
Alveolar duct
Alveolar ducts are formed by a series of rings which support the openings of alveoli. When cut in cross section, each ring appears as a pair of knobs bordering the alveolar opening. The rings (and, therefore, the knobs too) are lined by simple cuboidal epithelium, without cilia or club cells, that overlies a thin layer of connective tissue and smooth muscle fibers. 100x

Alveolar ducts
Alveolar ducts are formed by a series of rings which support the openings of alveoli. When cut in cross section, each ring appears as a pair of knobs bordering the alveolar opening. The rings (and, therefore, the knobs too) are lined by simple cuboidal epithelium, without cilia or club cells, that overlies a thin layer of connective tissue and smooth muscle fibers. 100x
Knobs
Alveolar ducts are formed by a series of rings which support the openings of alveoli. When cut in cross section, each ring appears as a pair of knobs bordering the alveolar opening. The rings (and, therefore, the knobs too) are lined by simple cuboidal epithelium, without cilia or club cells, that overlies a thin layer of connective tissue and smooth muscle fibers. 100x
Associated alveoli
Alveolar ducts are formed by a series of rings which support the openings of alveoli. When cut in cross section, each ring appears as a pair of knobs bordering the alveolar opening. The rings (and, therefore, the knobs too) are lined by simple cuboidal epithelium, without cilia or club cells, that overlies a thin layer of connective tissue and smooth muscle fibers. 100x
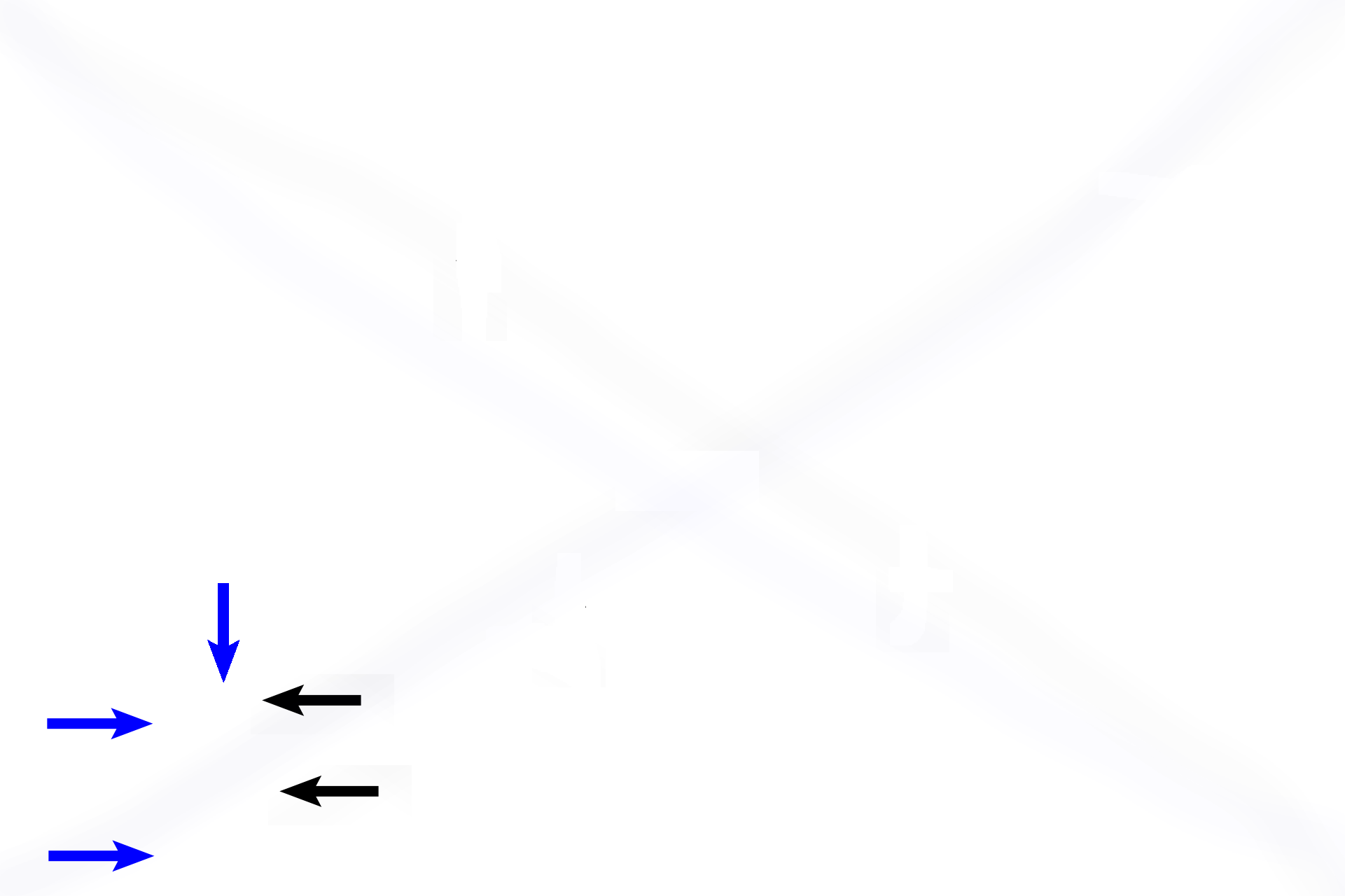

Alveolar sac >
An alveolar sac is a group of alveoli (blue arrows) that are all attached to a single supporting ring (black arrows).

Next image
The next image is similar to the area outlined by the rectangle.