
Bone: endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification begins with formation of a hyaline cartilage model of the bone. In this developing long bone, chondrocytes at the center of the model, at the future primary center of ossification, begin regressive changes. These changes result in the formation of calcified spicules of cartilage on which bone is later deposited. 10x

Cartilage model
Endochondral ossification begins with formation of a hyaline cartilage model of the bone. In this developing long bone, chondrocytes at the center of the model, at the future primary center of ossification, begin regressive changes. These changes result in the formation of calcified spicules of cartilage on which bone is later deposited. 10x
Perichondrium
Endochondral ossification begins with formation of a hyaline cartilage model of the bone. In this developing long bone, chondrocytes at the center of the model, at the future primary center of ossification, begin regressive changes. These changes result in the formation of calcified spicules of cartilage on which bone is later deposited. 10x
Normal cartilage
Endochondral ossification begins with formation of a hyaline cartilage model of the bone. In this developing long bone, chondrocytes at the center of the model, at the future primary center of ossification, begin regressive changes. These changes result in the formation of calcified spicules of cartilage on which bone is later deposited. 10x

Regressive cartilage >
At this future primary center of ossification, chondrocytes have matured and hypertrophied. These enlarged cells will produce alkaline phosphatase, allowing the cartilage matrix to calcify. Nutrients are, thus, prohibited from reaching the chondrocytes, and these cells die. The spicules of calcified cartilage remaining after cells die serves as a framework on which bone is deposited.
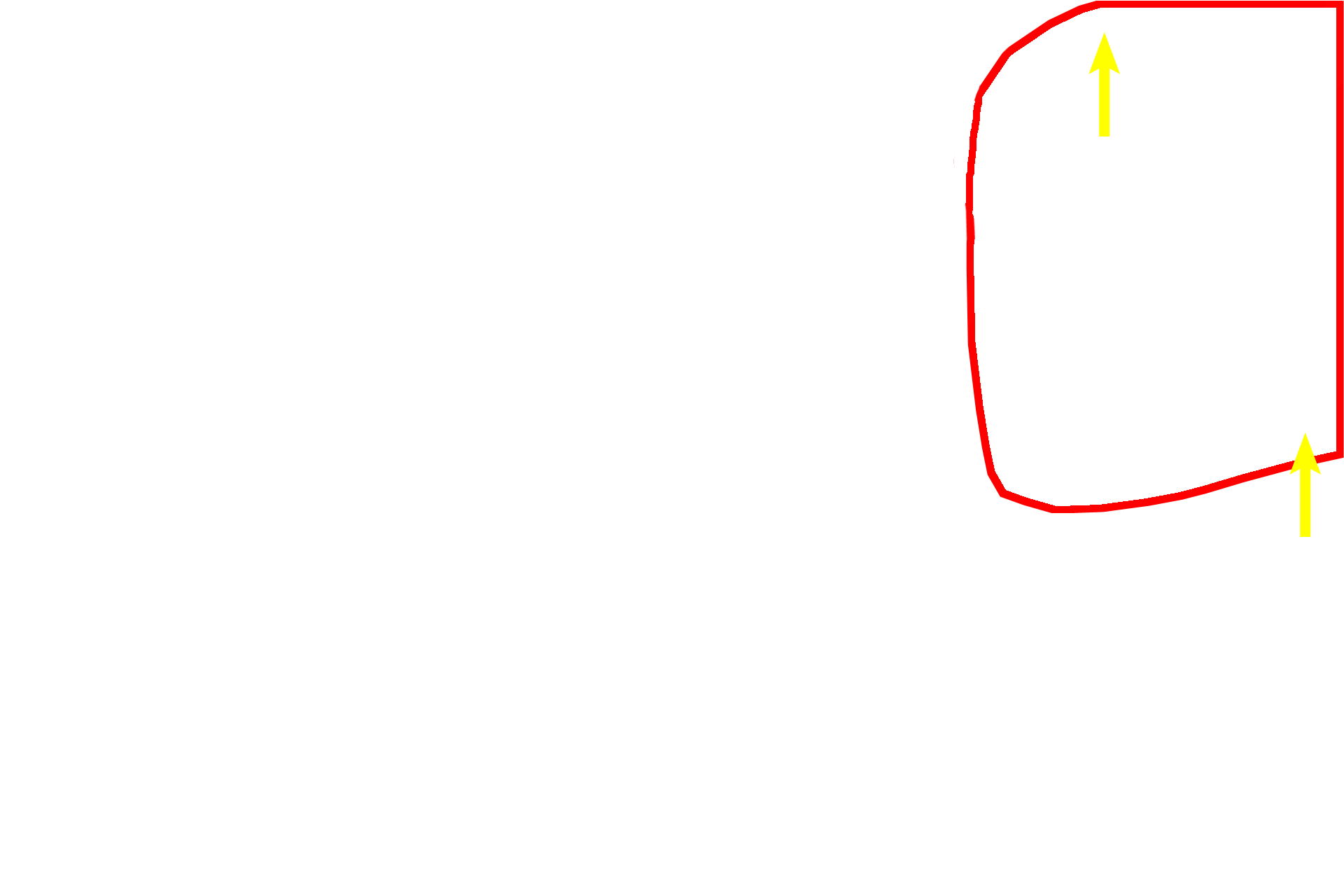
Joint >
A developing joint, with its surround ligaments and capsule (arrows) is visible between these two adjacent bones.
Next image >
The next image is similar to the area outlined by the rectangle.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS