
Eosinophilic myelocytes
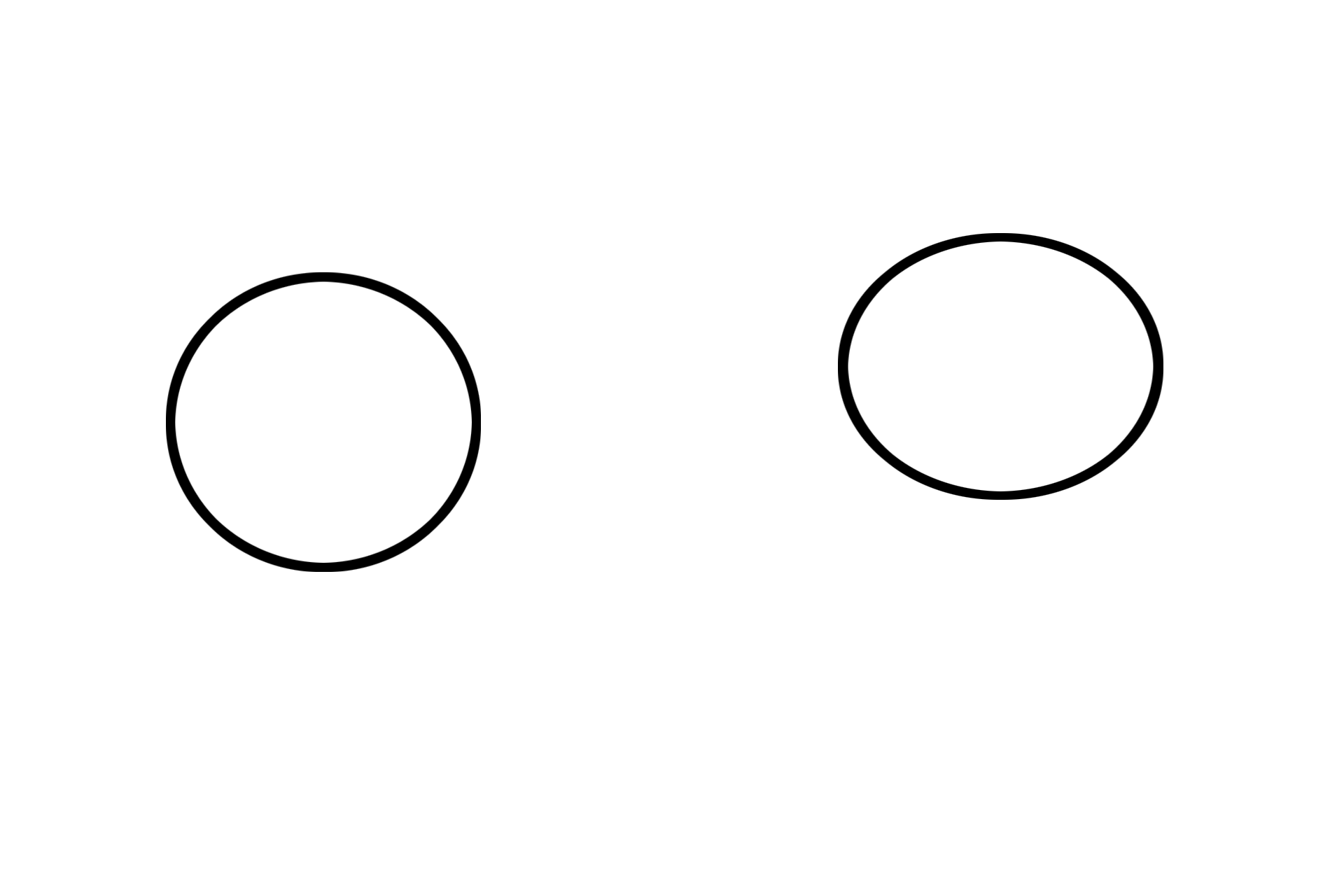
Eosinophilic myelocytes are the first definitive cell type in the eosinophilic lineage. At this stage, the cells begin to synthesize eosinophil-specific granules, which then come to predominate since azurophilic granules are no longer being produced. The nucleus of an eosinophilic myelocyte will develop a distinct indentation, at which point they become metamyelocytes. 1000x, 1000x
Eosinophilic myelocytes
Eosinophilic myelocytes are the first definitive cell type in the eosinophilic lineage. At this stage, the cells begin to synthesize eosinophil-specific granules, which then come to predominate since azurophilic granules are no longer being produced. The nucleus of an eosinophilic myelocyte will develop a distinct indentation, at which point they become metamyelocytes. 1000x, 1000x
- Nuclei
Eosinophilic myelocytes are the first definitive cell type in the eosinophilic lineage. At this stage, the cells begin to synthesize eosinophil-specific granules, which then come to predominate since azurophilic granules are no longer being produced. The nucleus of an eosinophilic myelocyte will develop a distinct indentation, at which point they become metamyelocytes. 1000x, 1000x
- Granules >
Specific or secondary granules in eosinophils contain a variety of proteins including eosinophil major basic protein, RNAases and peroxidase; enzymes important for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections. Due to the cationic nature of these contents, the granules stain intensely with eosin.

Segmented neutrophils
Specific or secondary granules in eosinophils contain a variety of proteins including eosinophil major basic protein, RNAases and peroxidase; enzymes important for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections. Due to the cationic nature of these contents, the granules stain intensely with eosin.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS