
Junctional complex
Located at the apical-lateral surface of adjacent epithelial cells, junctional complexes are sites of membrane sealing (zonula occludens) and cell attachment (zonula adherens, desmosomes). These structures can be resolved individually at the EM level; however, with the LM they appear as a single, tiny bar or dot called the terminal bar. Small intestine (electron micrograph) 35,000x
Terminal bar >
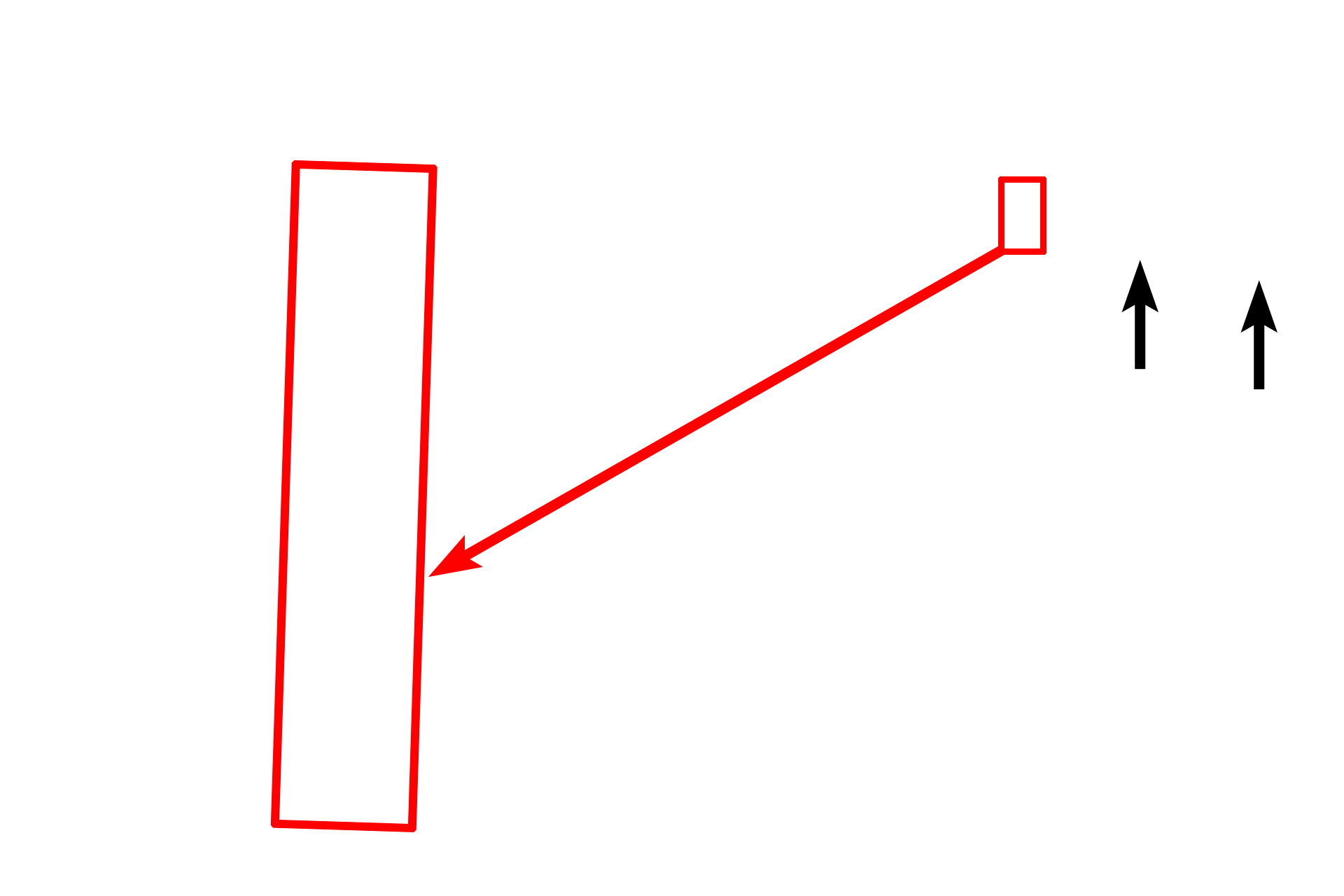
The light micrograph illustrates the single, tiny dot, called the terminal bar (arrows), which is the light microscopic appearance of the junctional complex. The three parts of the junctional complex are only visible with the electron microscope. The complex is visible by light microscopy due to the large accumulation of various proteins that comprise the complex.
Junctional complex >
A junctional complex consists of three components. A zonula occludens, or tight junction, encircles the cell apex, providing a barrier between the lumen and the intercellular space. Zonula adherens, also belt-like, is located below the zonula occludens, providing attachment and stability between adjacent cells. The desmosome or macula adherens functions like a “spot-weld” to attach and anchor adjacent cells.
- Zonula occludens
A junctional complex consists of three components. A zonula occludens, or tight junction, encircles the cell apex, providing a barrier between the lumen and the intercellular space. Zonula adherens, also belt-like, is located below the zonula occludens, providing attachment and stability between adjacent cells. The desmosome or macula adherens functions like a “spot-weld” to attach and anchor adjacent cells.

- Zonula adherens
A junctional complex consists of three components. A zonula occludens, or tight junction, encircles the cell apex, providing a barrier between the lumen and the intercellular space. Zonula adherens, also belt-like, is located below the zonula occludens, providing attachment and stability between adjacent cells. The desmosome or macula adherens functions like a “spot-weld” to attach and anchor adjacent cells.

- Desmosome
A junctional complex consists of three components. A zonula occludens, or tight junction, encircles the cell apex, providing a barrier between the lumen and the intercellular space. Zonula adherens, also belt-like, is located below the zonula occludens, providing attachment and stability between adjacent cells. The desmosome or macula adherens functions like a “spot-weld” to attach and anchor adjacent cells.

Microvilli and stereocilia >
Microvilli (red arrows) extend from the surface of the small intestine cells shown in the electron micrograph, while stereocilia (long microvilli, black arrows) are associated with the epididymis in the light micrograph. Both structures increase surface area of the organs on which they are located.
Microfilaments and terminal web >
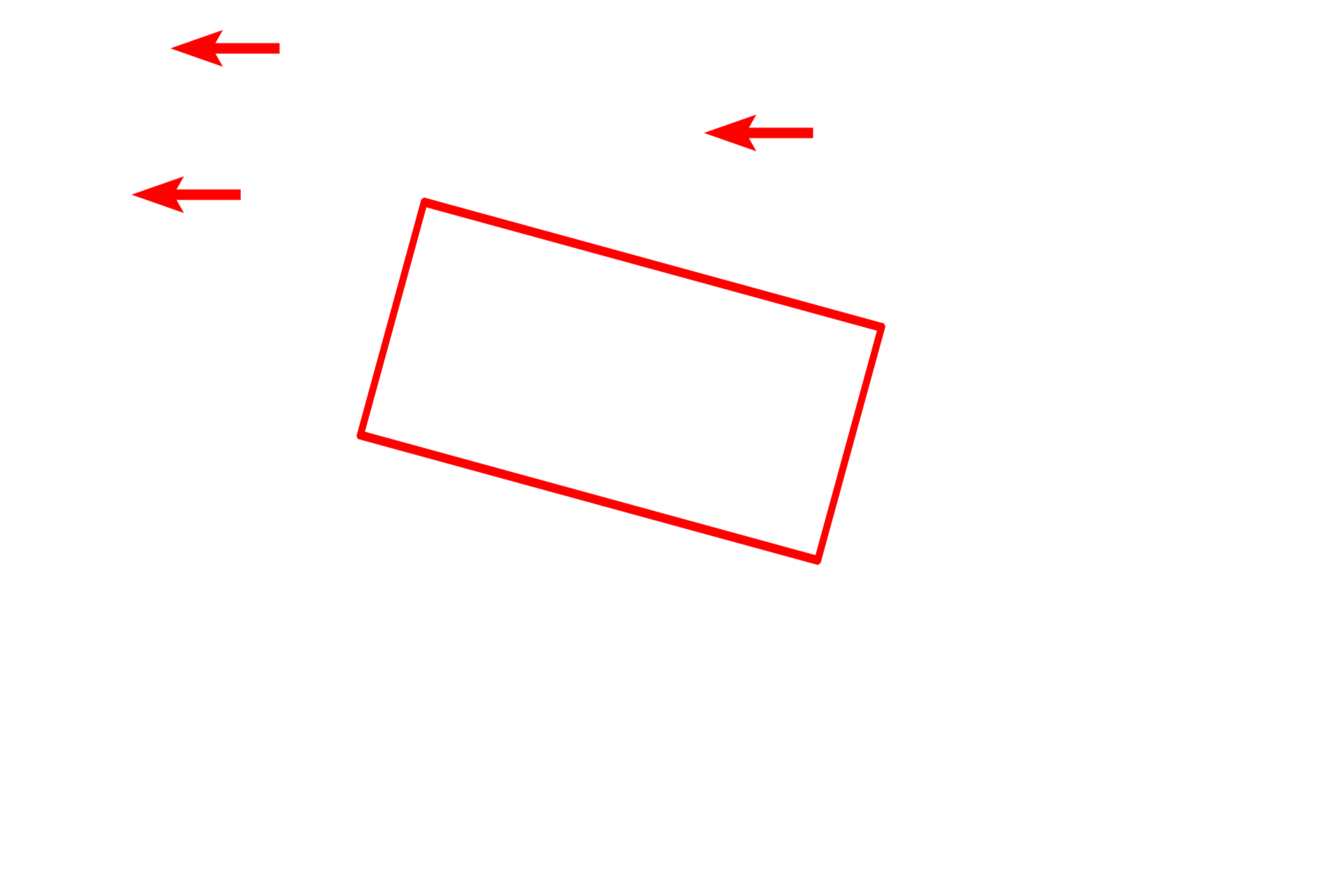
Microfilaments (red arrows) form a central core for the microvilli, providing support and form. The filaments are anchored into a horizontal web of microfilaments, the terminal web (red box), located in the apical region of each cell.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS