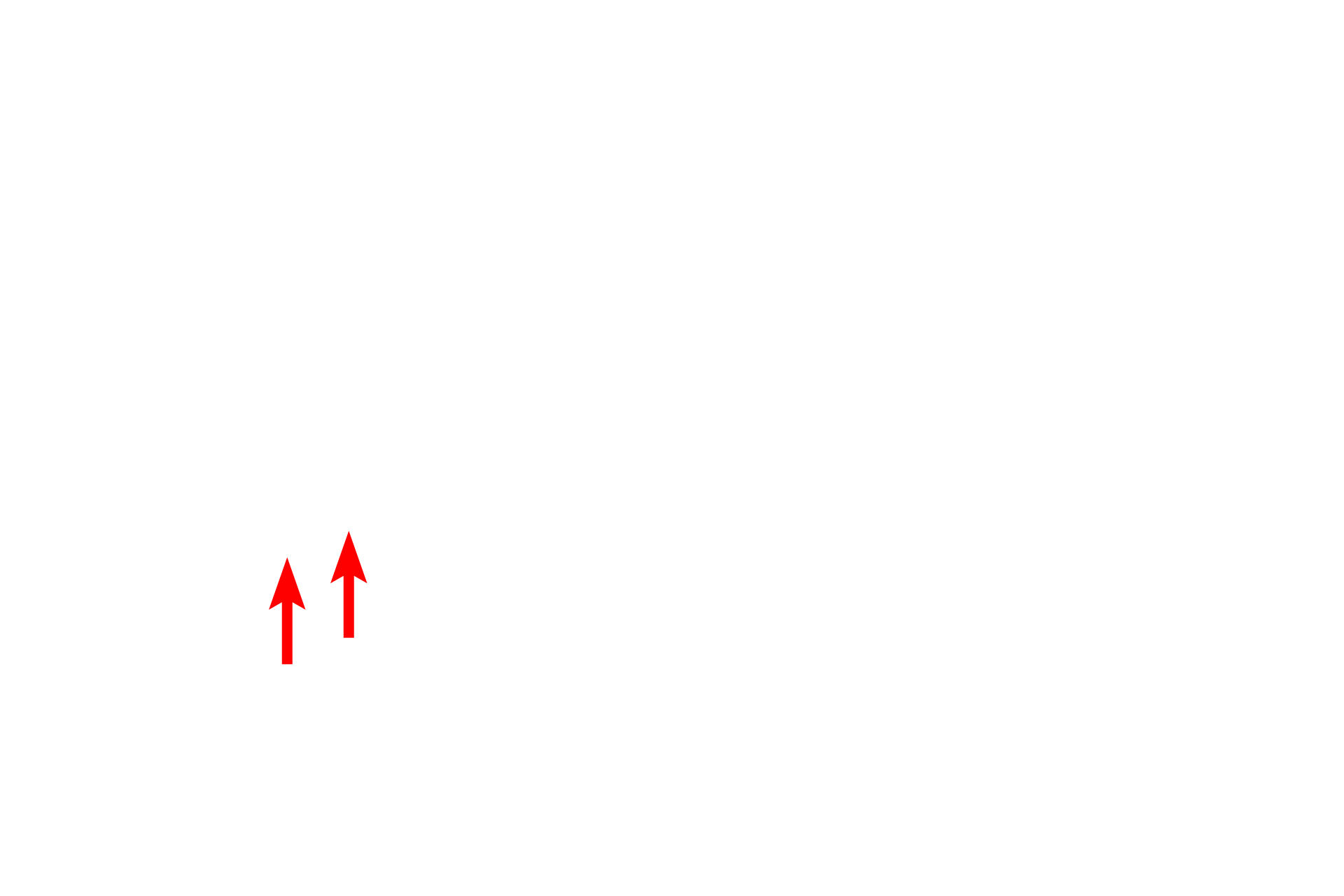
Axon >
The axon is a singular process that conducts the action potential. It lacks Nissl and originates from the cell body at the axon hillock. The first portion of the axon is the initial segment which is rich in sodium channels and is the initiation site for the action potential.
Myelin sheaths >
Myelin is an insulating wrapping of axons, produced by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system. This section is counterstained with Luxol fast blue which stains the myelin sheath turquoise-blue.
Glial cell nuclei >
Glial cells are the supporting cells in the CNS and are comprised by astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. In most preparations, only the nuclei of these cells are visible. Special stains, such as a silver stain, are required to reveal the cytoplasm and cell processes. Supporting cells dramatically outnumber neurons in the CNS.
Artifactual space >
An artifactual space caused during tissue processing surrounds the neuron. Artifactual spaces often occur when tissue components shrink or swell at different rates.