
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
SER consists of interconnected tubules and is the major site of lipid synthesis and calcium storage in the cell. The majority of the SER in this field is cut in cross section and, thus, appears as circular profiles. The amount of SER in a cell varies greatly depending on the function of the cell, e.g., SER is abundant in steroid secreting cells and liver cells (hepatocytes) for detoxification. 25,000x
SER
SER consists of interconnected tubules and is the major site of lipid synthesis and calcium storage in the cell. The majority of the SER in this field is cut in cross section and, thus, appears as circular profiles. The amount of SER in a cell varies greatly depending on the function of the cell, e.g., SER is abundant in steroid secreting cells and liver cells (hepatocytes) for detoxification. 25,000x
RER
SER consists of interconnected tubules and is the major site of lipid synthesis and calcium storage in the cell. The majority of the SER in this field is cut in cross section and, thus, appears as circular profiles. The amount of SER in a cell varies greatly depending on the function of the cell, e.g., SER is abundant in steroid secreting cells and liver cells (hepatocytes) for detoxification. 25,000x
Polysomes
SER consists of interconnected tubules and is the major site of lipid synthesis and calcium storage in the cell. The majority of the SER in this field is cut in cross section and, thus, appears as circular profiles. The amount of SER in a cell varies greatly depending on the function of the cell, e.g., SER is abundant in steroid secreting cells and liver cells (hepatocytes) for detoxification. 25,000x
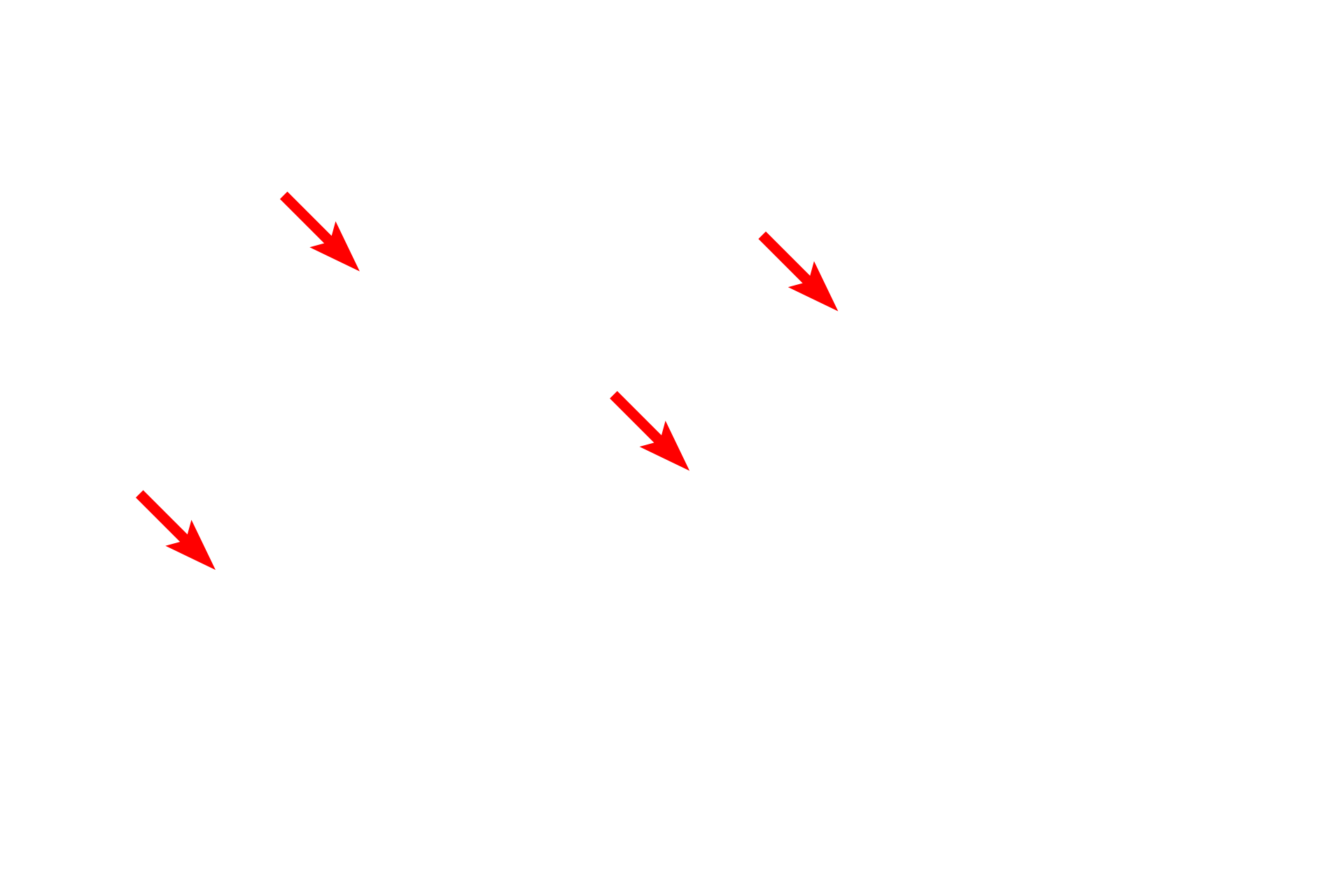

Mitochondria
SER consists of interconnected tubules and is the major site of lipid synthesis and calcium storage in the cell. The majority of the SER in this field is cut in cross section and, thus, appears as circular profiles. The amount of SER in a cell varies greatly depending on the function of the cell, e.g., SER is abundant in steroid secreting cells and liver cells (hepatocytes) for detoxification. 25,000x
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS