
Connective tissue proper overview
The components of connective tissue proper are cells and an extracellular matrix consisting of fibers and ground substance. Varying the types and quantities of each of these components results in the formation of the different types of connective tissue proper. 400x
Cells of connective tissue >
Many different types of connective tissue cells exist. Fibroblasts produce both fibers and ground substance; adipocytes store fat; a variety of white blood cells and their derivatives are involved in phagocytosis and in immune and inflammatory responses.
- Fibroblasts
Many different types of CT cells exist. Fibroblasts produce both fibers and ground substance; adipocytes store fat; a variety of white blood cells and their derivatives are involved in phagocytosis and in immune and inflammatory responses.
- Adipocytes
Many different types of CT cells exist. Fibroblasts produce both fibers and ground substance; adipocytes store fat; a variety of white blood cells and their derivatives are involved in phagocytosis and in immune and inflammatory responses.

- Macrophages -
Many different types of CT cells exist. Fibroblasts produce both fibers and ground substance; adipocytes store fat; a variety of white blood cells and their derivatives are involved in phagocytosis and in immune and inflammatory responses.
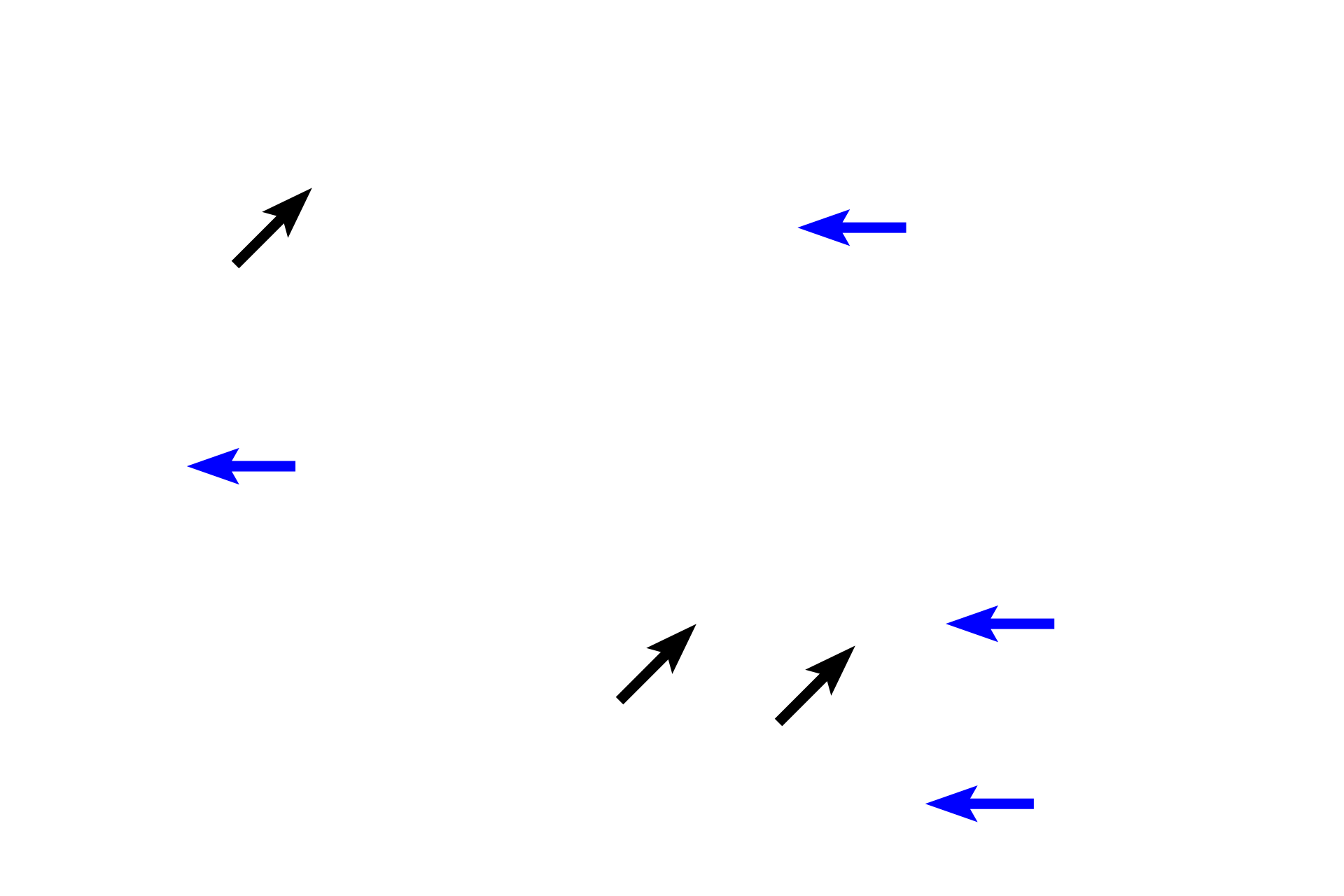
Extracellular matrix >
The extracellular matrix is composed of fibers (black arrows), and a gelatinous ground substance (blue arrows) rich in proteoglycans and tissue fluid. Both the ground substance and fibers are synthesized by fibroblasts.
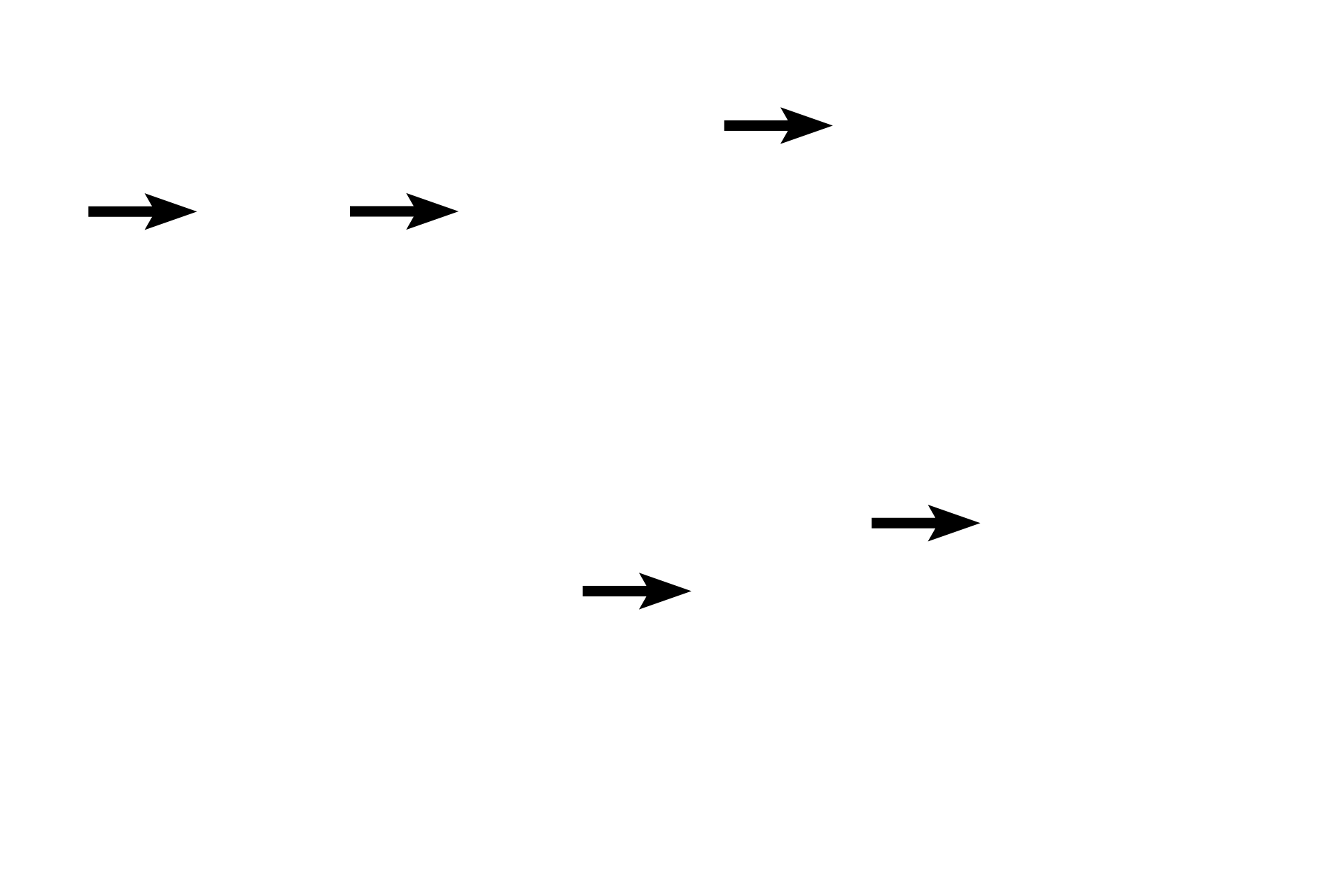
- Fibers >
Three fiber types are located in the extracellular matrix: Collagen fibers (arrows), which do not stretch, provide great tensile strength to a tissue; reticular fibers which are also inelastic, provide delicate strength to a tissue; and elastic fibers which allow connective tissues to stretch and rebound. Reticular and elastic fibers often require special stains in order to distinguishing them from collagen fibers, and therefore, cannot be identified in this image.
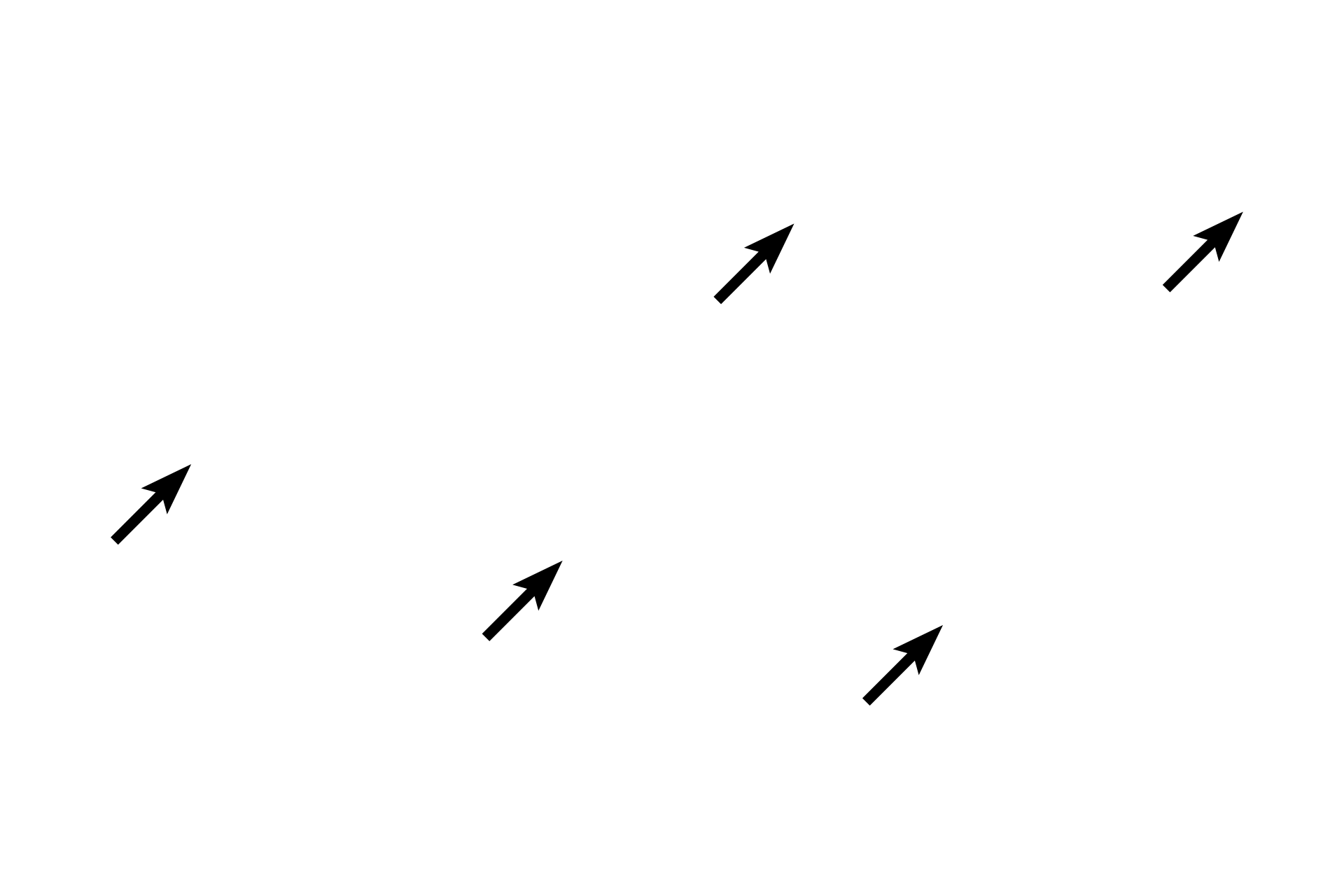
- Ground substance >
In connective tissue proper, the ground substance is present as a gel. Such a consistency provides excellent padding around connective tissue cells and fibers, as well as between layers of other tissues and organs. The molecules composing ground substance attract water, maintaining the hydration of the matrix. Numerous blood vessels course through the ground substance.
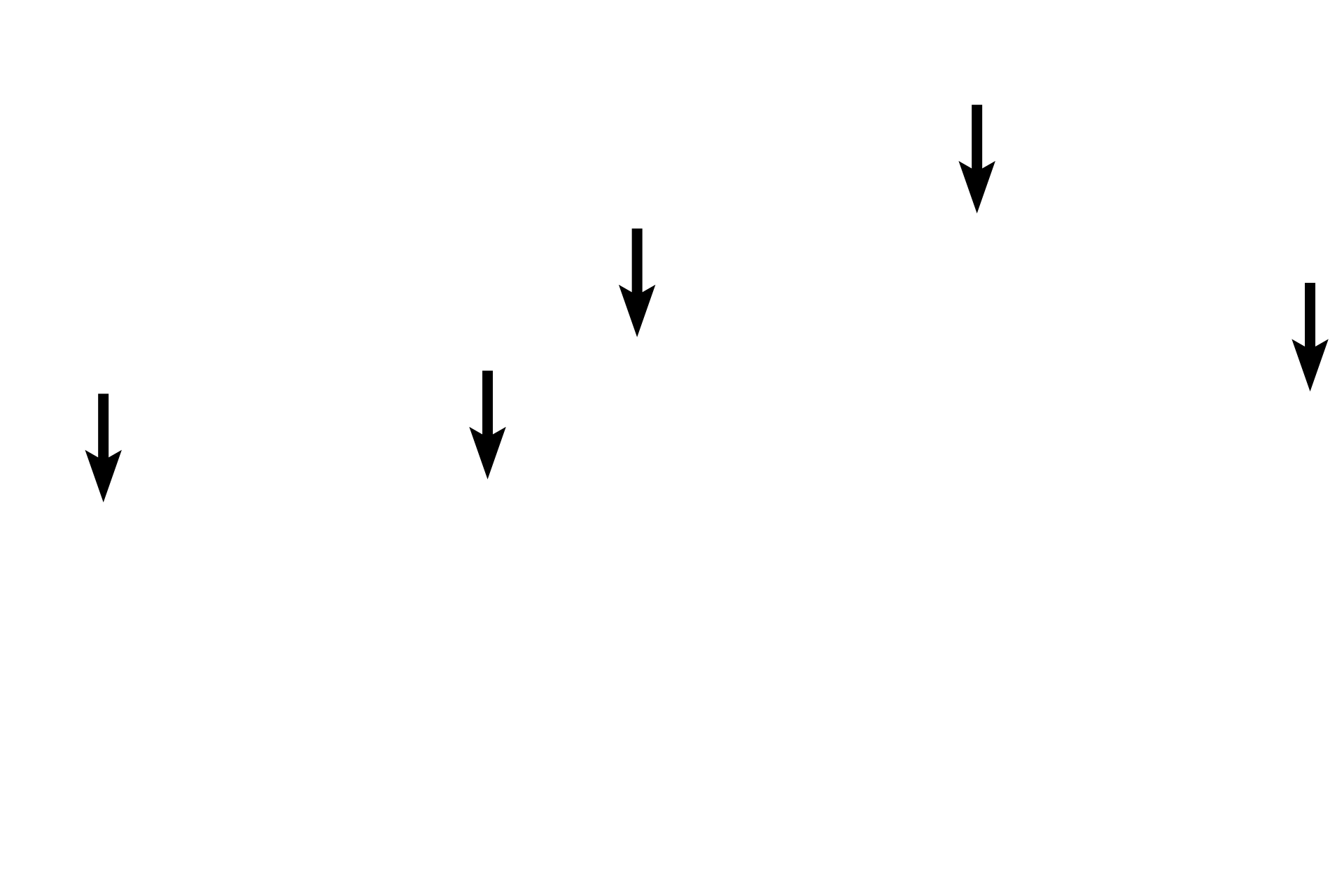
- Blood vessels
In connective tissue proper, the ground substance is present as a gel. Such a consistency provides excellent padding around connective tissue cells and fibers, as well as between layers of other tissues that connective tissue frequently separates. The molecules composing ground substance attract water, maintaining the hydration of the matrix. Numerous blood vessels course through the ground substance.