
Semicircular canals
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x
Vestibule
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x
Utricle
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x
- Macula of utricle
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x

Saccule
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x

- Macula of saccule
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x

Semicircular canals
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x
- Ampullae of semicircular ducts
Both images show the ampulla of a semicircular duct at its connection with the utricle. In the left image the saccule is also present. 30x, 30x
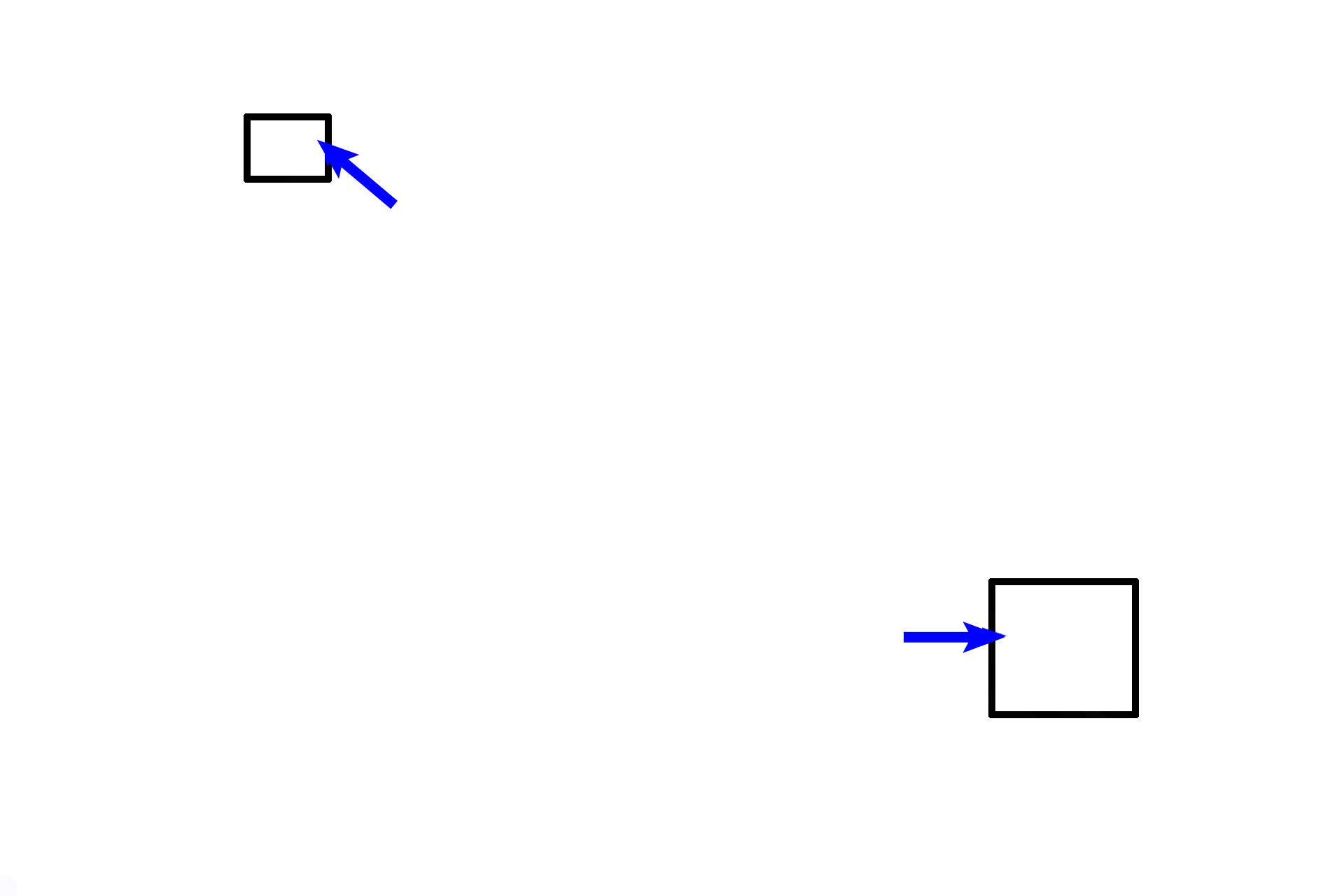
-- Cristae ampullares >
The crista ampullaris is a ridge-shaped receptor in each ampulla, lying perpendicular to the long axis of the duct. The hair cells of each crista are embedded in a cone-shaped, gelatinous layer, the cupula (blue arrows), which spans the ampulla to reach the opposite wall. Cristae lack otoliths.
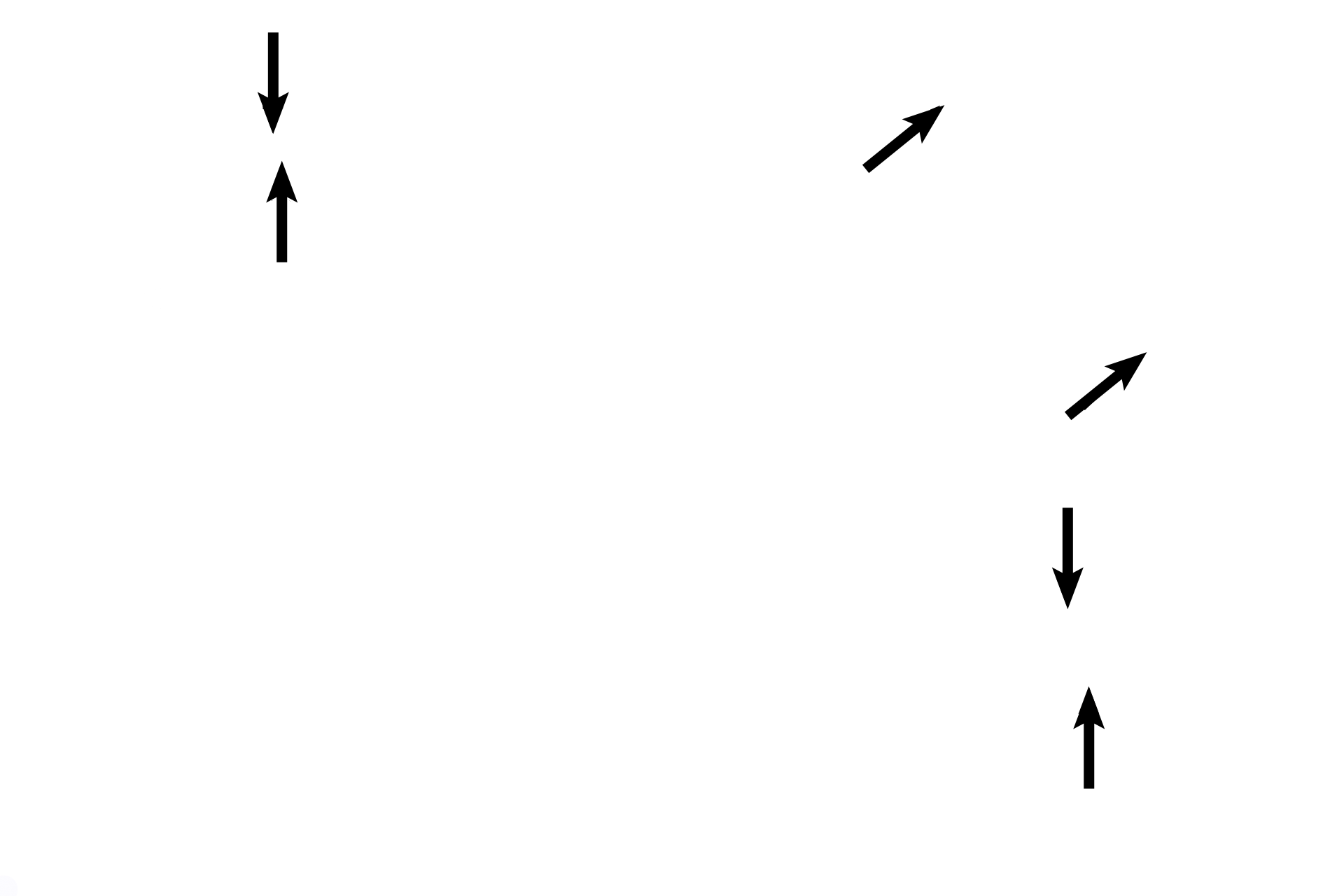
--- Planum semilunatum >
Planum semilunatum cells are located on the sloping sides around the bases of the cristae and maculae. These cells, along with other cells in the cochlear duct, produce endolymph. In the right image, these cells of the crista are distorted, buckled outward like a pleat.
