
Cilia
This higher magnification of cilia better reveals the microtubular structure of the axoneme. The axoneme consists of an outer cylinder formed by nine doublets of microtubules. These microtubules originate from the basal body. At the center of the axoneme is a pair of individual microtubules. The interactions between all of these tubules produce the whip-like motion of the cilium. 20,000x

Cilia
This higher magnification of cilia better reveals the microtubular structure of the axoneme. The axoneme consists of an outer cylinder formed by nine doublets of microtubules. These microtubules originate from the basal body. At the center of the axoneme is a pair of individual microtubules. The interactions between all of these tubules produce the whip-like motion of the cilium. 20,000x
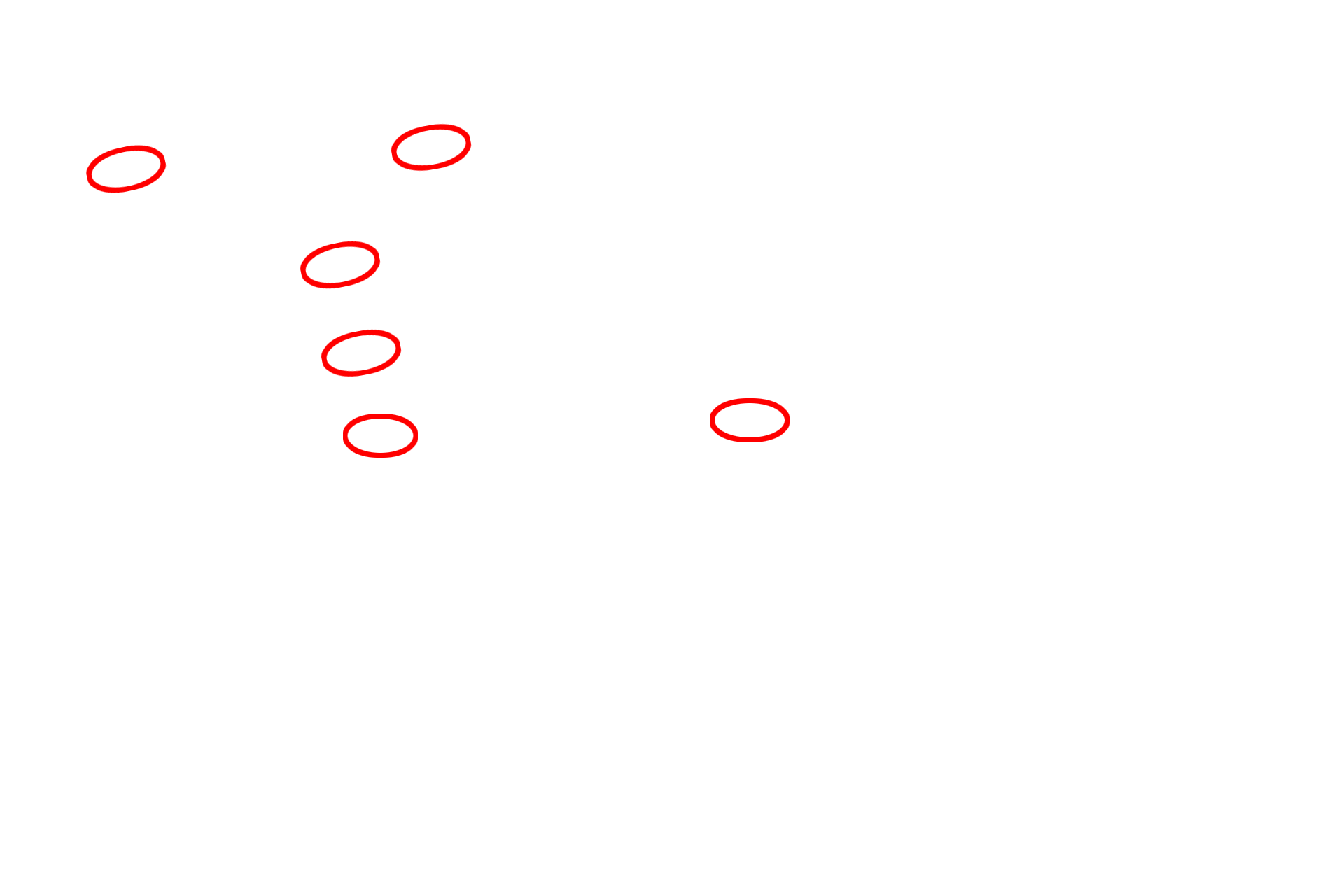
- Axoneme
This higher magnification of cilia better reveals the microtubular structure of the axoneme. The axoneme consists of an outer cylinder formed by nine doublets of microtubules. These microtubules originate from the basal body. At the center of the axoneme is a pair of individual microtubules. The interactions between all of these tubules produce the whip-like motion of the cilium. 20,000x

- Outer microtubule doublet
This higher magnification of cilia better reveals the microtubular structure of the axoneme. The axoneme consists of an outer cylinder formed by nine doublets of microtubules. These microtubules originate from the basal body. At the center of the axoneme is a pair of individual microtubules. The interactions between all of these tubules produce the whip-like motion of the cilium. 20,000x

- Inner microtubule pair
This higher magnification of cilia better reveals the microtubular structure of the axoneme. The axoneme consists of an outer cylinder formed by nine doublets of microtubules. These microtubules originate from the basal body. At the center of the axoneme is a pair of individual microtubules. The interactions between all of these tubules produce the whip-like motion of the cilium. 20,000x
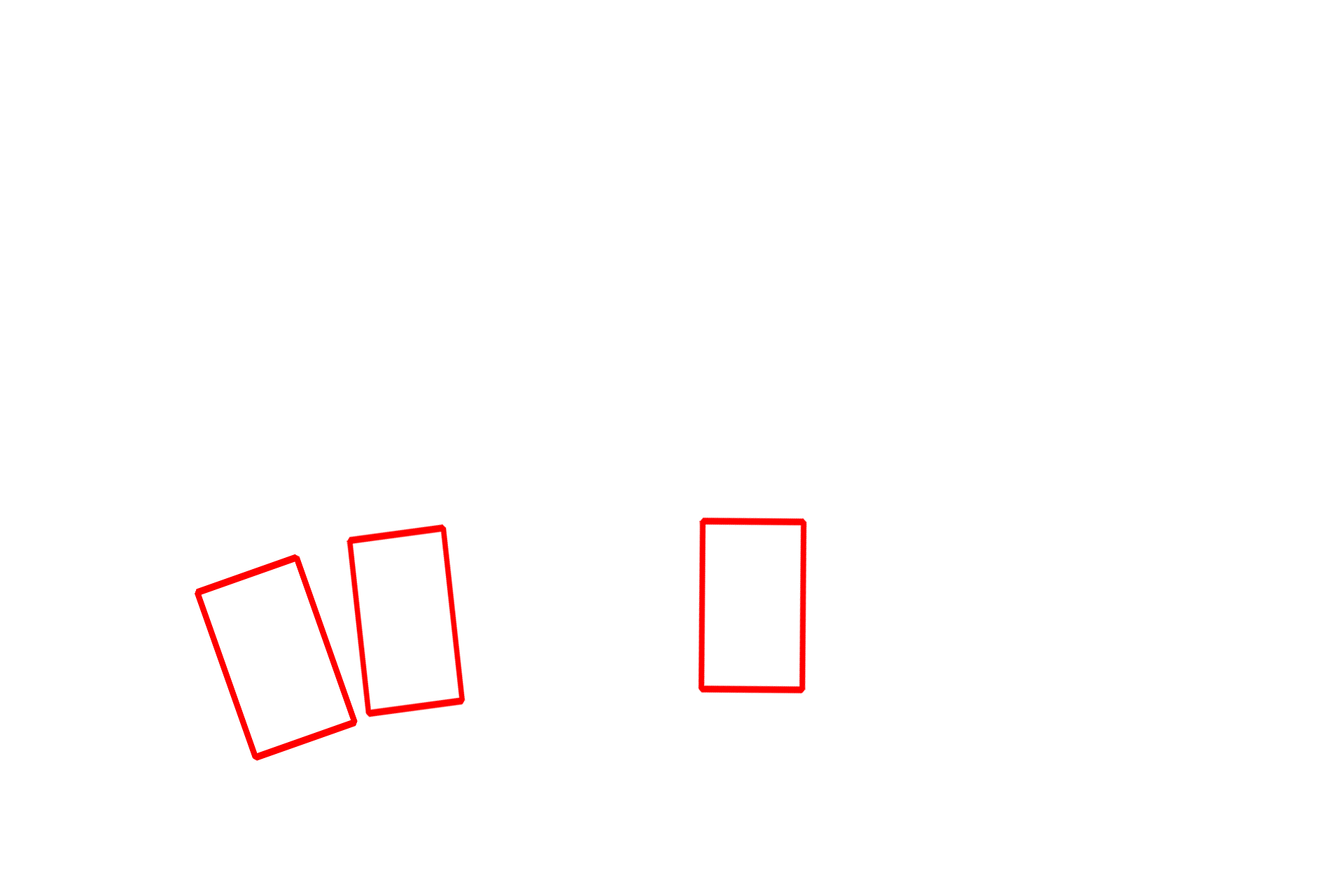
Basal bodies >
Basal bodies have the same structure as centrioles, namely, nine triplets of microtubules. However, they lack the central pair of microtubules present in the axoneme.
Microvilli >
Also visible are shorter microvilli, which contain a core of microfilaments and are non-motile. The microfilaments are not resolved at this magnification.

Junctional complex
Also visible are shorter microvilli, which contain a core of microfilaments and are non-motile. The microfilaments are not resolved at this magnification.
Plasma membrane
Also visible are shorter microvilli, which contain a core of microfilaments and are non-motile. The microfilaments are not resolved at this magnification.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS