
Junctional complex
This image is similar to the previous one and will be used to illustrate the molecular components of the junctional complex. Small intestine 35,000x
Junctional complex
This image is similar to previous one and will be used to illustrate the molecular components of the junctional complex. Small intestine 35,000x
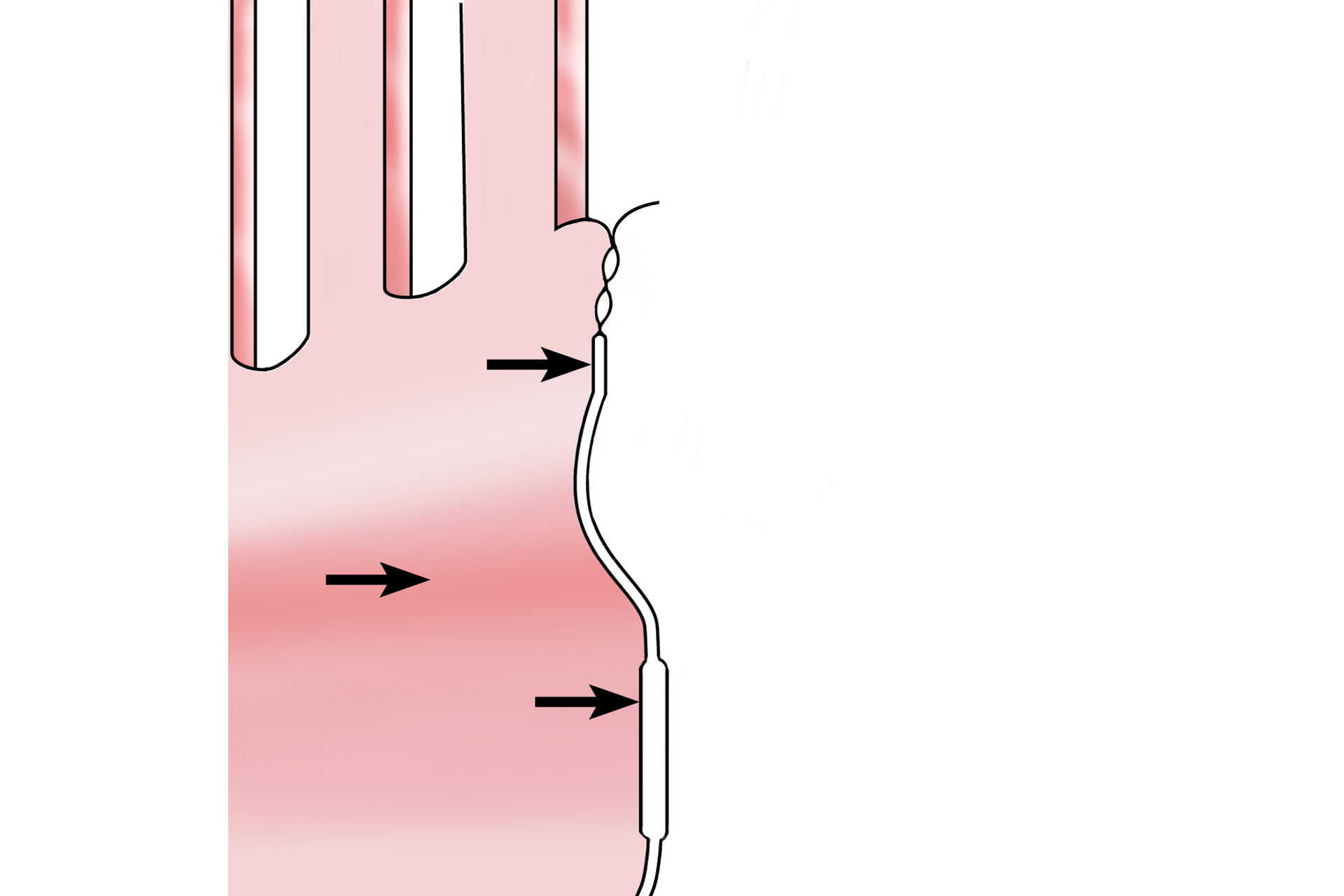
Illustration >
In this illustration, most of the cell on the left side of the junctional complex has been removed, leaving only a view of the inner surface of its plasma membrane (arrows) and microvilli. The complexity, composition and extent of the components of the junctional complex will be illustrated using this figure as a foundation.
- Zonula occludens >
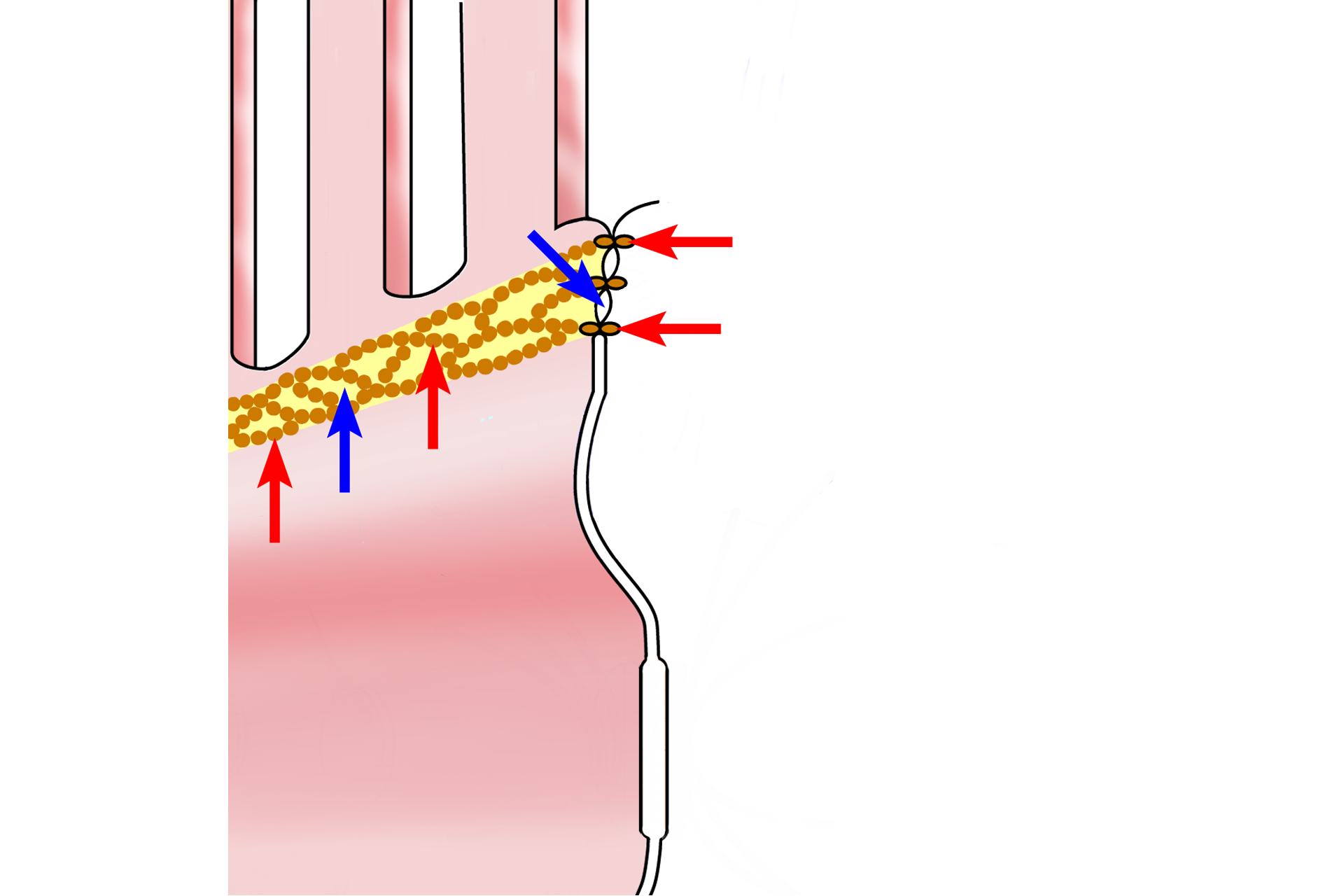
The zonula occludens, or tight junction, forms a band encircling the apical portion of the cell. Transmembrane proteins in the cell membranes of adjacent cells contact each other in the intercellular space (red arrows). These proteins are distributed in the membrane as an interlacing meshwork around the perimeter of the cells (blue arrows) that effectively seal the membranes, prohibiting passage of material from the lumen to the intercellular space. These contacts do not provide cell adhesion.
- Zonula adherens >
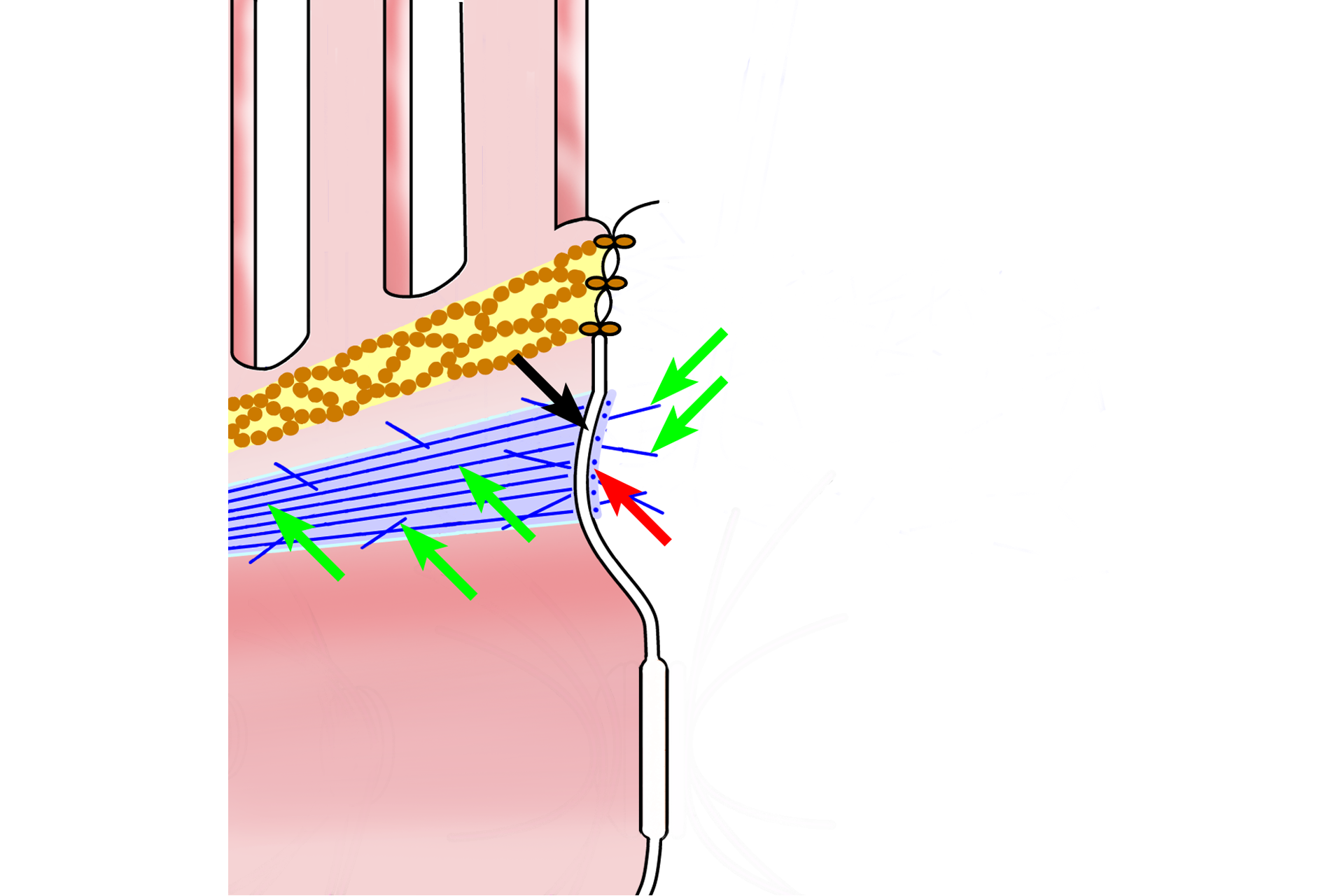
The zonula adherens is a belt-like structure that provides adhesion for adjacent cells and integrity of the epithelium. The zonula adherens consists of protein complexes (red arrow) on the cytoplasmic side of adjacent plasma membranes. Transmembrane proteins in the complexes extend into the intercellular space (black arrow) to provide adhesion. Microfilaments (green arrows) extend from the plaque into the cytoplasm to provide stability.
