
Liver
The liver, the largest organ in the body, plays a major role in the uptake, storage and distribution of nutrients. It also maintains blood glucose levels, degrades drugs and toxins, and recycles aged red blood cells. Its secretory products include the majority of circulating plasma proteins (endocrine function) and bile (exocrine function). Bile primarily contains bile salts (e.g., deoxycholic acid) for emulsifying fat in the intestine, bile pigments (e.g., bilirubin) from the breakdown of hemoglobin, phospholipids and cholesterol. Bile is transported to the duodenum via the common bile duct. Pig liver, 40x
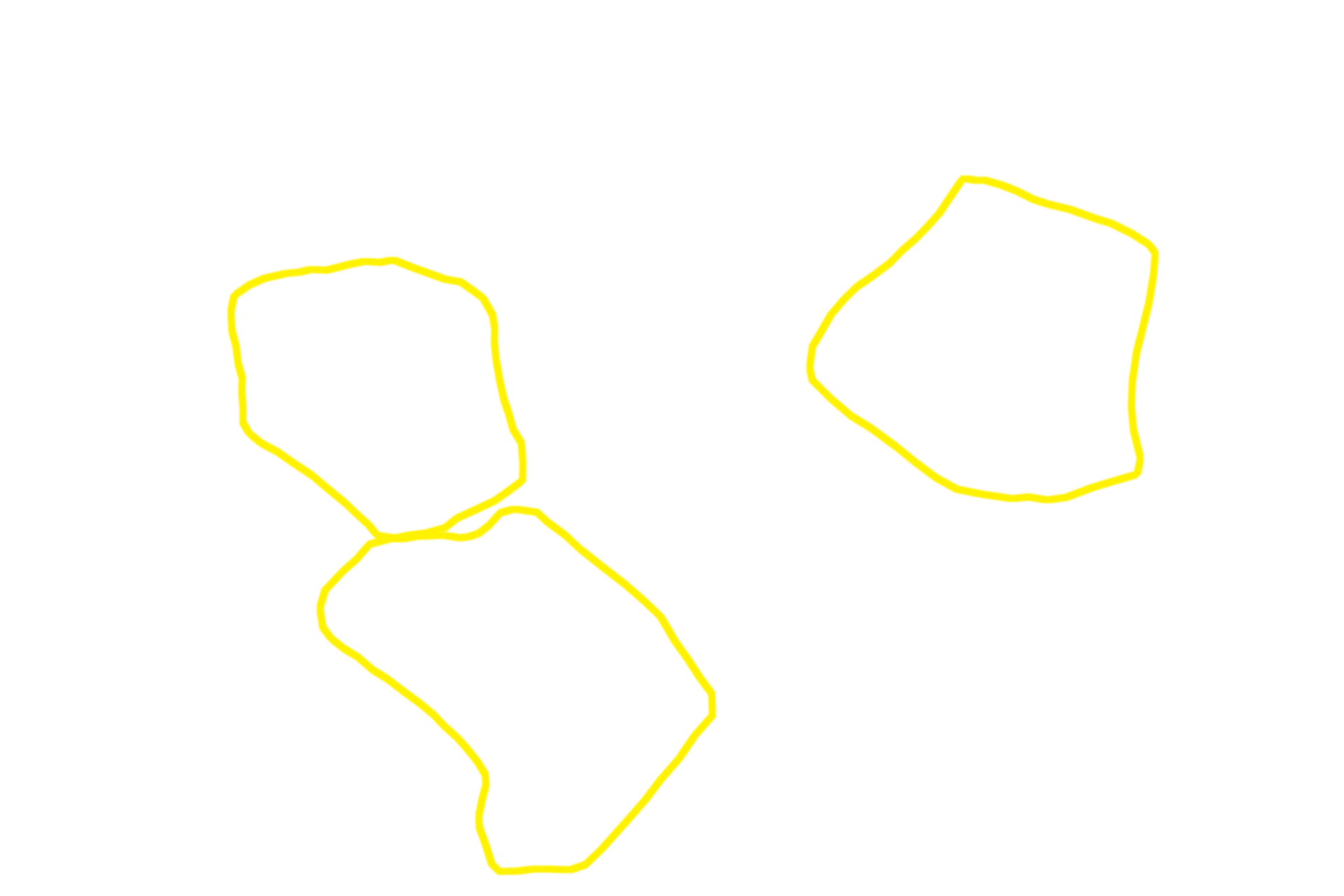
Liver lobules >
The lobule, the basic structure of the liver, is formed by anastomosing rows of hepatocytes and intervening sinusoids, which extend from the periphery of the lobule toward a central vein. Portal canals, located at the marginal angles around the perimeter of the lobule, contain branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct. This image of pig liver shows bands of connective tissue outlining lobules; these distinctions are not so obvious in the human.
- Connective tissue
The lobule, the basic structure of the liver, is formed by anastomosing rows of hepatocytes and intervening sinusoids, which extend from the periphery of the lobule toward a central vein. Portal canals, located at the marginal angles around the perimeter of the lobule, contain branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct. This image of pig liver shows bands of connective tissue outlining lobules; these distinctions are not so obvious in the human.
- Portal canals
The lobule, the basic structure of the liver, is formed by anastomosing rows of hepatocytes and intervening sinusoids, which extend from the periphery of the lobule toward a central vein. Portal canals, located at the marginal angles around the perimeter of the lobule, contain branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct. This image of pig liver shows bands of connective tissue outlining lobules; these distinctions are not so obvious in the human.
- Central veins
The lobule, the basic structure of the liver, is formed by anastomosing rows of hepatocytes and intervening sinusoids, which extend from the periphery of the lobule toward a central vein. Portal canals, located at the marginal angles around the perimeter of the lobule, contain branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct. This image of pig liver shows bands of connective tissue outlining lobules; these distinctions are not so obvious in the human.
- Hepatocytes
The lobule, the basic structure of the liver, is formed by anastomosing rows of hepatocytes and intervening sinusoids, which extend from the periphery of the lobule toward a central vein. Portal canals, located at the marginal angles around the perimeter of the lobule, contain branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct. This image of pig liver shows bands of connective tissue outlining lobules; these distinctions are not so obvious in the human.
- Sinusoids
The lobule, the basic structure of the liver, is formed by anastomosing rows of hepatocytes and intervening sinusoids, which extend from the periphery of the lobule toward a central vein. Portal canals, located at the marginal angles around the perimeter of the lobule, contain branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct. This image of pig liver shows bands of connective tissue outlining lobules; these distinctions are not so obvious in the human.

Image source >
Image taken of a slide in the University of Michigan collection.