
Connective tissue proper overview
Connective tissue proper is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix, consisting of fibers and ground substance. Cells of connective tissue produce matrix, store fat, phagocytose, or provide immunological defense. Fibers provide strength and elasticity. Cells and fibers are surrounded by a gelatinous ground substance that provides padding and allows diffusion. The functional and physical characteristics of a connective tissue depend on the composition and arrangement of these elements.
Cells >
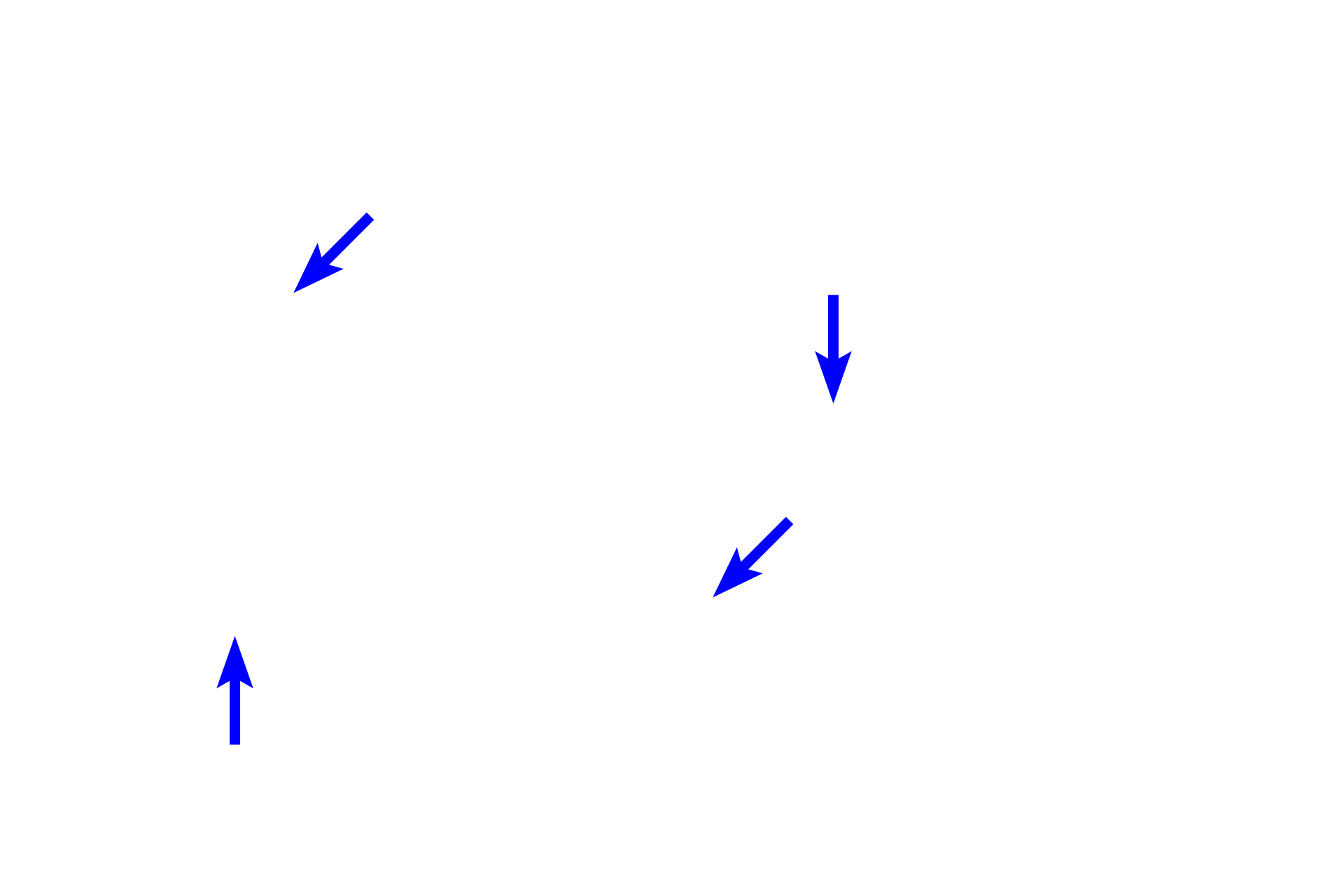
A wide variety of cells are present in connective tissue proper. Fibroblasts produce extracellular matrix (ground substance and fibers). Macrophages phagocytose foreign matter. Plasma cells and mast cells, along with several other cell types, provide immunologic defense. Other cells, such as adipocytes (not illustrated), store fat.

- Fibroblast
A wide variety of cells are present in connective tissue proper. Fibroblasts produce extracellular matrix (ground substance and fibers). Macrophages phagocytose foreign matter. Plasma cells and mast cells along with several other cell types, provide immunologic defense. Other cells, such as adipocytes (not illustrated), store fat.
- Macrophage
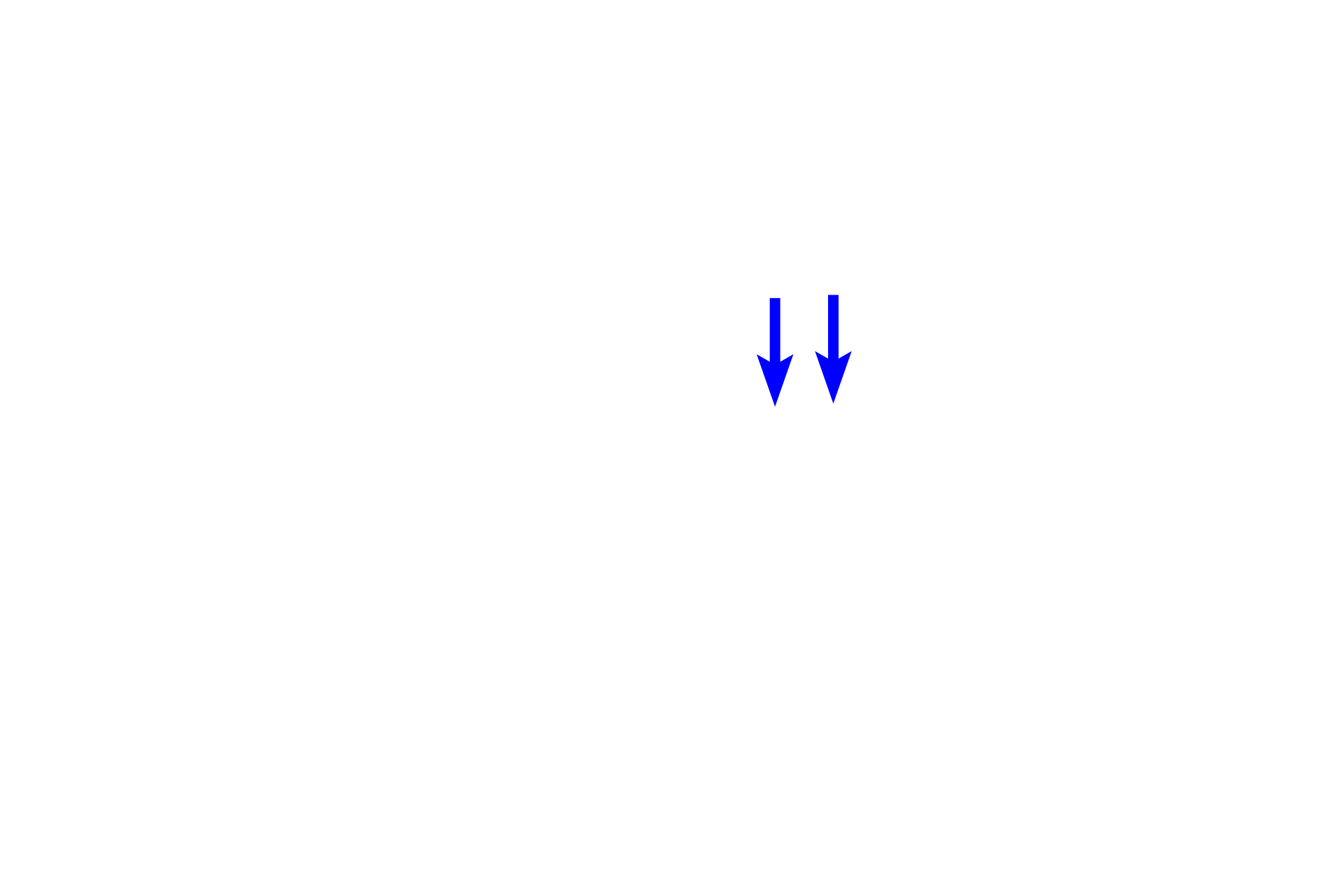
A wide variety of cells are present in connective tissue proper. Fibroblasts produce extracellular matrix (ground substance and fibers). Macrophages phagocytose foreign matter. Plasma cells and mast cells along with several other cell types, provide immunologic defense. Other cells, such as adipocytes (not illustrated), store fat.
- Plasma cell
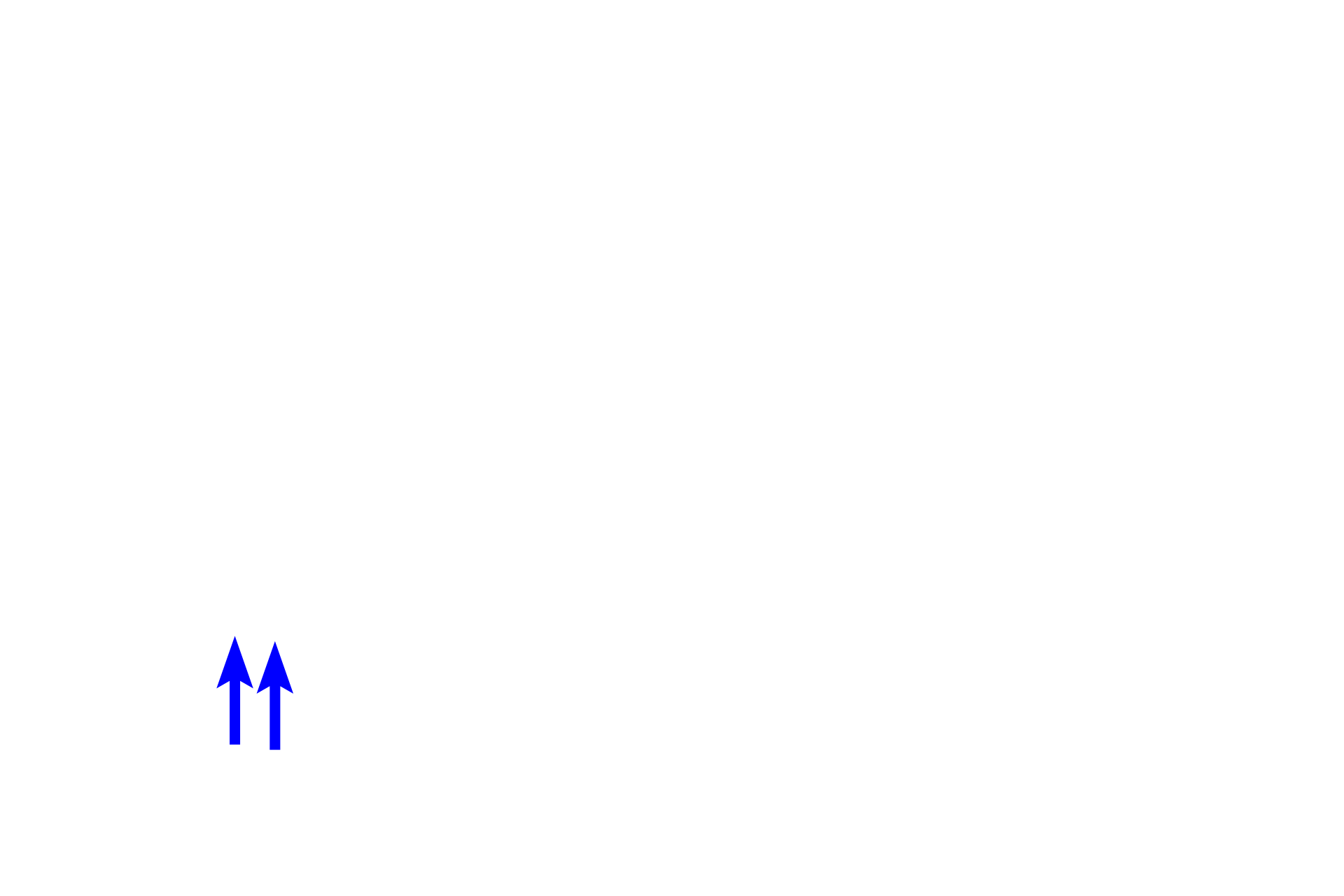
A wide variety of cells are present in connective tissue proper. Fibroblasts produce extracellular matrix (ground substance and fibers). Macrophages phagocytose foreign matter. Plasma cells and mast cells along with several other cell types, provide immunologic defense. Other cells, such as adipocytes (not illustrated), store fat.
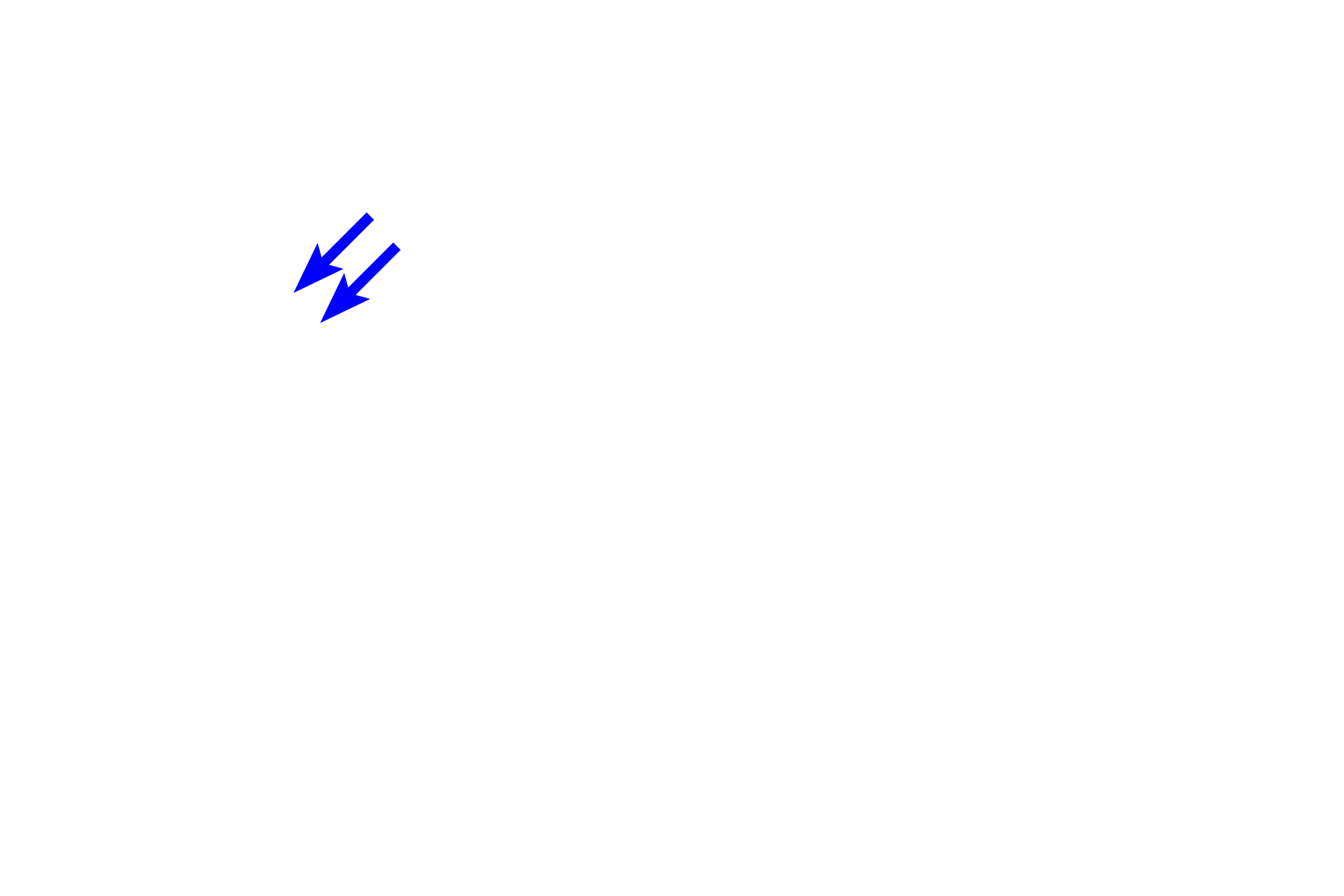

- Mast cell
A wide variety of cells are present in connective tissue proper. Fibroblasts produce extracellular matrix (ground substance and fibers). Macrophages phagocytose foreign matter. Plasma cells and mast cells along with several other cell types, provide immunologic defense. Other cells, such as adipocytes (not illustrated), store fat.
Extracellular matrix >
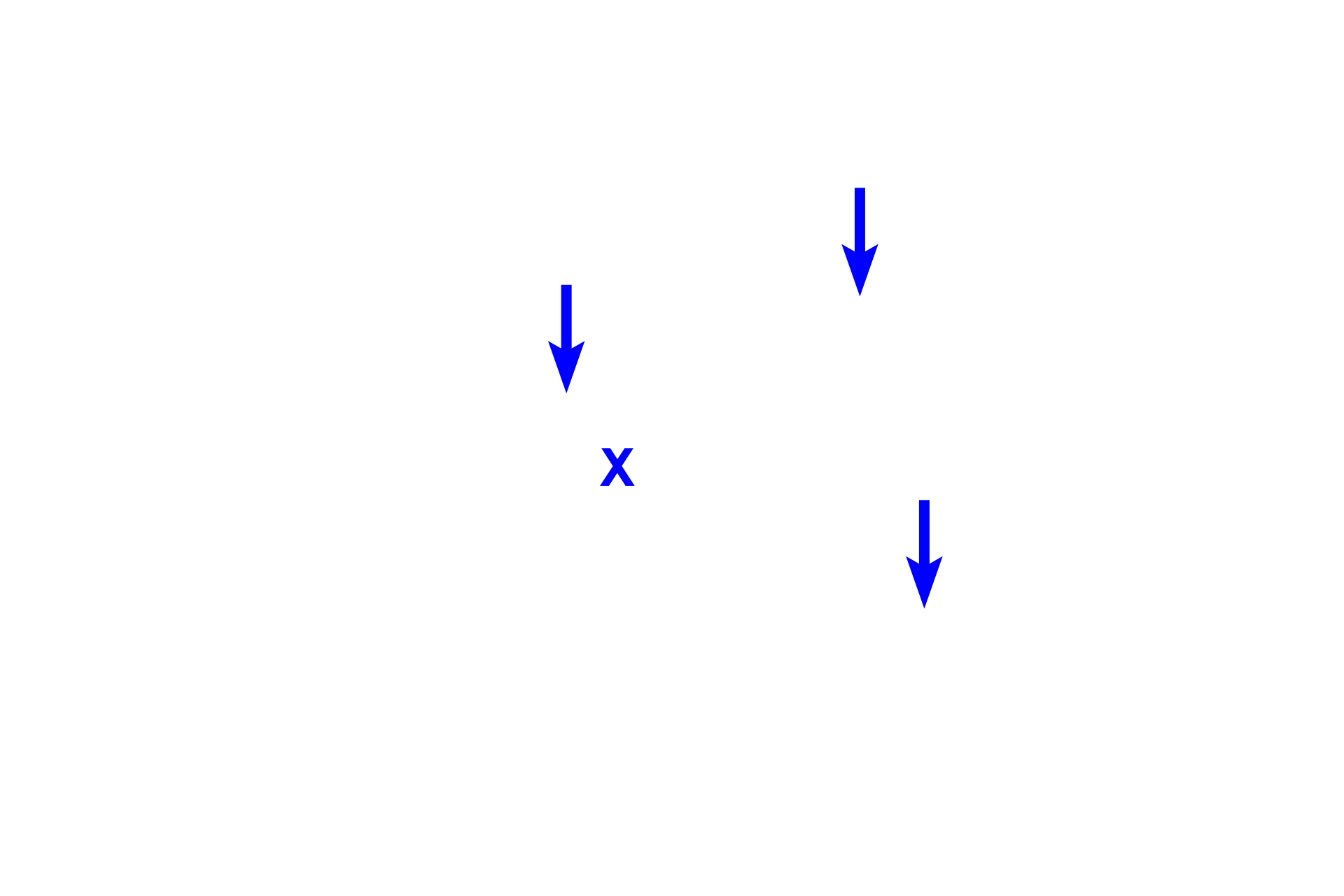
The extracellular matrix of connective tissue proper is composed of a gelatinous ground substance (X) and collagen, elastic and reticular fibers (arrows).
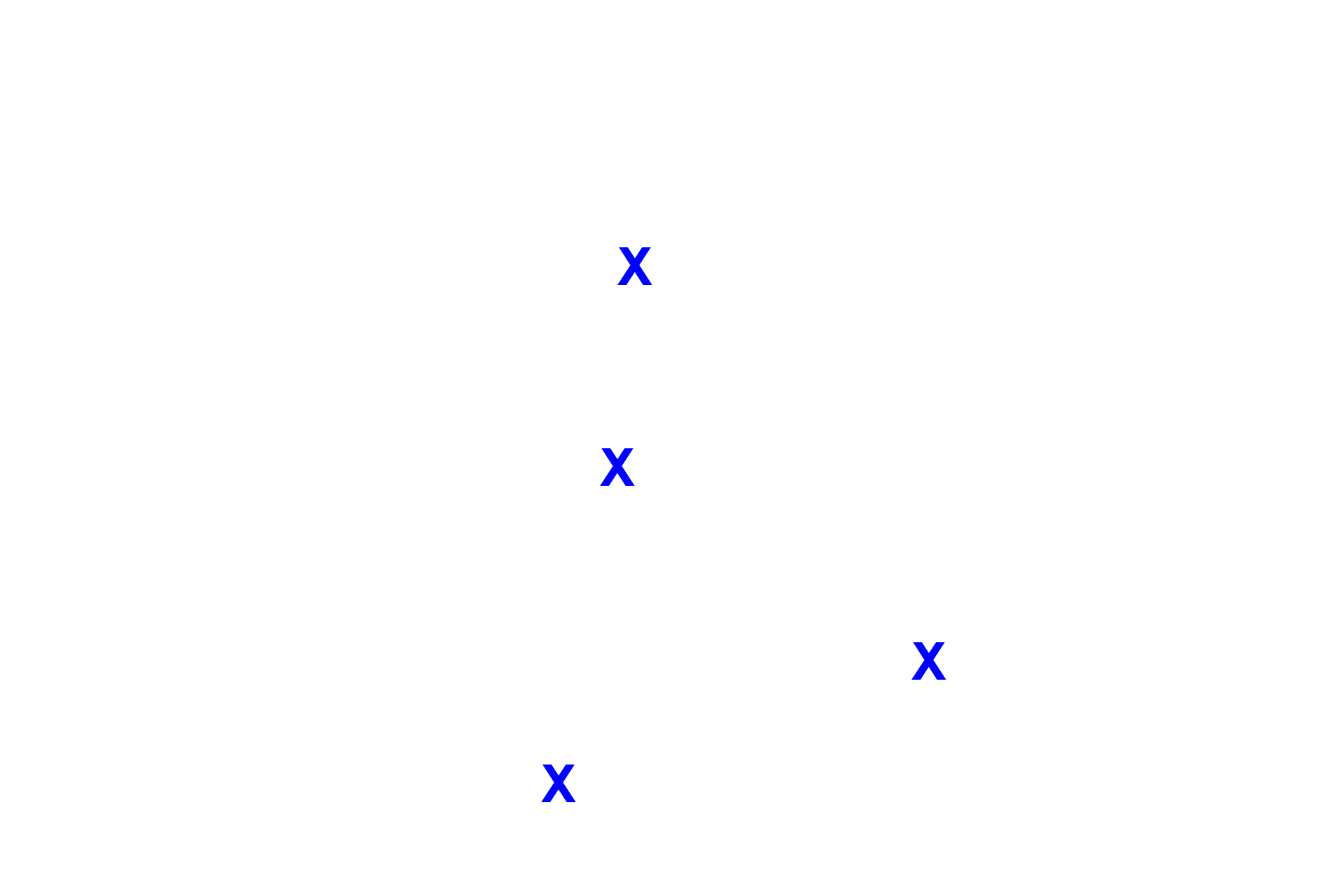
- Ground substance >
The ground substance of connective tissue proper is composed mostly of proteoglycans and abundant tissue fluid. In this image, the ground substance is the pink background surrounding the cells and fibers.
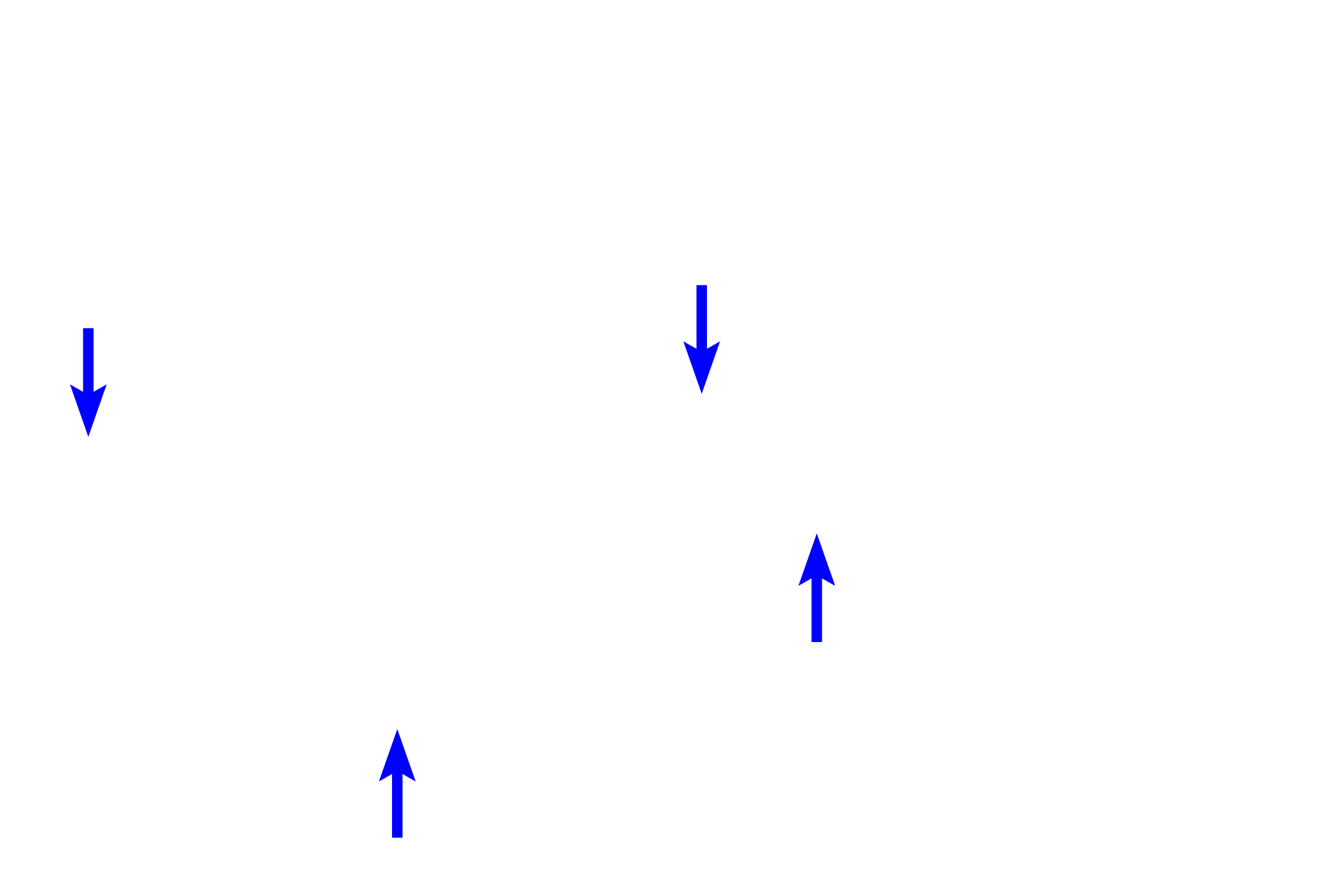
- Collagen fibers >
Three fiber types are present in connective tissue proper: collagen fibers providing tensile strength; elastic fibers allowing stretch; and reticular fibers providing light support.
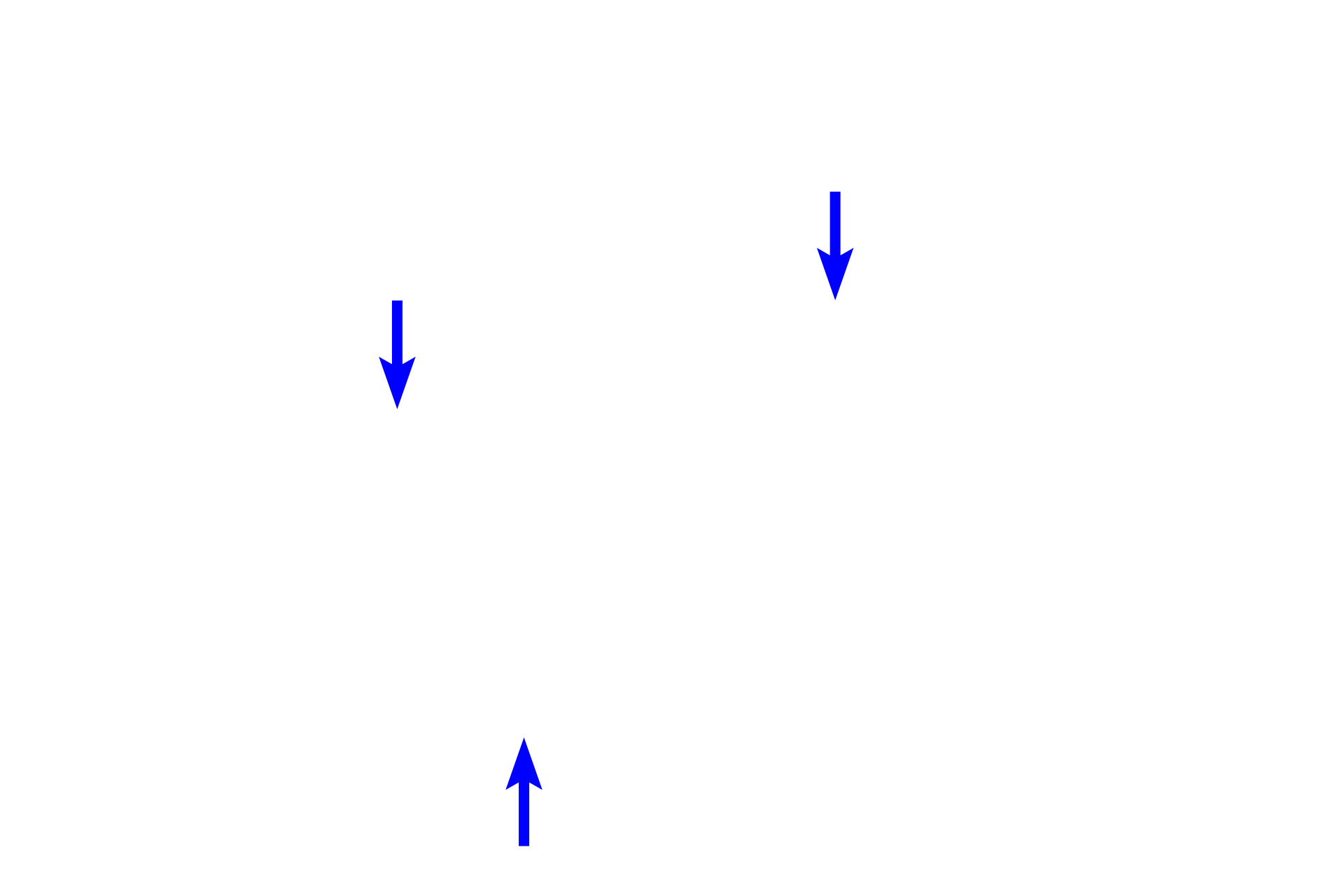
- Elastic fibers
Three fiber types are present in connective tissue proper: collagen fibers providing tensile strength; elastic fibers allowing stretch; and reticular fibers providing light support.
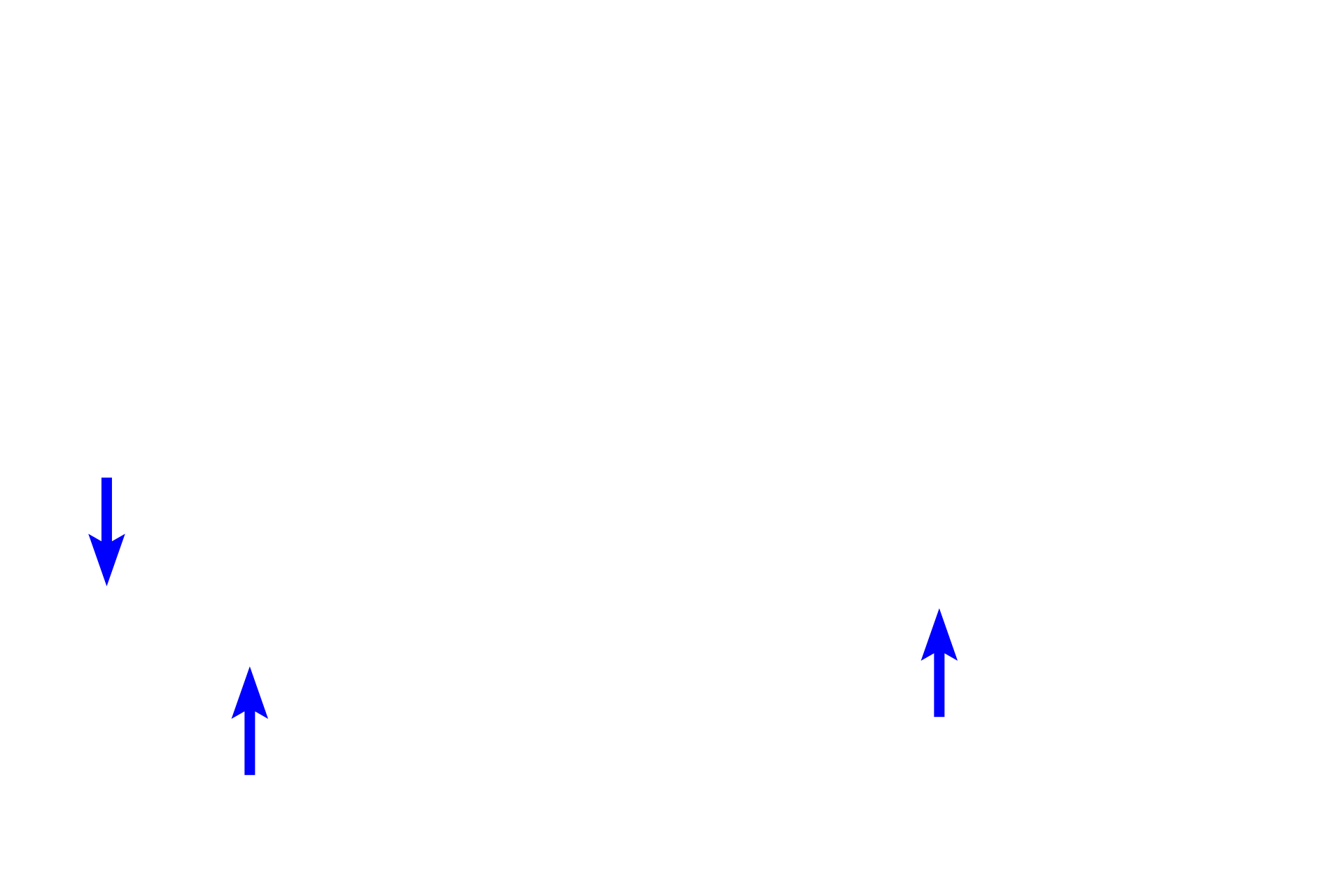
- Reticular fibers
Three fiber types are present in connective tissue proper: collagen fibers providing tensile strength; elastic fibers allowing stretch; and reticular fibers providing light support.