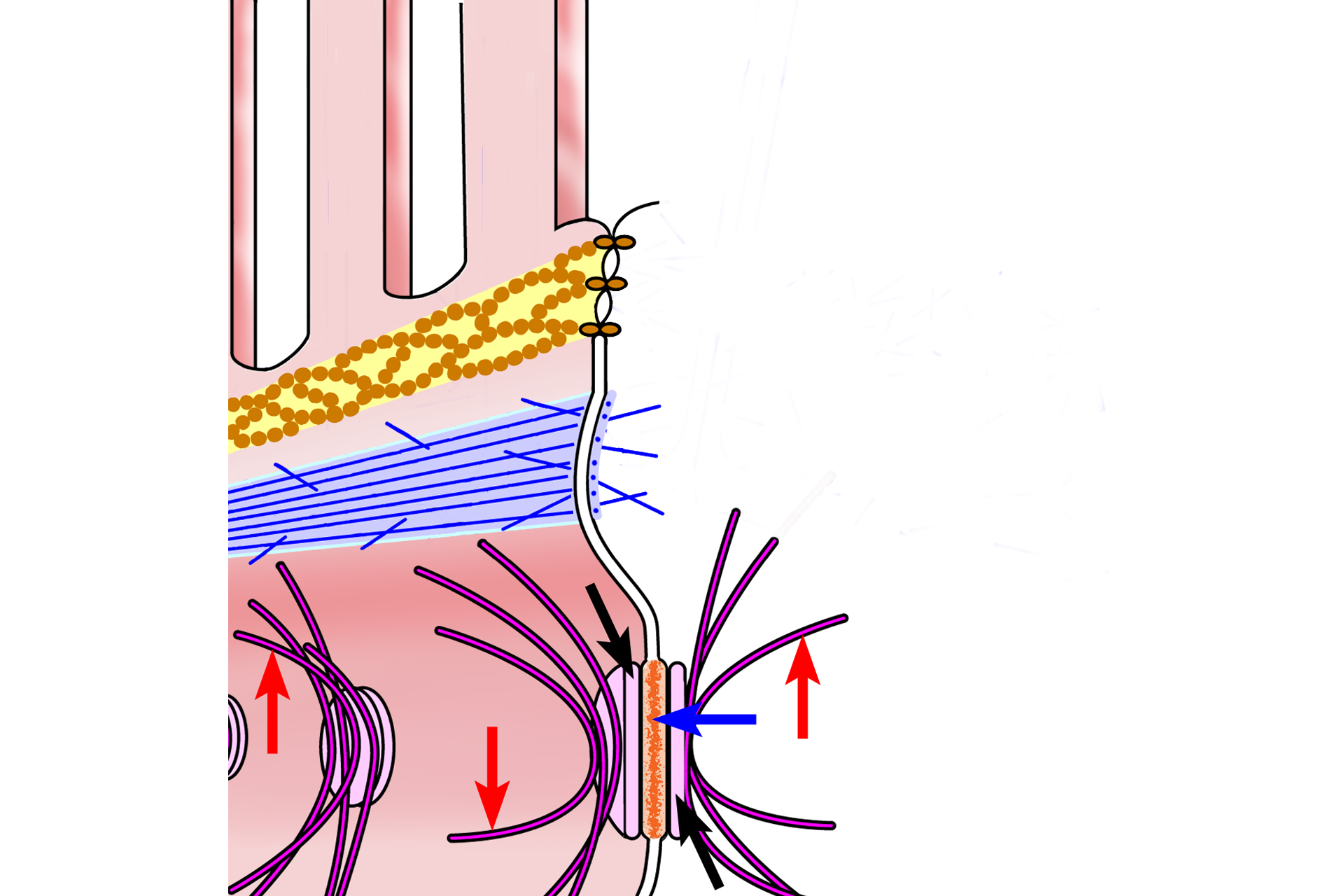
- Desmosome >
The desmosome, or macula adherens, is a spot-like weld between cells that occurs in junctional complexes and throughout the cell. Desmosomes provide adhesion and consist of attachment plaques (black arrows) with membrane proteins (blue arrow) extending into the intercellular space. Intracellularly, these plaques also serve as attachment sites for intermediate filaments (red arrows) that extend into the cytoplasm for stability.
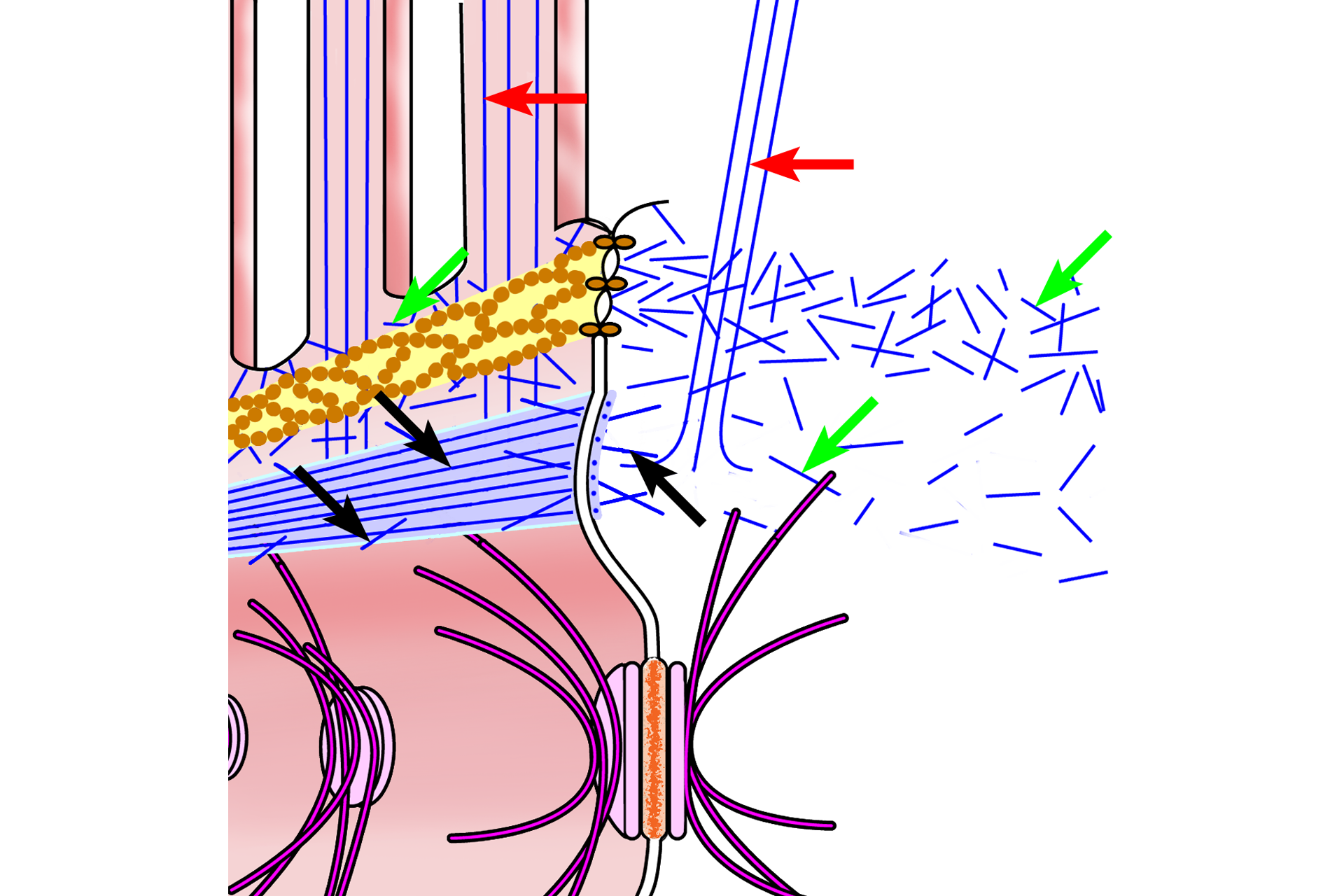
Microfilaments >
Microfilaments are important components of the cell apex. They form an integral part of the zonula adherens (black arrows) and extend from this band into the cell cytoplasm. Microfilaments form the structural support for microvilli (red arrows) and are anchored in the terminal web (green arrows), a meshwork of microfilaments just beneath the apical plasma membrane.

Begin again >
This image is similar to previous one and will be used to illustrate the molecular components of the junctional complex. Small intestine 35,000x