
Bone: flat bones
Flat bones of the skull (upper image) represent another bone type based on shape. Adult flat bones consist of a diploe of spongy bone sandwiched between inner and outer tables of compact bone. Flat bones originally form in the fetus (lower image) as spongy bone; peripheral regions of this spongy bone are converted to compact bone of the inner and outer tables. 3x, 10x
Outer table
Flat bones of the skull represent another bone type based on shape. Adult flat bones consist of a diploe of spongy bone sandwiched between inner and outer tables of compact bone. Flat bones originally form in the fetus (lower image) as spongy bone; peripheral regions of this spongy bone are converted to compact bone of the inner and outer tables. 3x, 10x
Diploe
Flat bones of the skull represent another bone type based on shape. Adult flat bones consist of a diploe of spongy bone sandwiched between inner and outer tables of compact bone. Flat bones originally form in the fetus (lower image) as spongy bone; peripheral regions of this spongy bone are converted to compact bone of the inner and outer tables. 3x, 10x
Inner table
Flat bones of the skull represent another bone type based on shape. Adult flat bones consist of a diploe of spongy bone sandwiched between inner and outer tables of compact bone. Flat bones originally form in the fetus (lower image) as spongy bone; peripheral regions of this spongy bone are converted to compact bone of the inner and outer tables. 3x, 10x

Suture
Flat bones of the skull represent another bone type based on shape. Adult flat bones consist of a diploe of spongy bone sandwiched between inner and outer tables of compact bone. Flat bones originally form in the fetus (lower image) as spongy bone; peripheral regions of this spongy bone are converted to compact bone of the inner and outer tables. 3x, 10x
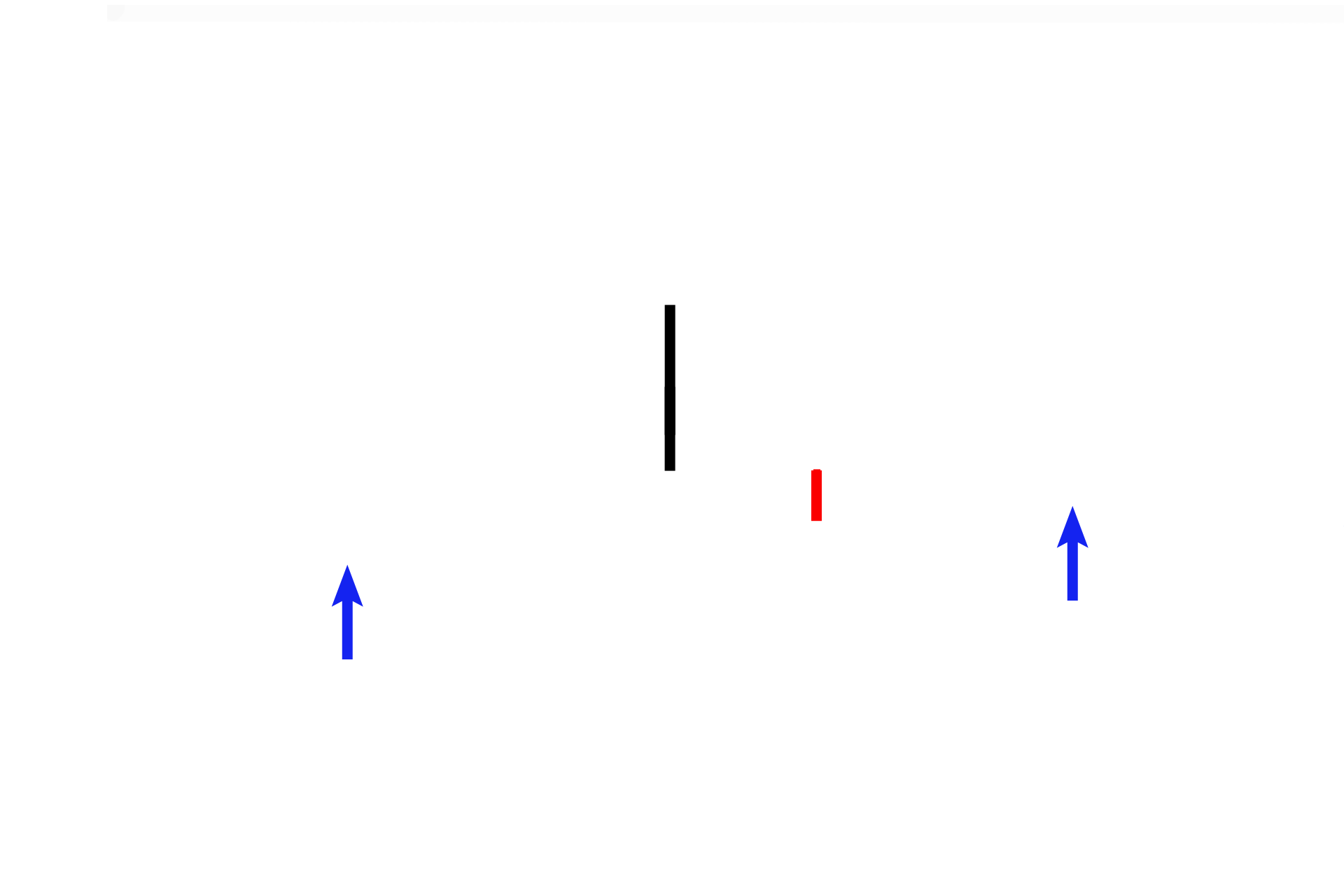
Surface coverings >
The surface coverings over the developing bone include: skin (black line), subcutaneous connective tissue (red line, hypodermis) and skeletal muscle (blue arrows).

Spongy woven bone >
The dark pink spicules visible in the section represent spongy, woven bone forming in the fetus. The peripheral portions of this bone will be converted to the compact bone forming the inner and outer tables, while the central region will remain as the spongy diploe of the adult flat bone.

Periosteum >
The periosteum on the exterior surface of the plate of spongy bone (black arrows) is also called the pericranium in gross anatomy. The periosteum on the internal surface (blue arrows) adjacent to the brain will form the major portion of the dura mater.
Endosteum >
An endosteum surrounds the individual spicules of spongy bone and will continue to line all interior surfaces of the flat bone in the adult.