
Epididymis: body and tail
The epithelium of the duct of the epididymis consists of a pseudostratified columnar epithelium composed primarily of principal cells with tall stereocilia. Principle cells absorb luminal fluid thereby concentrating the sperm. This epithelium decreases in height as the duct progresses from the head to the tail region. 600x
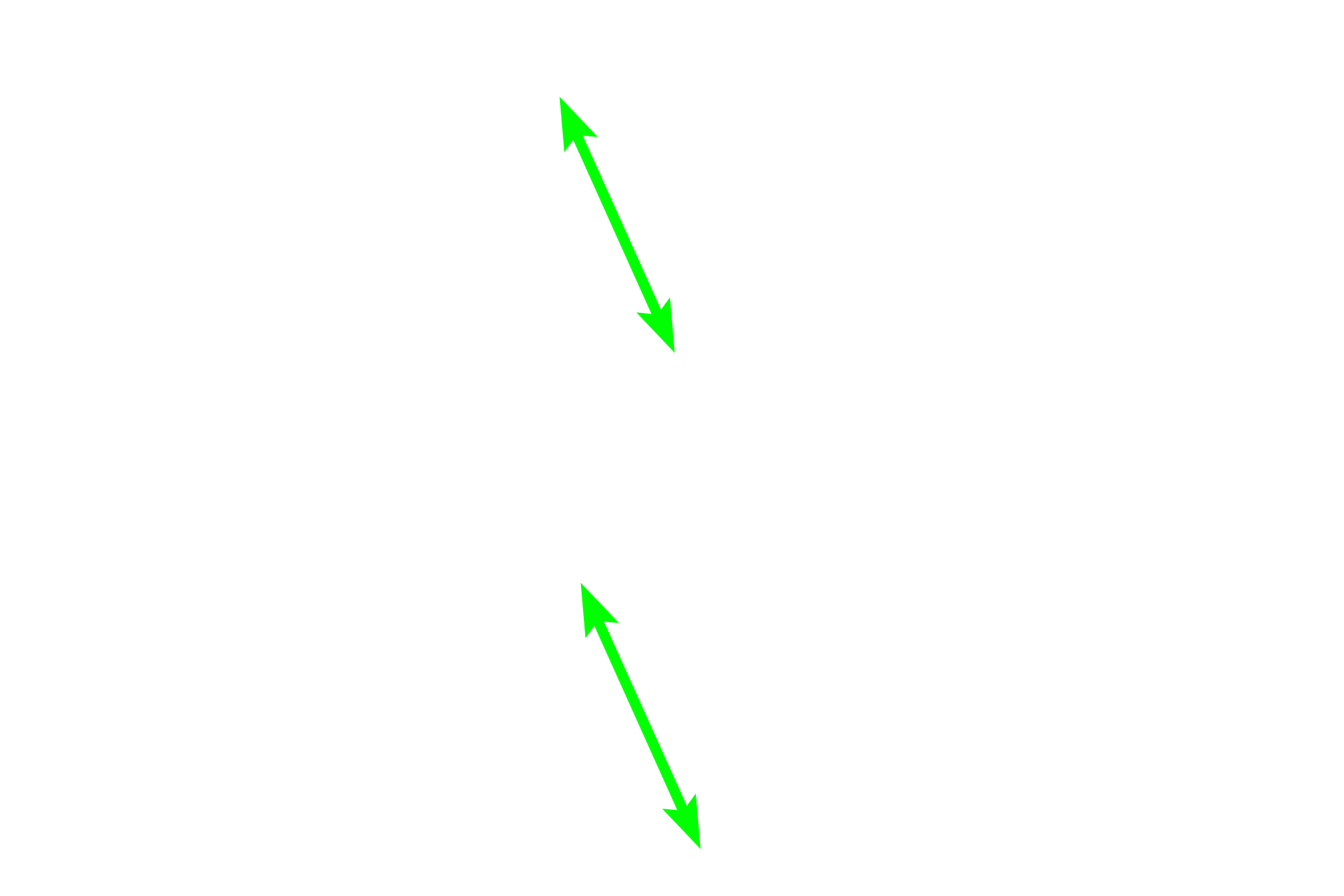
Epithelium
The epithelium of the duct of the epididymis consists of a pseudostratified columnar epithelium composed primarily of principal cells with tall stereocilia. Principle cells absorb luminal fluid thereby concentrating the sperm. This epithelium decreases in height as the duct progresses from the head to the tail region. 600x
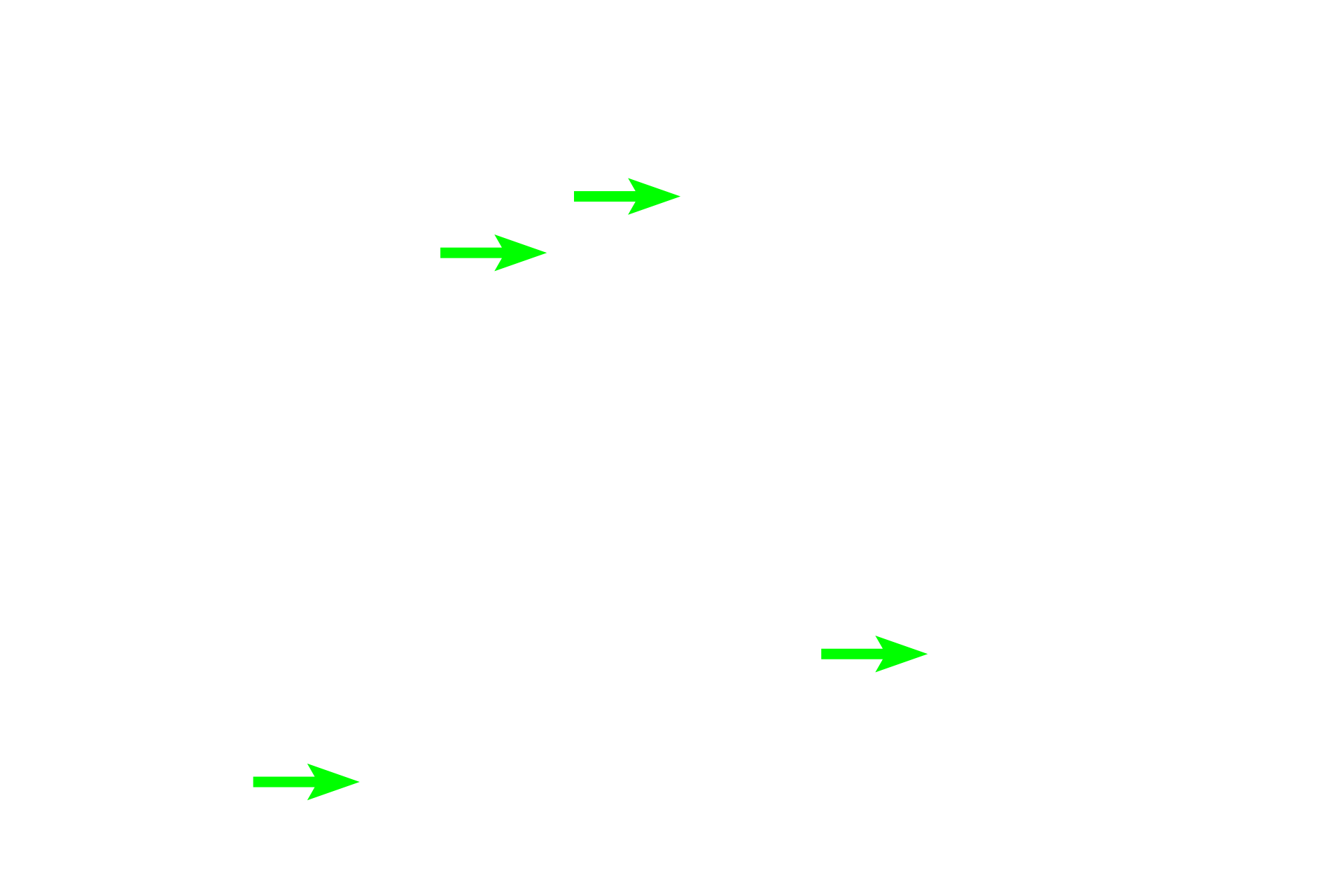
- Stereocilia
The epithelium of the duct of the epididymis consists of a pseudostratified columnar epithelium composed primarily of principal cells with tall stereocilia. Principle cells absorb luminal fluid thereby concentrating the sperm. This epithelium decreases in height as the duct progresses from the head to the tail region. 600x
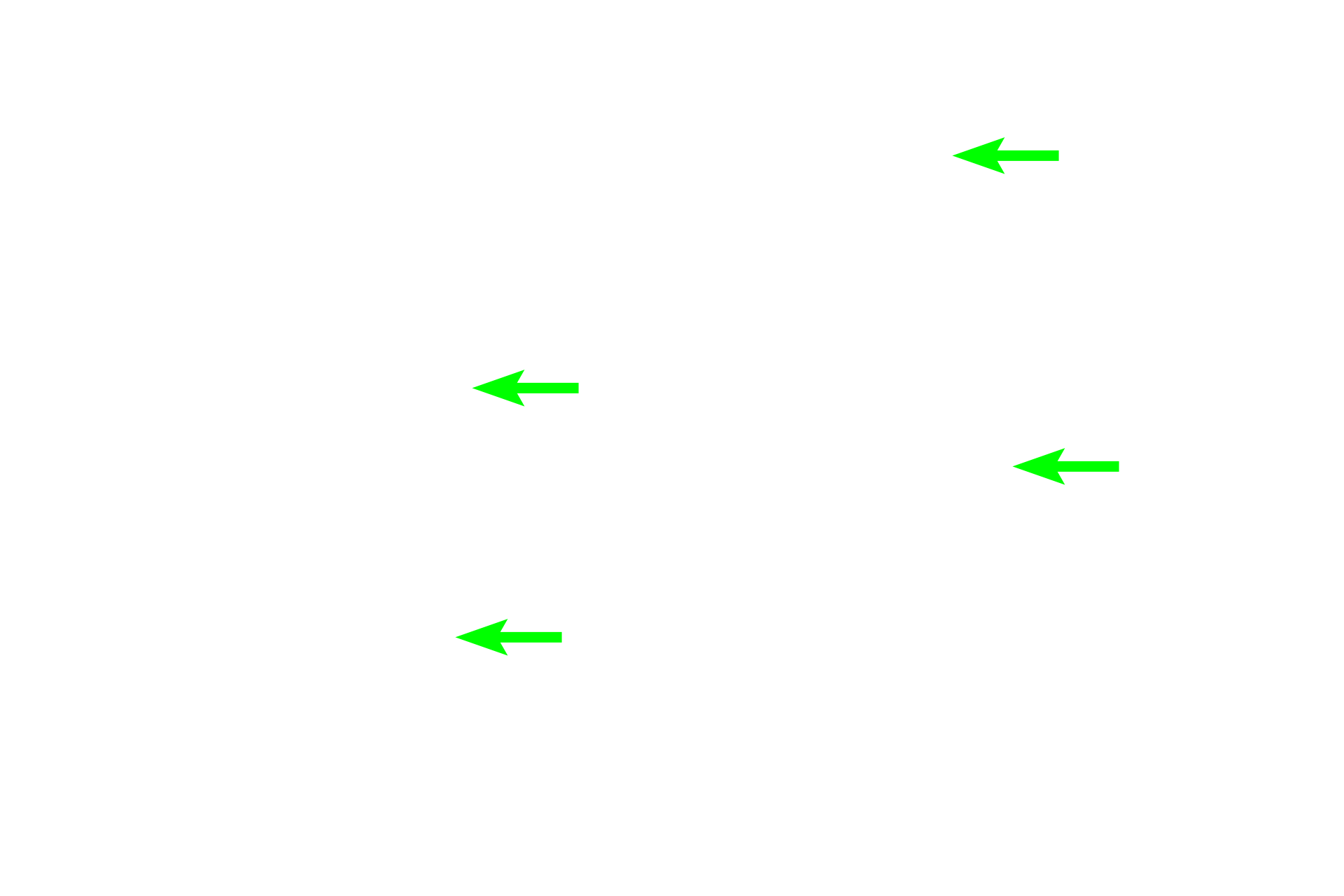
- Basal cells >
Basal cells are small, round basal cells that rest on the basement membrane and serve as stem cells for the epithelium.
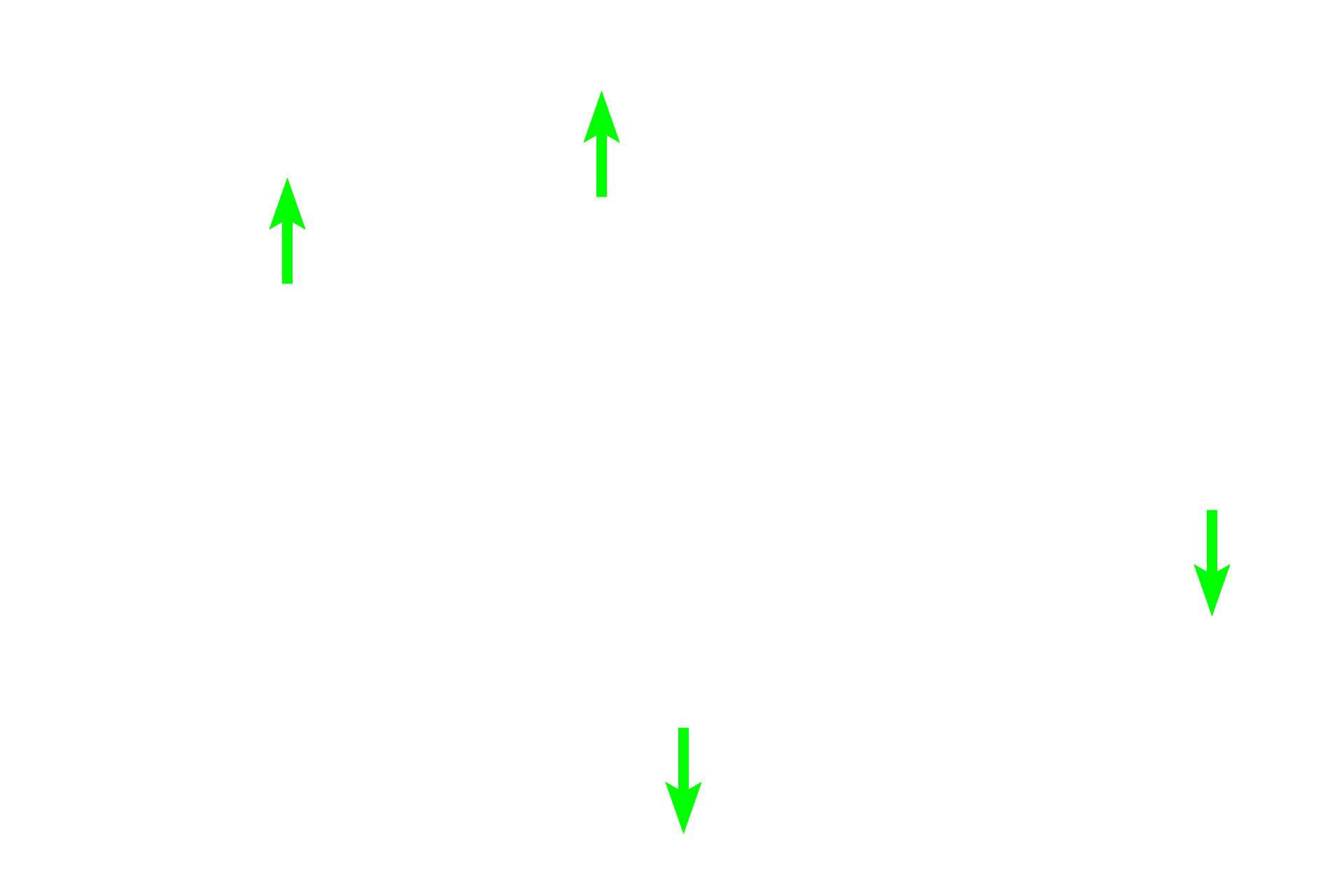
- Migrating cells >
Numerous of types of migratory immune cells are present in the epithelium lining the duct of the epididymis.
Smooth muscle >
Smooth muscle surrounding the epithelium gradually increases in thickness from the head to tail regions. In the head, smooth muscle is circularly arranged, but an outer longitudinal layer is added in the body region and a third layer is added in the tail, characteristic of the three muscle layers seen in the ductus deferens. Peristaltic contractions of the smooth muscle propel the sperm.
Spermatozoa >
Spermatozoa entering the epididymis are immature. While stored in the epididymis, they mature, acquiring motility and the ability to fertilize an ovum.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS