
Endochondral ossification
The end of the zone of maturation-hypertrophy-calcification is located at the top of this image. The zone of degeneration is in the middle, and the zone of ossification is at the bottom. 400x
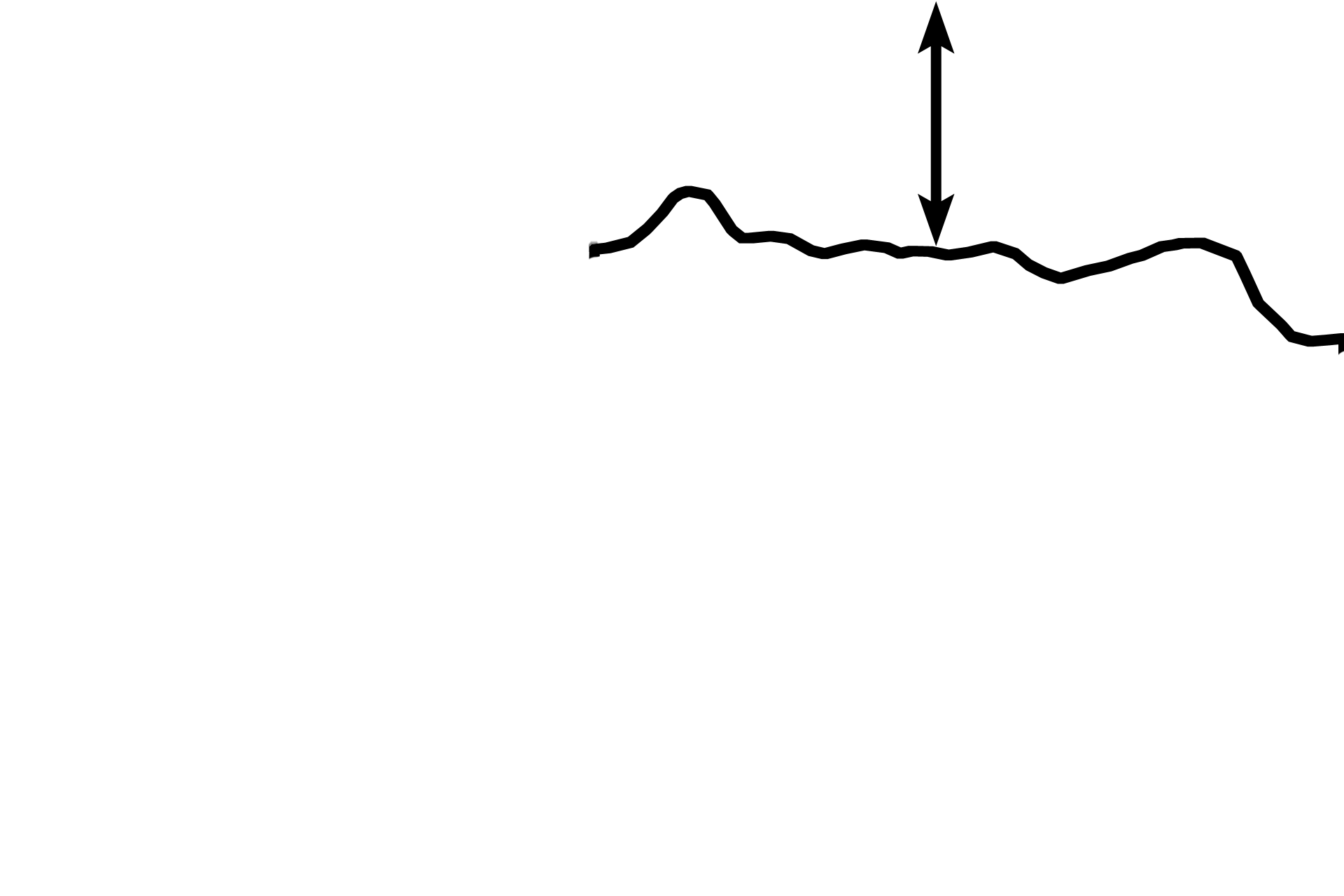
Zones of M-H-C >
In the zone of maturation-hypertrophy-calcification, linearly arranged chondrocytes increase in size and secrete alkaline phosphatase, thus allowing the matrix to calcify.
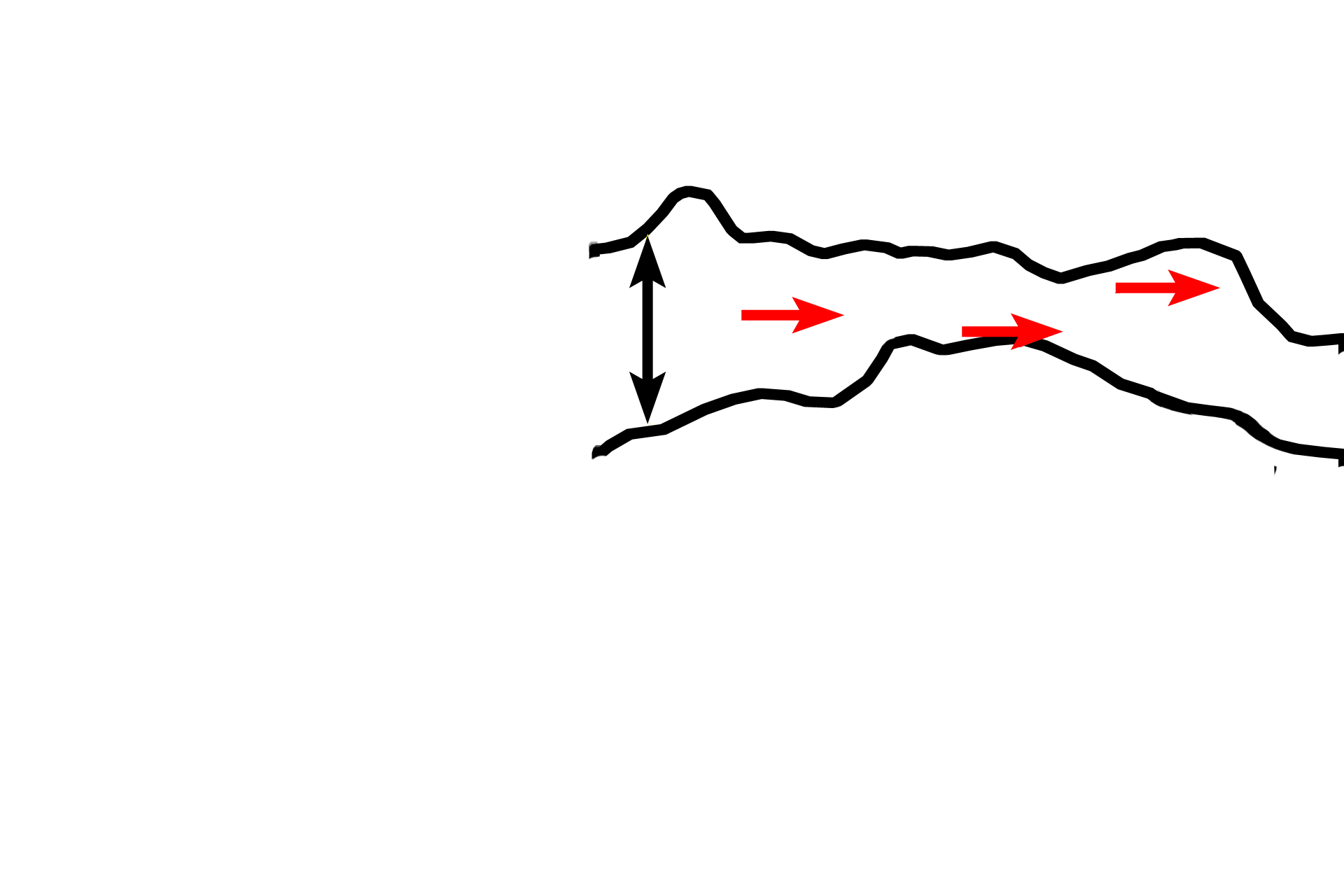

Zone of degeneration >
In the zone of degeneration, chondrocytes have died, leaving behind calcified cartilage spicules (red arrows).
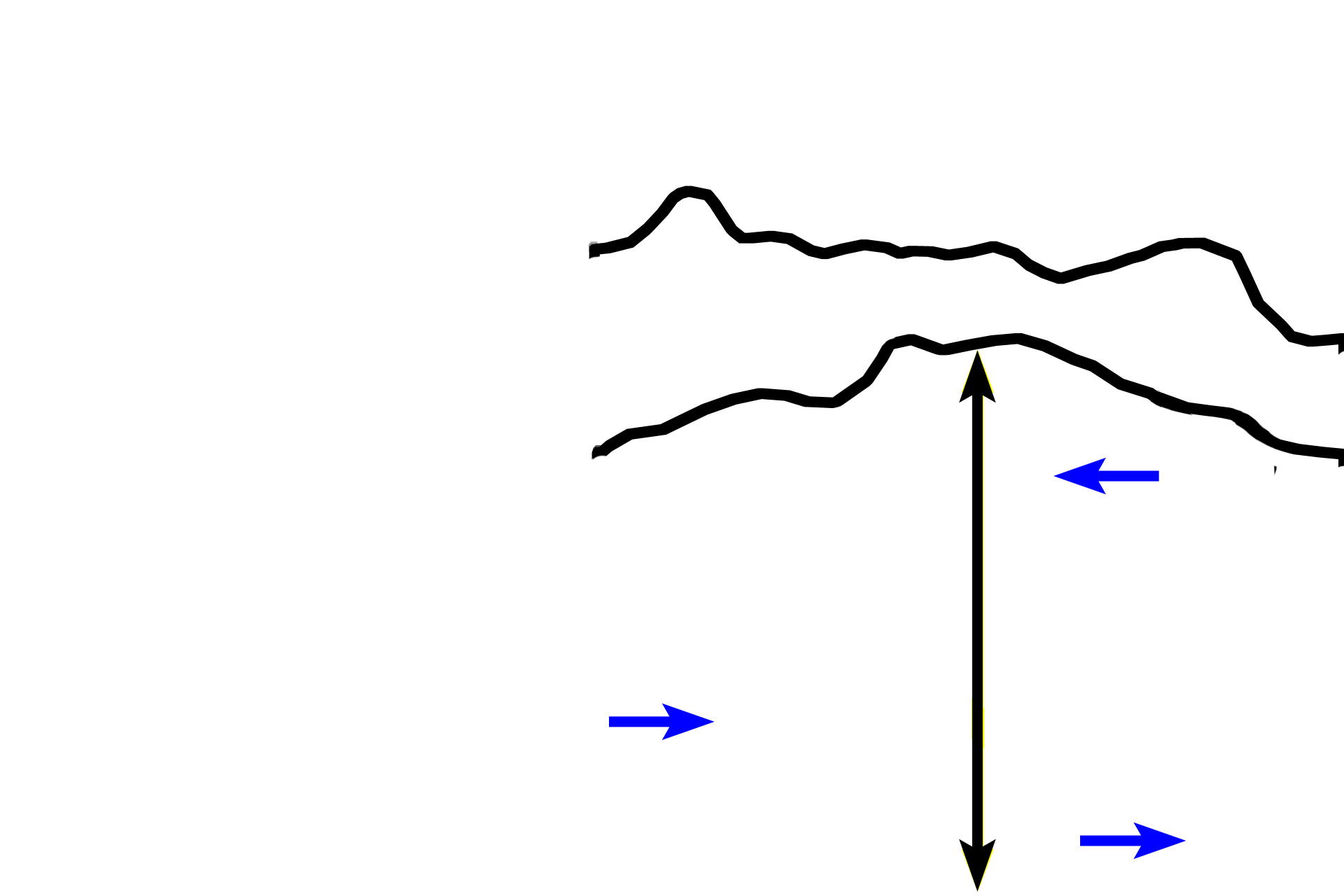
Zone of ossification >
In the zone of ossification, osteoblasts deposit woven bone (blue arrows), on the calcified cartilage framework. The distinctly red-staining bone is readily distinguishable from the blue-staining calcified cartilage matrix. Because this bone is replacing cartilage, this type of bone formation called endochondral bone formation.