
Vestibular macula
The image on the left shows a portion of the utricle, the larger membranous chamber in the vestibule, adjacent to its junction with the ampulla of a semicircular duct. The receptors for both structures (the macula of the utricle and the crista ampullaris of the semicircular duct) are present as well. 30x
Plane of section >
The left image is similar to a plane of section indicated by the double arrow in the illustration on the right.

Utricle >
The utricle is a portion of the membranous labyrinth located in the vestibule. A thickening in the epithelial lining of the utricle forms the macula, a neuroepithelial receptor, innervated by the vestibular division of cranial nerve VIII. The macula of the saccule would be identical to that shown here in the utricle.

- Utricular macula
The utricle is a portion of the membranous labyrinth located in the vestibule. A thickening in the epithelial lining of the utricle forms the macula, a neuroepithelial receptor, innervated by the vestibular division of cranial nerve VIII. The macula of the saccule would be identical to that shown here in the utricle.
-- Macular components >
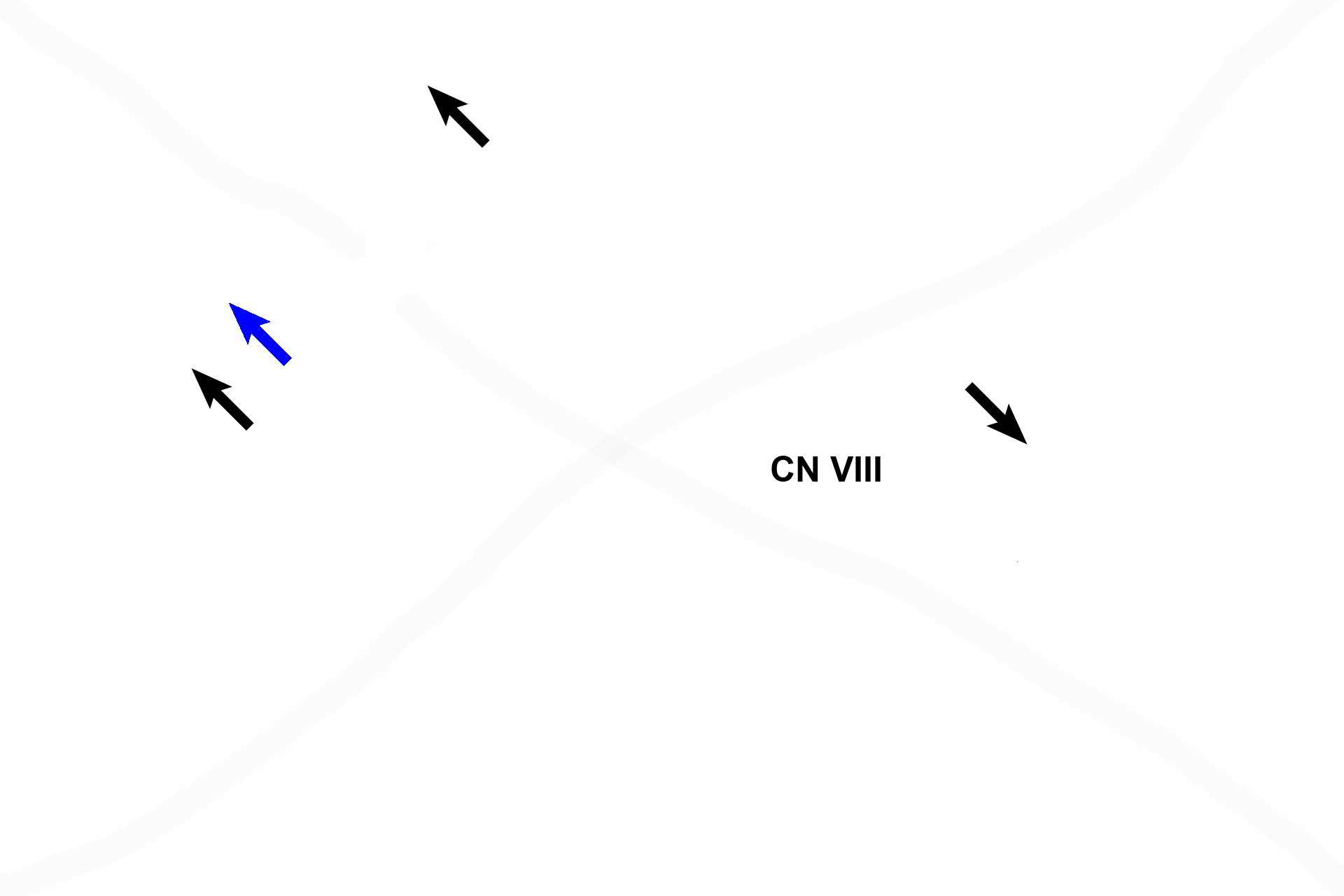
Each macula contains hair cells that possess stereocilia and a cilium, embedded in a gelatinous layer. Otoliths (blue arrow) are suspended at the surface of the gel. Cells of the planum semilunatum (black arrows) produce endolymph. Changes in gravity and linear motion displace the otoliths, which deflect the stereocilia and cilium, thereby initiating an impulse in CN VIII.

Semicircular ducts >
Each semicircular duct, suspended in its bony semicircular canal, is a circularly arranged tube; both ends of the tube join the utricle. An enlargement, the ampulla, at one end of the tube houses its receptor, the crista ampullaris.

- Ampullae
Each semicircular duct, suspended in its bony semicircular canal, is a circularly arranged tube; both ends of the tube join the utricle. An enlargement, the ampulla, at one end of the tube houses its receptor, the crista ampullaris.
-- Cristae ampullares >
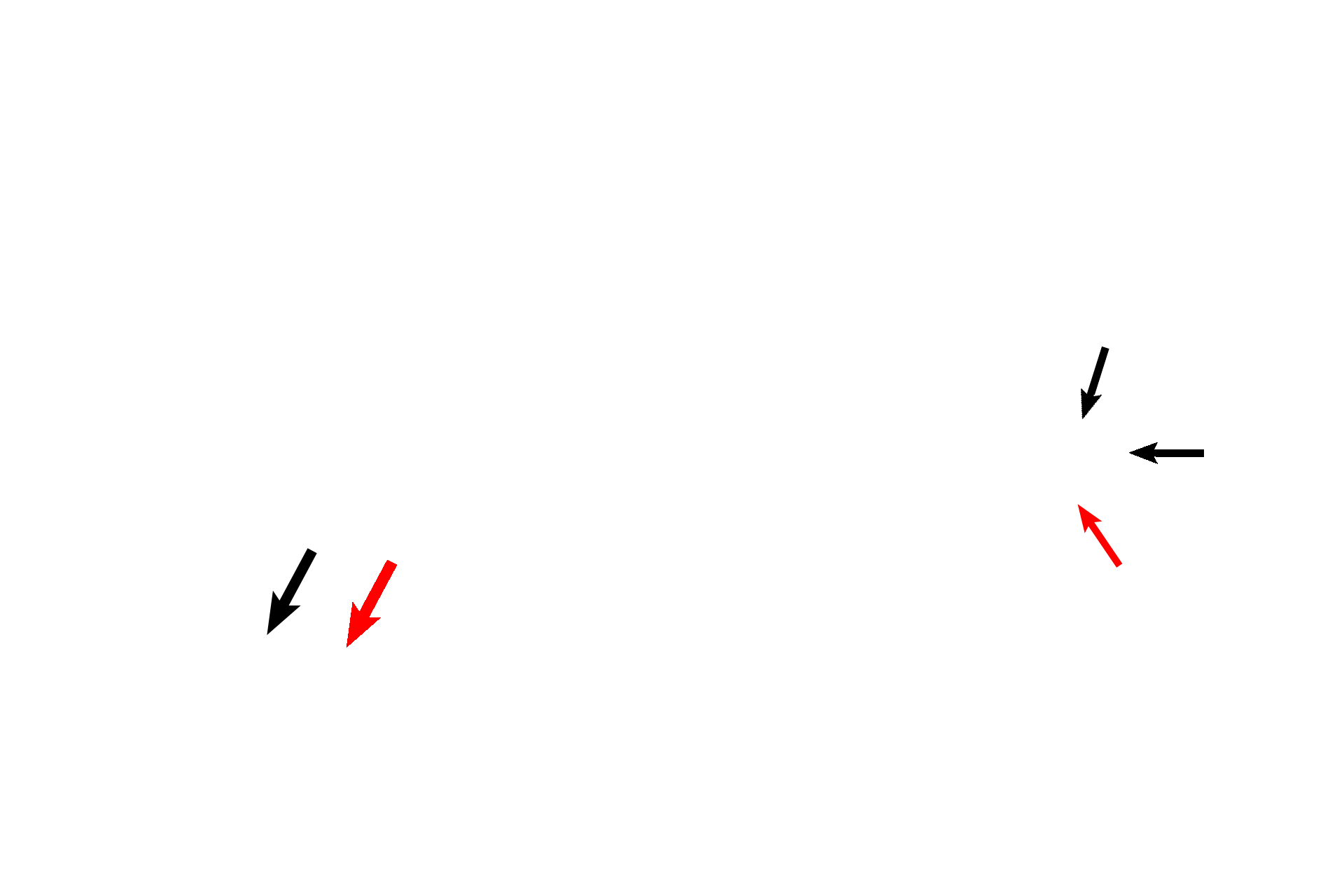
The ampulla, at one end of the semicircular duct houses the receptor, the crista ampullaris (black arrow). Each receptor possesses a gelatinous cupula (red arrow) that extends to the opposite wall of the ampulla.
Connective tissue reticulum >
Connective tissue cells that appear scattered in the perilymph around the outside of the ampulla are part of the connective tissue reticulum that secures the membranous labyrinth in the osseous labyrinth.
Temporal bone >
The temporal bone comprises the wall of the spaces forming the osseous labyrinth.

Ganglion of CN VIII >
The sensory cell bodies of the neurons supplying the maculae and cristae ampullares are located adjacent to these receptors. These neurons are part of the vestibular division of the vestibulocochlear nerve, CN VIII.