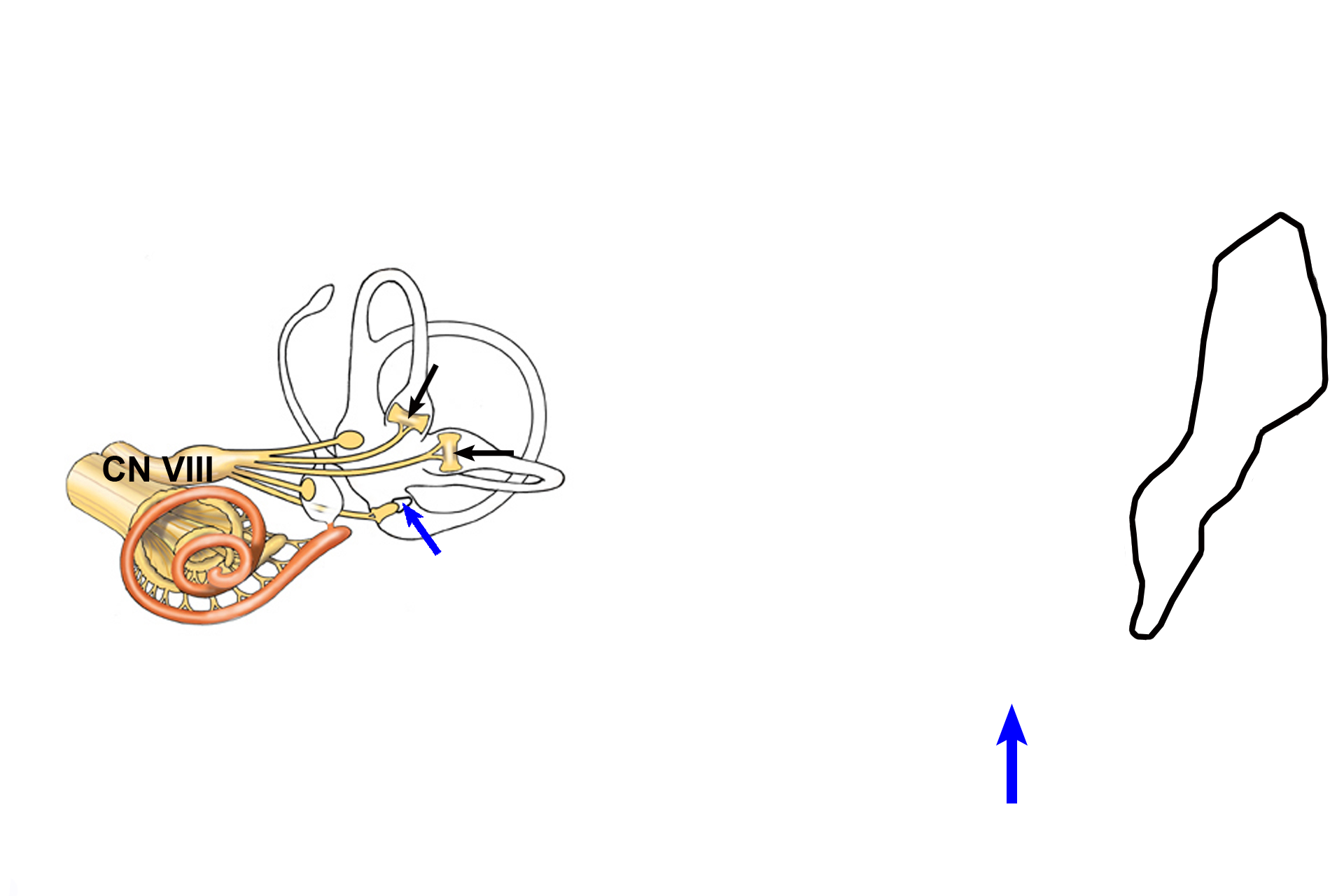
CN VIII >
The vestibular division of cranial nerve VIII innervates each crista ampullaris (black arrows) Movement of endolymph, caused by angular acceleration, displaces the gelatinous cupula (blue arrows) and triggers a neural, sensory impulse in this nerve. The cupula in the right image is shown spanning the ampulla. The sensory ganglion of CN VIII (black outline) is also seen.

Connective tissue reticulum >
A specialized reticulum of connective tissue cells (arrows and X) spans the interval between the membranous labyrinth and the periosteum of the osseous labyrinth. The structures of the membranous labyrinth are surrounded and supported in the osseous labyrinth by this reticulum.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS