
Purkinje fibers
Purkinje fibers are highly specialized cardiac muscle fibers that serve as the impulse conduction system within the heart, insuring that the impulse arrives almost simultaneously to the entire right and left ventricles. Purkinje fibers are located in the connective tissue just beneath the inner layer of the heart chambers (endocardium). Purkinje fibers are larger than cardiac muscle fibers, they have clear cytoplasm and sparse myofibrils that are mostly confined to the periphery of the cell. They often have two, centrally-located nuclei. 200x (top), 800x (bottom)
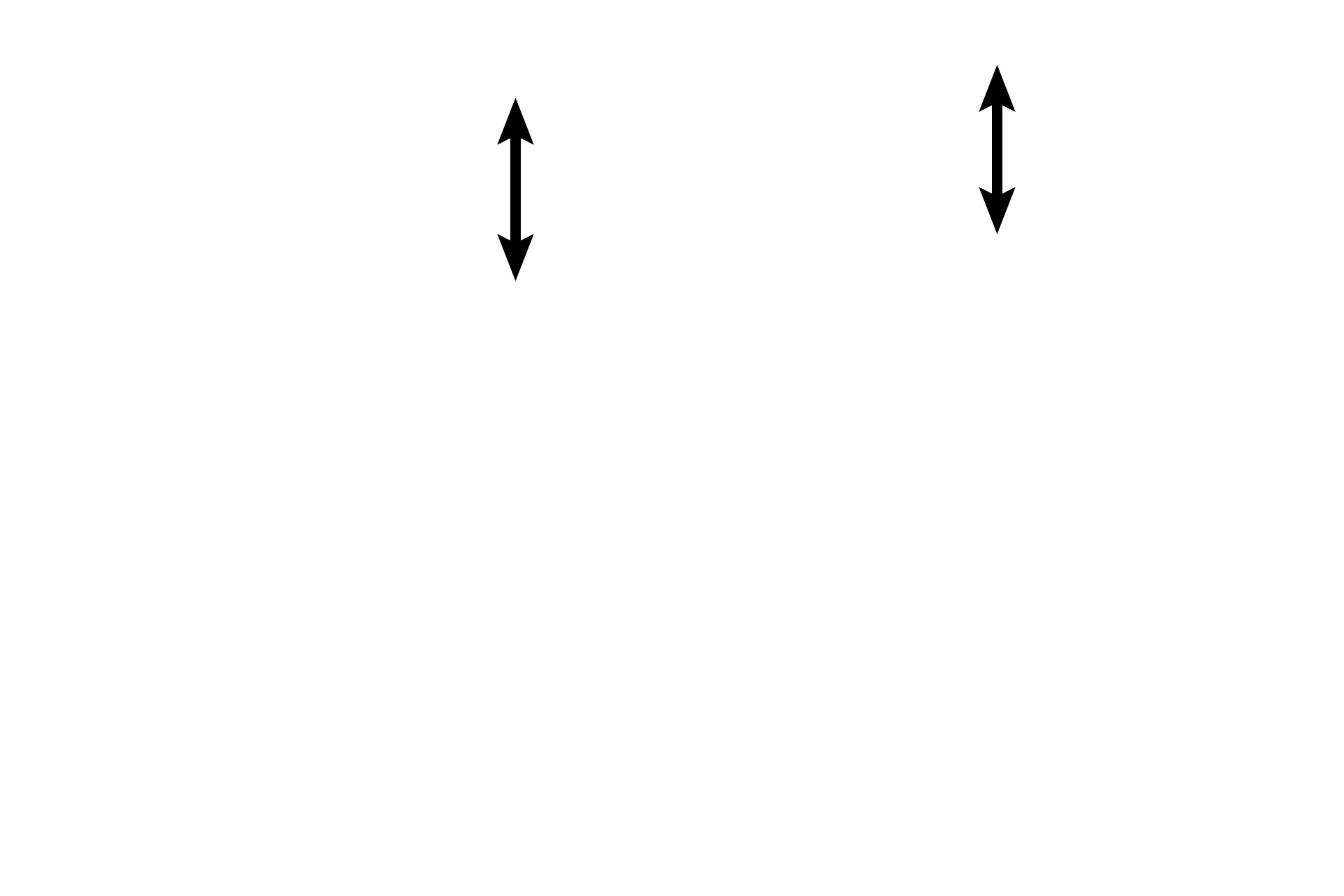
Endocardium >
The endocardium forms the inner lining of the heart chambers. The space within the chamber is located at the top of the image.

- Endothelium
The endocardium forms the inner lining of the heart chambers. The space within the chamber is located at the top of the image.
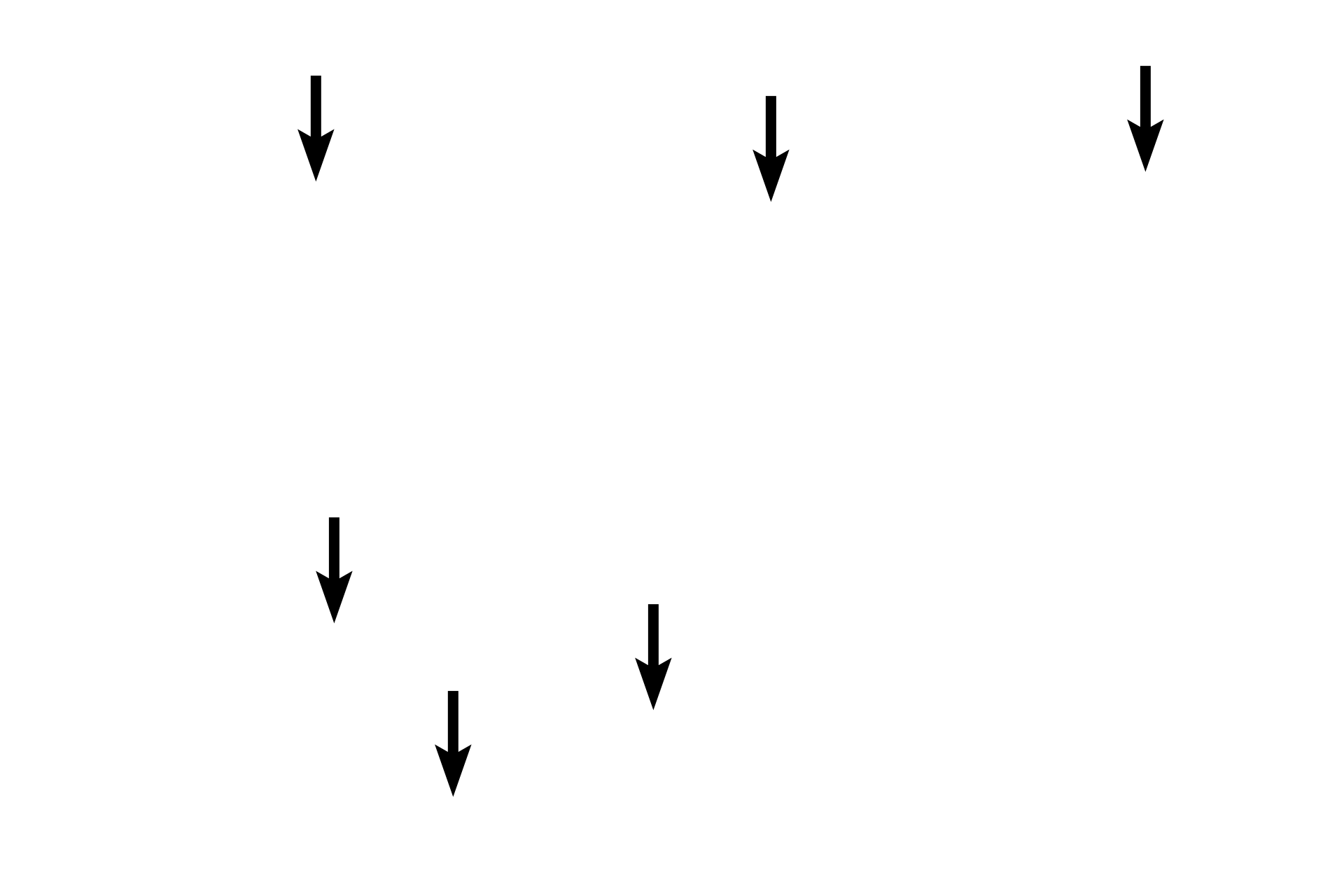
Purkinje fibers >
These images show Purkinje fibers at low and high magnifications. They are larger than cardiac muscle fibers and align in fascicles to conduct action potentials along their length.
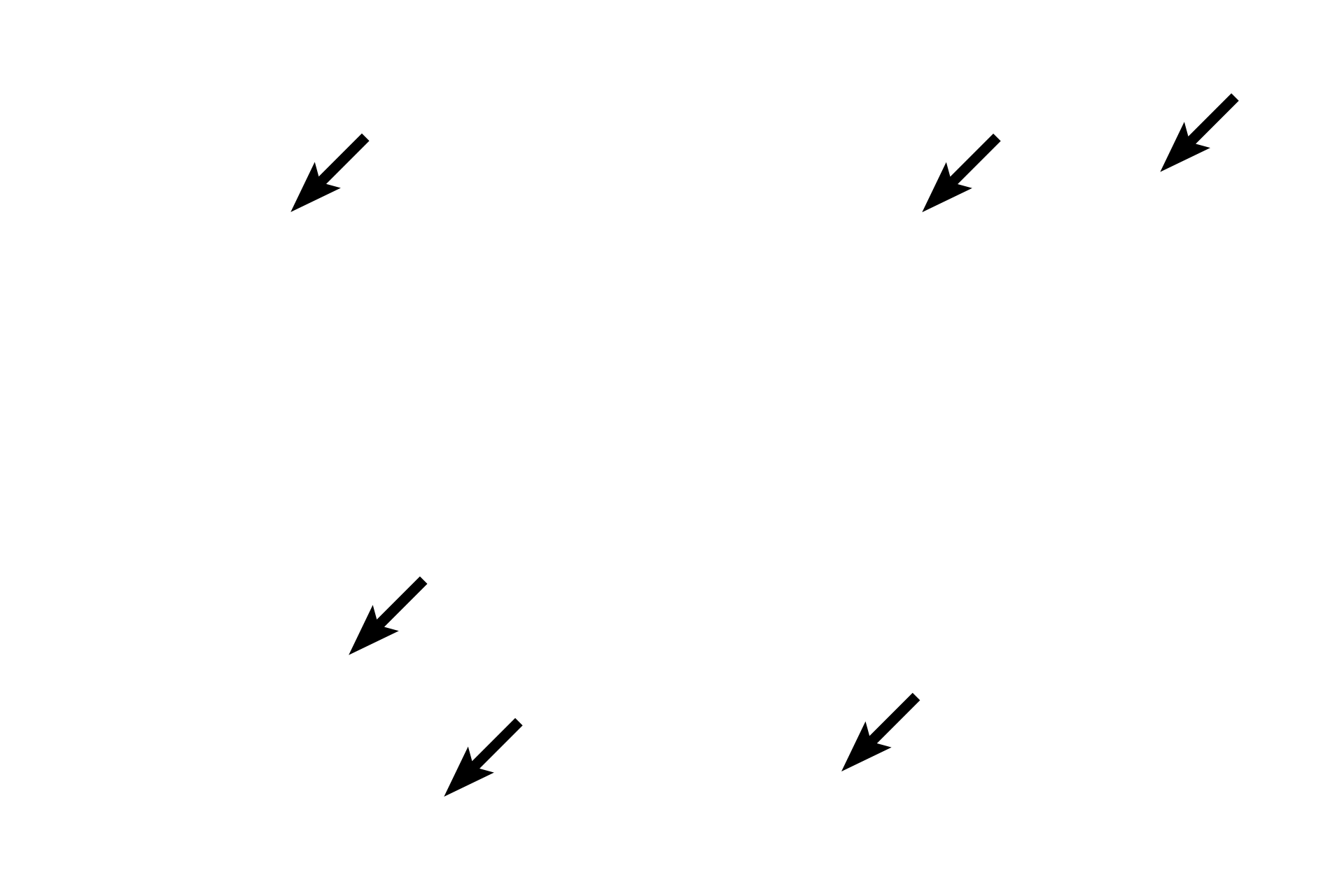
- Nuclei
Purkinje fibers often have two nuclei which are larger than regular cardiac muscle fibers.
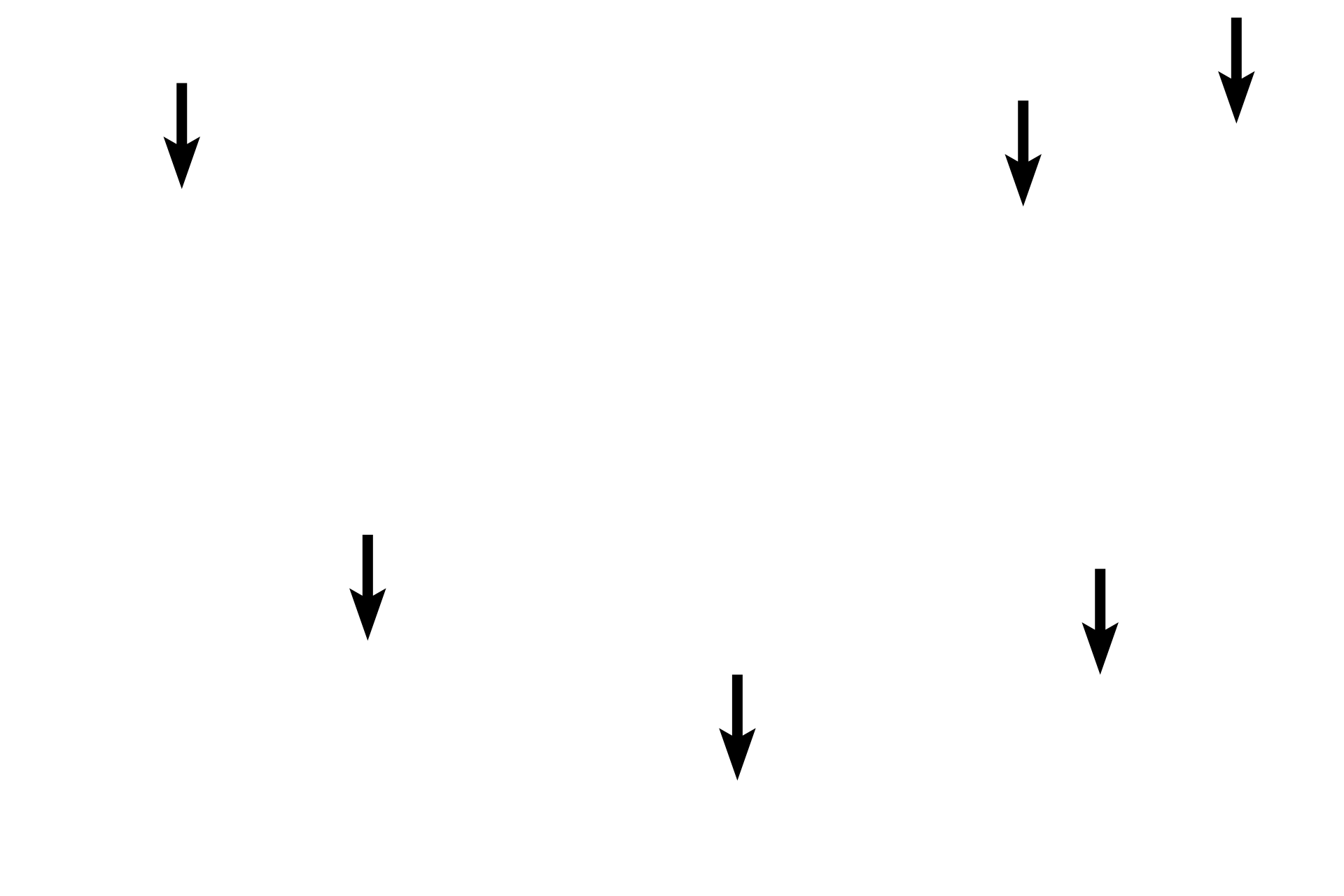
- Cytoplasm >
The cytoplasm of Purkinje fibers is very pale staining due to the presence of large amounts of glycogen.

- Myofibrils >
Purkinje fibers have fewer myofibrils and they are mostly confined to the periphery of the cell. This distribution is apparent in the cross-sectioned fiber (blue arrow). Myofilaments are present and the banding pattern of the myofibrils is similar to that in cardiac fibers.

- Intercalated discs
Purkinje fibers are attached to each by intercalated discs.

Cardiac muscle fibers of the myocardium >
Cardiac muscle fibers, comprising the myocardium, are present beneath the endocardium.

Image source >
Image from the University of Mississippi slide collection.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS