
Transition of bronchiole to alveolar duct
As a respiratory bronchiole transitions to an alveolar duct, alveoli increase in number and the wall of the respiratory bronchiole is reduced to a series of knobs forming the wall of an alveolar duct. The knobs are really cross-sectional views of the rings that support the alveoli that are attached to them. 150x
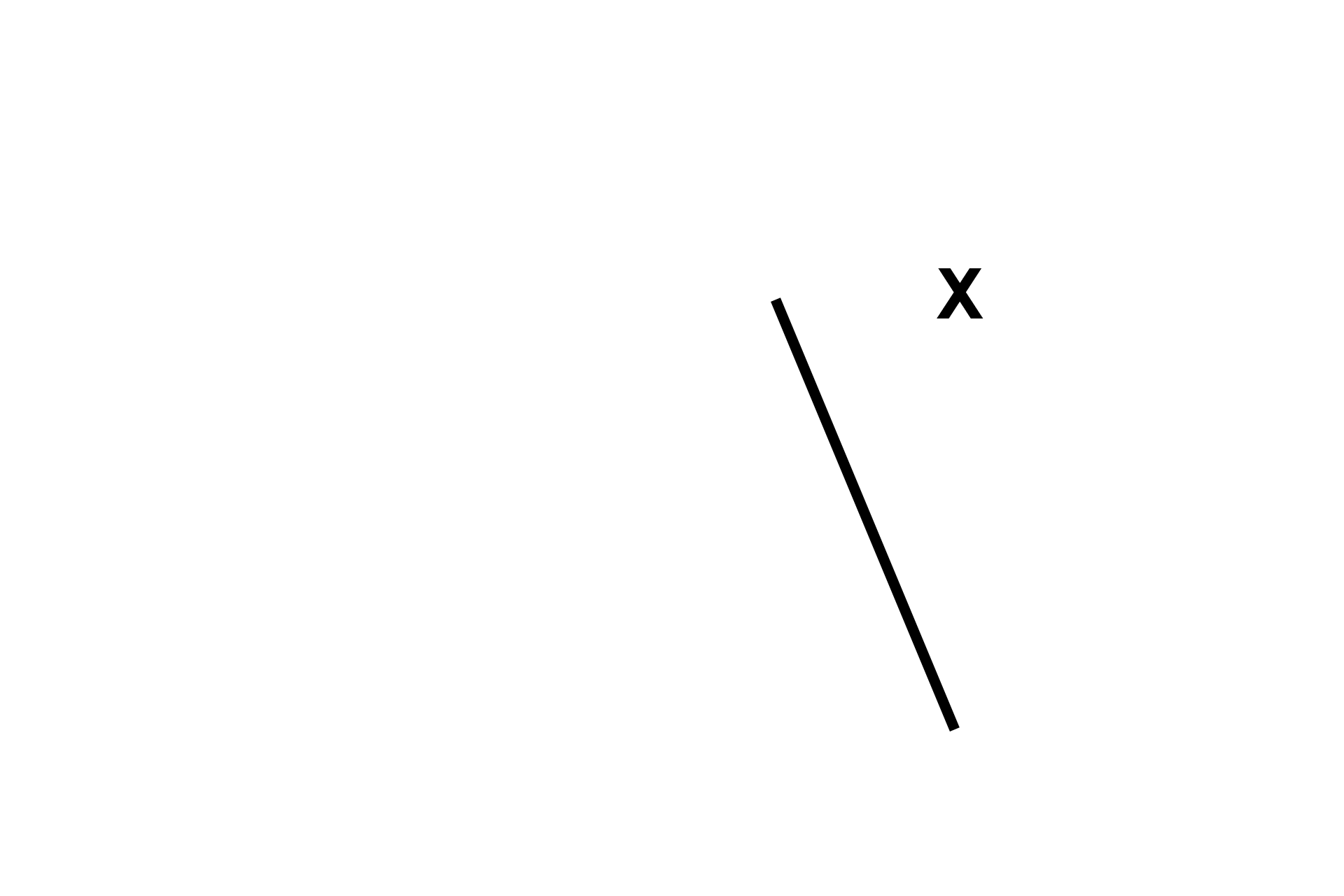
Respiratory bronchiole
As a respiratory bronchiole transitions to an alveolar duct, alveoli increase in number and the wall of the respiratory bronchiole is reduced to a series of knobs forming the wall of an alveolar duct. The knobs are really cross-sectional views of the rings that support the alveoli that are attached to them. 150x
Alveolar duct >
The respiratory bronchiole transitions to the alveolar duct, where the wall consists entirely of alveoli.
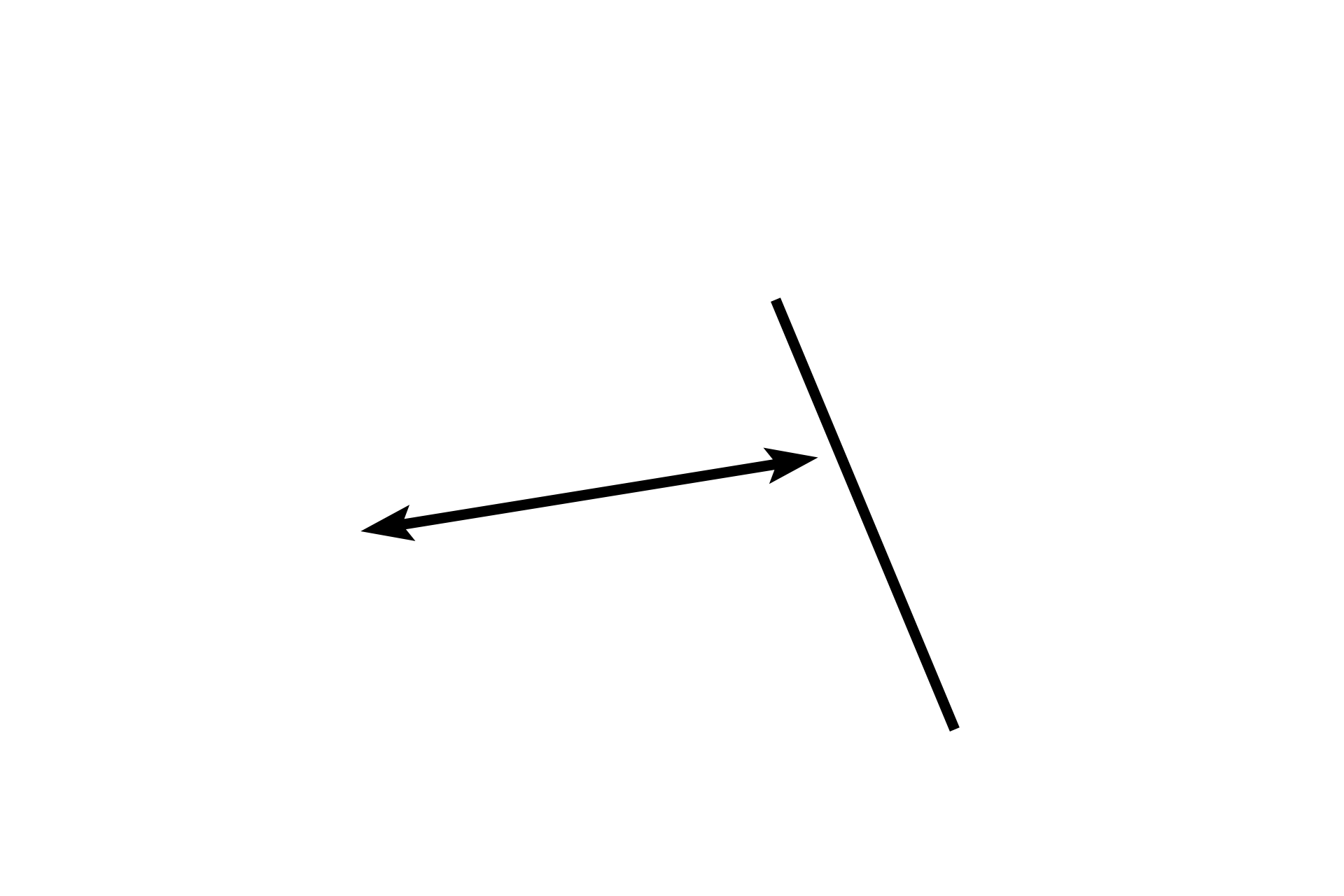
- Knobs >
The wall of the alveolar duct is formed by contiguous rings, resembling chicken wire rolled into a tube. When sectioned, one ring is represented by a pair of knobs. The rings provide support for the attached alveoli. Each ring (or pair of knobs) is lined by a simple cuboidal epithelium (blue arrows) overlying a thin layer of connective tissue and strands of smooth muscle.
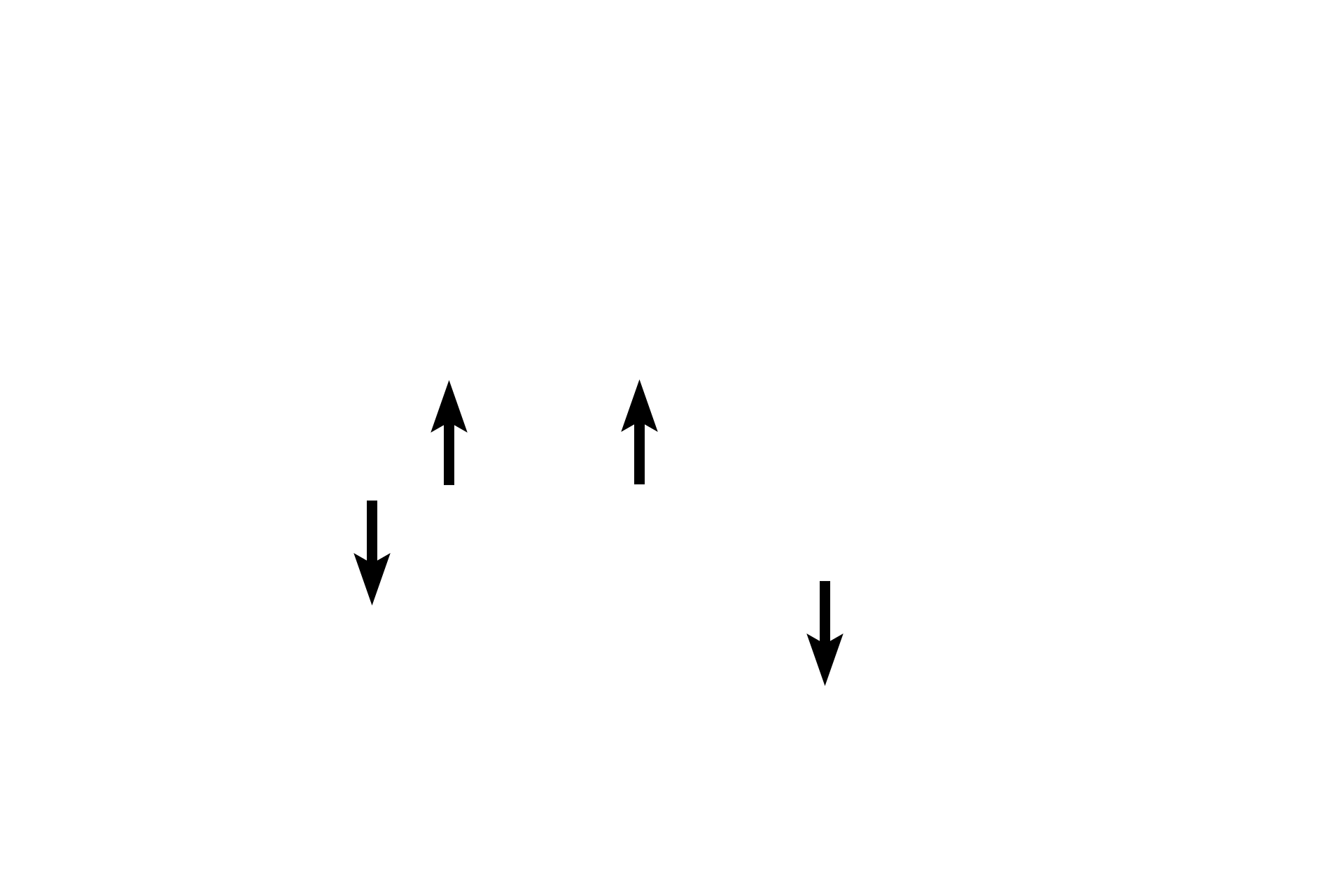
Alveoli >
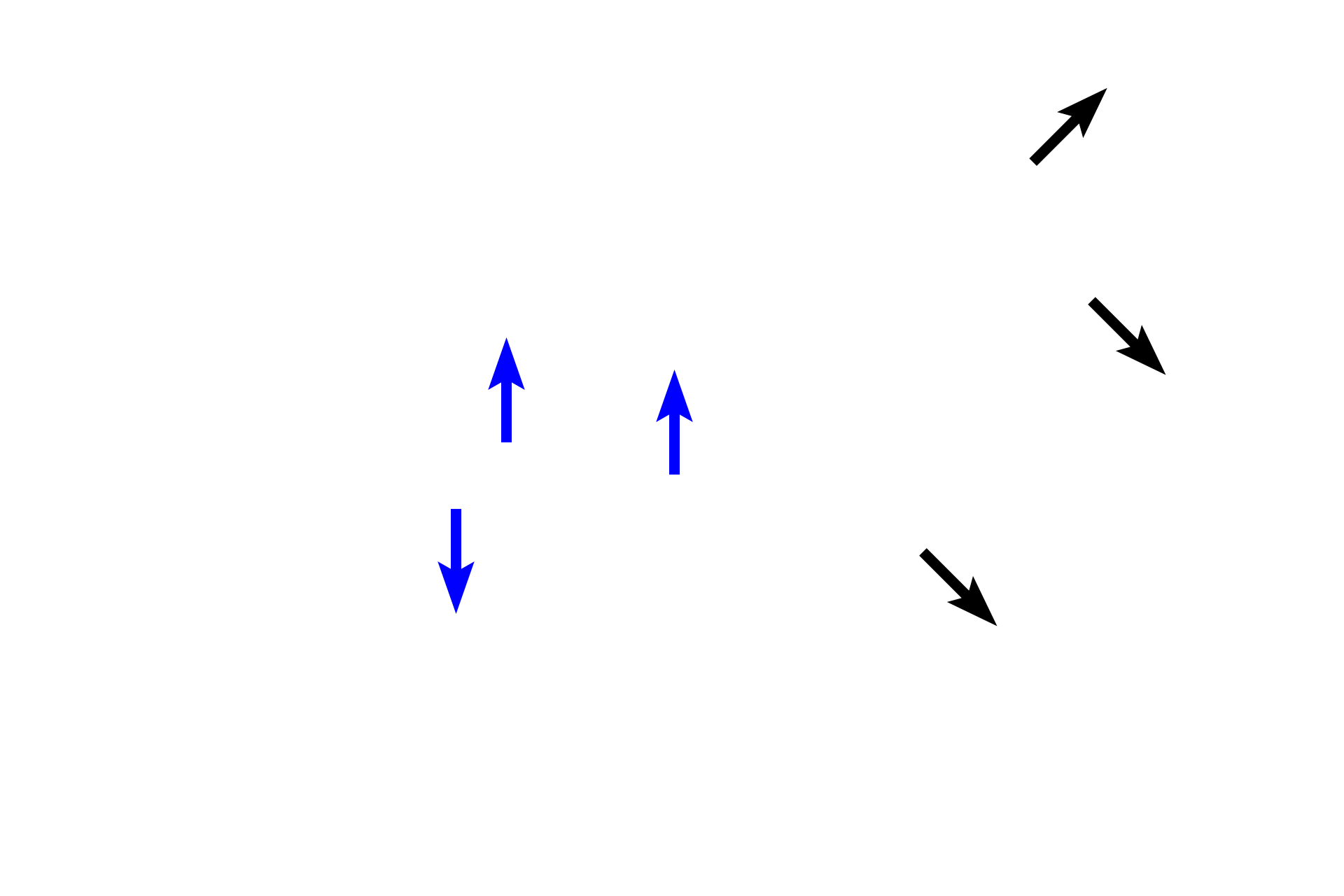
Alveoli form an integral part of the respiratory bronchiole (black arrows) and alveolar duct (blue arrows).
Non-associated alveoli >
Alveoli associated with similar adjacent passageways surround this respiratory bronchiole and alveolar duct.
Alveolar sac >
An alveolar sac is two or more alveoli attached to a pair of knobs (representing a single ring) that forms the wall of the alveolar duct.

Pulmonary artery >
These vessels accompany the respiratory passageway carrying deoxygenated blood to the alveoli.

Image source >
This image was taken of a slide in the University of Michigan collection.