
Peripheral nerve
This electron micrograph shows a longitudinal section of a myelinated axon in the region of the node of Ranvier. Myelin internodes terminate on either side of the node in a region called the paranode, corresponding to the position of paranodal loops. 40,000x

Axon
This electron micrograph shows a longitudinal section of a myelinated axon in the region of the node of Ranvier. Myelin internodes terminate on either side of the node in a region called the paranode, corresponding to the position of paranodal loops. 40,000x
Node of Ranvier >
The node of Ranvier is a specialized region of the axon located in the gap between adjacent paranodes. The plasma membrane of the axon at the node of Ranvier possesses a high concentration of sodium channels, which propagate the action potential.

Internodes >
A segmental unit of the myelin sheath consists of an internode and paranodes. The internodal portion (only a small segment of which is visible) contains compacted wrappings of myelin and is flanked by paranodal regions, containing uncompacted membranes that form paranodal loops.
Paranode >
The paranode is the subdivision of the segmental myelin unit located between the node of Ranvier and the internode. The paranode consists of folds of Schwann cell membrane forming paranodal loops. The paranodal loops contain Schwann cell cytoplasm, and the membranes form attachments that anchor the myelin segment to the axonal plasma membrane.
- Paranodal loops
The paranode is the subdivision of the segmental myelin unit located between the node of Ranvier and the internode. The paranode consists of folds of Schwann cell membrane forming paranodal loops. The paranodal loops contain Schwann cell cytoplasm, and the membranes form attachments that anchor the myelin segment to the axonal plasma membrane.
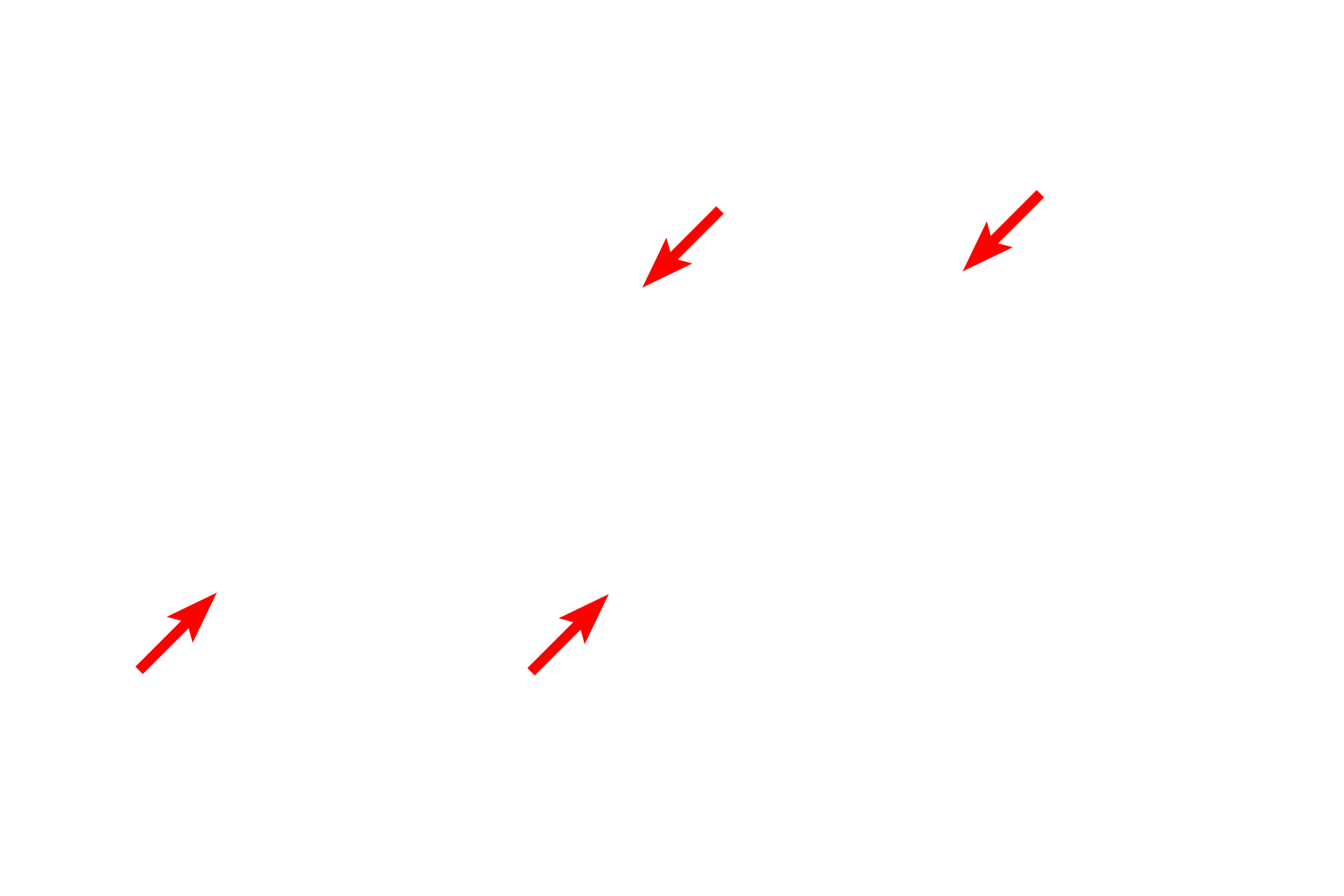
Microtubules >
Large number of microtubules (red arrows) in the axon condense as they pass through the node. The apparent thinness (green arrow) of the axon in the node of Ranvier is the result of a tangential section through this region.

Schwann cell processes >
The node of Ranvier is covered by microvillous processes of Schwann cells.
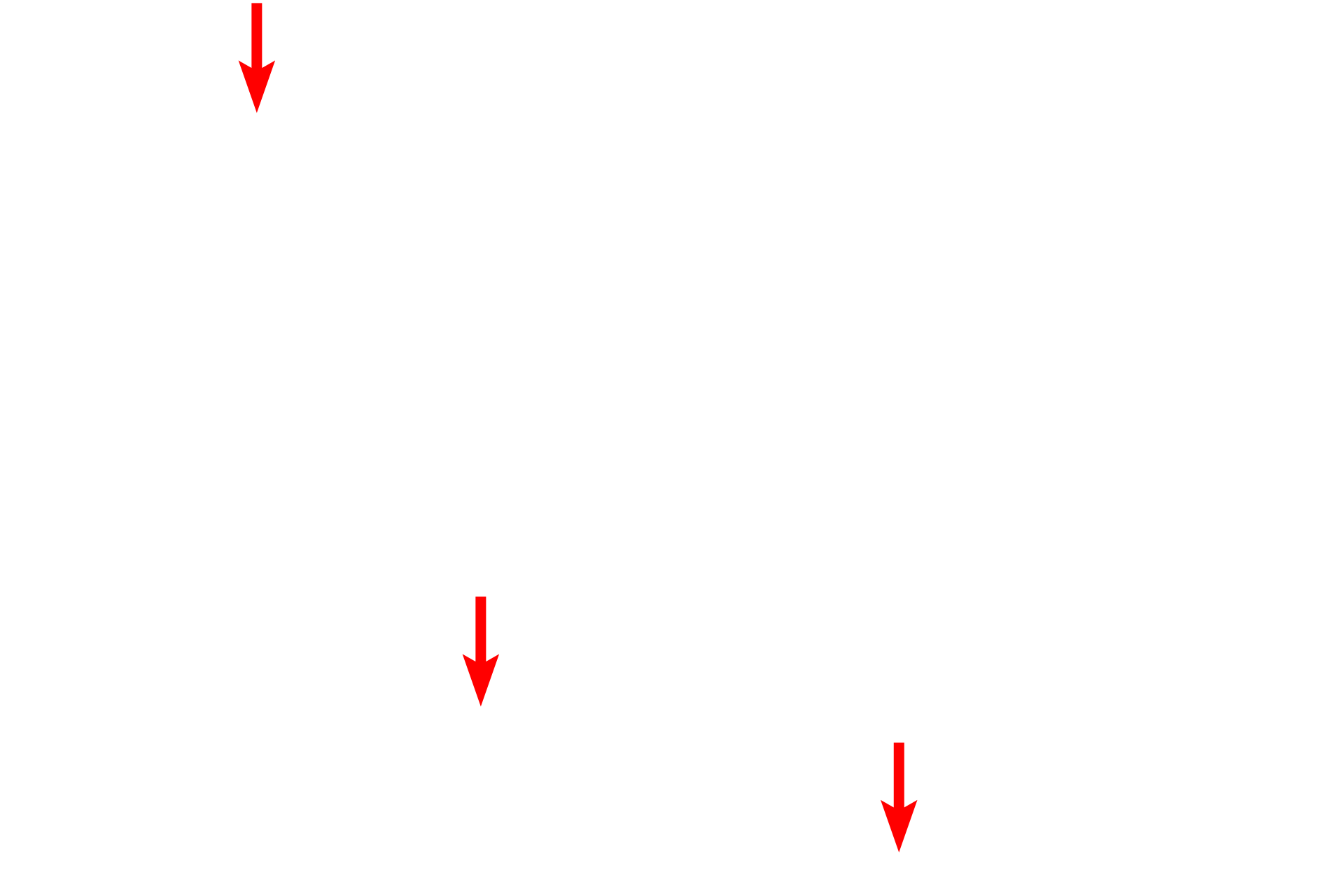
External lamina >
Schwann cells secrete an external lamina, which is similar to a basal lamina produced by epithelial cells. Surrounding the external lamina are delicate collagen fibrils which contribute to the endoneurium.
Collagen fibrils
Schwann cells secrete an external lamina, which is similar to a basal lamina produced by epithelial cells. Surrounding the external lamina are delicate collagen fibrils which contribute to the endoneurium.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS