
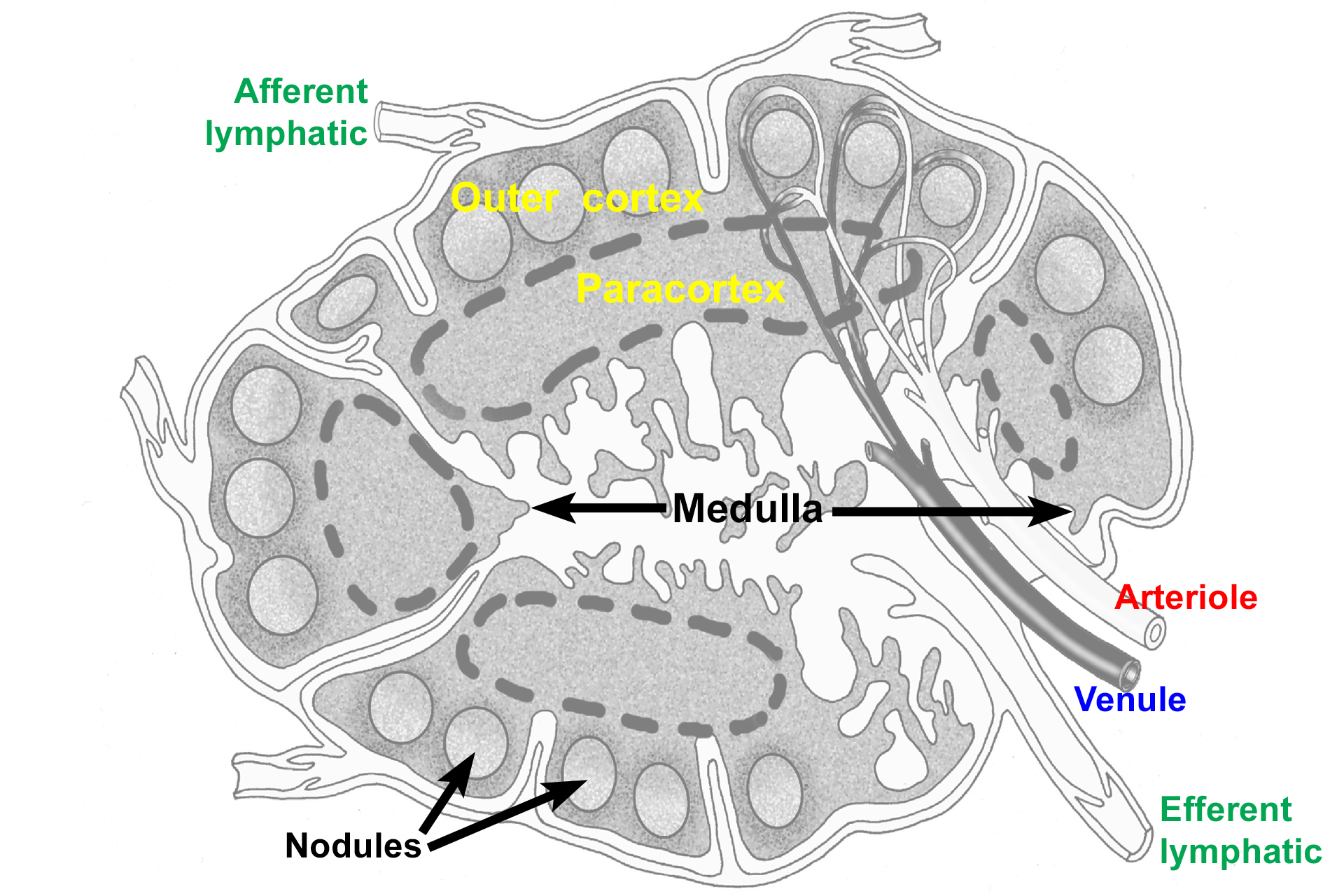
Lymph node
A low power micrograph of the lymph node displays the components illustrated in the preceding drawing. 10x
Overlay
A low power micrograph of the lymph node displays the components illustrated in the preceding drawing. 10x
Hilum >
The hilum is the indented portion of lymph nodes where the efferent lymphatics and venules exit and where arterioles enter.
Capsule >
Each lymph node is surrounded by a dense connective tissue capsule. Afferent lymphatics pierce the capsule to enter the subcapsular sinus lying beneath it. The subcapsular sinus drains into trabecular (intermediate) sinuses that traverse the cortex to connect with medullary sinuses. Medullary sinuses anastomose to form the efferent lymphatic that exits at the hilum.
Subcapsular sinus
Each lymph node is surrounded by a dense connective tissue capsule. Afferent lymphatics pierce the capsule to enter the subcapsular sinus lying beneath it. The subcapsular sinus drains into trabecular (intermediate) sinuses that traverse the cortex to connect with medullary sinuses. Medullary sinuses anastomose to form the efferent lymphatic that exits at the hilum.
Trabecular sinuses
Each lymph node is surrounded by a dense connective tissue capsule. Afferent lymphatics pierce the capsule to enter the subcapsular sinus lying beneath it. The subcapsular sinus drains into trabecular (intermediate) sinuses that traverse the cortex to connect with medullary sinuses. Medullary sinuses anastomose to form the efferent lymphatic that exits at the hilum.
Outer cortex >
The outer cortex is composed primarily of lymphoid nodules and is a B-dependent area.

Paracortex >
The paracortex is composed of tissue resembling diffuse lymphoid tissue and is a thymus-dependent (T-dependent) area.

Medullary cords >
Medullary cords are finger-like projections of B-dependent, lymphoid tissue, containing plasma cells and memory B cells.
Medullary sinuses >
Lymph drains from the subcapsular sinus into the cortical (trabecular or intermediate) sinuses and from there into the medullary sinuses. Eventually, all lymph exits at the hilum via efferent lymphatics, carrying antibodies and activated B cells.