
Simple tubular gland
Simple tubular glands resemble test tubes. Each gland forms a single, unbranched tubule that is directly connected to the overlying epithelium. Tubular glands in which a duct is absent, as in this case, or is unbranched, are both classified as simple. These glands, named intestinal glands, are composed primarily of goblet and absorptive cells and are located in the small and large intestines. Colon 200x
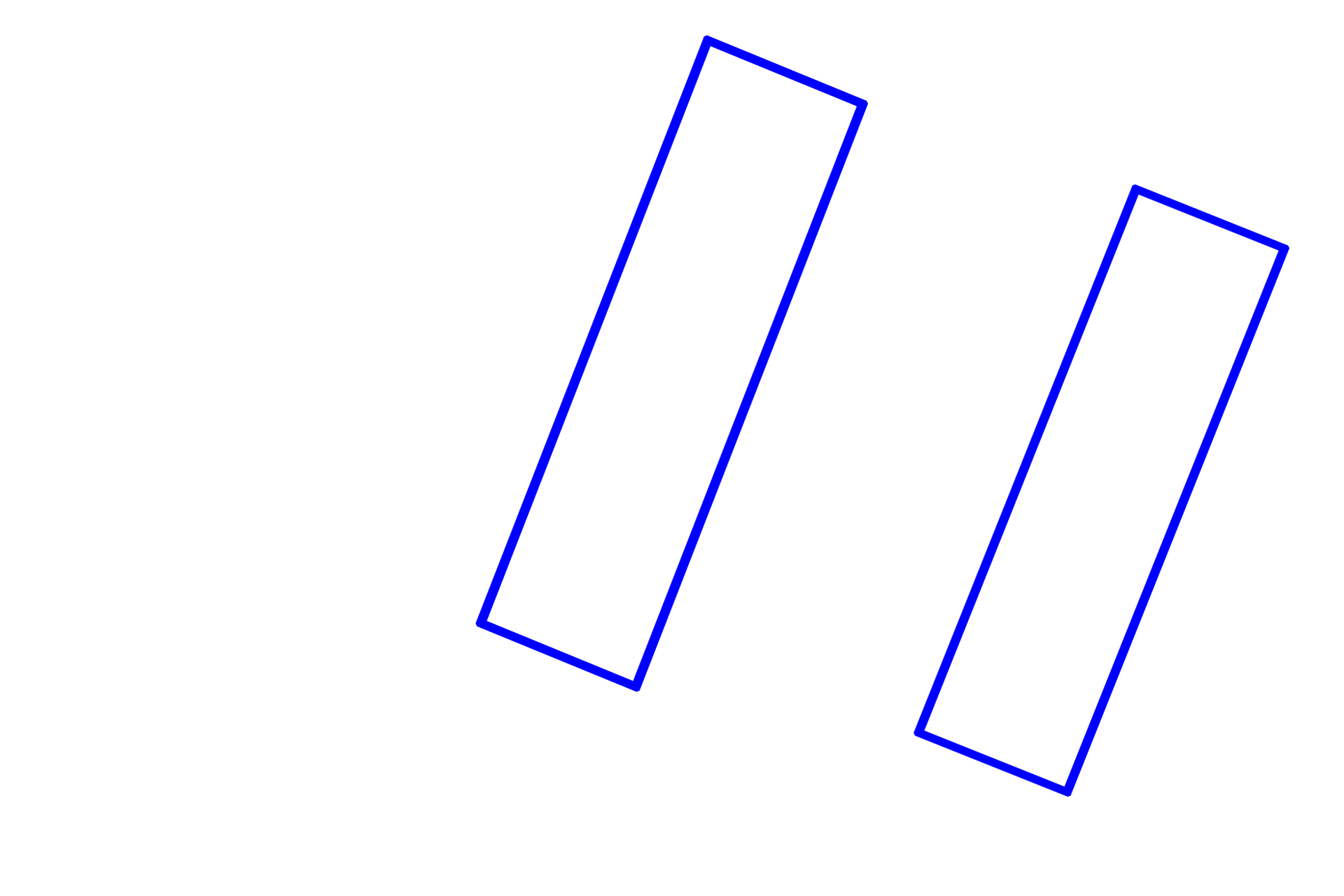
Simple tubular glands
Simple tubular glands resemble test tubes. Each gland forms a single, unbranched tubule that is directly connected to the overlying epithelium. Tubular glands in which a duct is absent, as in this case, or is unbranched, are both classified as simple. These glands, named intestinal glands, are composed primarily of goblet and absorptive cells and are located in the small and large intestines. Colon 200x
- Gland lumens
Simple tubular glands resemble test tubes. Each gland forms a single, unbranched tubule that is directly connected to the overlying epithelium. Tubular glands in which a duct is absent, as in this case, or is unbranched, are both classified as simple. These glands, named intestinal glands, are composed primarily of goblet and absorptive cells and are located in the small and large intestines. Colon 200x
- Goblet cells
Simple tubular glands resemble test tubes. Each gland forms a single, unbranched tubule that is directly connected to the overlying epithelium. Tubular glands in which a duct is absent, as in this case, or is unbranched, are both classified as simple. These glands, named intestinal glands, are composed primarily of goblet and absorptive cells and are located in the small and large intestines. Colon 200x
- Absorptive cells
Simple tubular glands resemble test tubes. Each gland forms a single, unbranched tubule that is directly connected to the overlying epithelium. Tubular glands in which a duct is absent, as in this case, or is unbranched, are both classified as simple. These glands, named intestinal glands, are composed primarily of goblet and absorptive cells and are located in the small and large intestines. Colon 200x
Muscularis mucosae >
In this section of the large intestine, the simple tubular glands are slightly longer than the mucosal layer in which they are located. Therefore, the bases of the glands curve as they reach the muscle layer (muscularis muscosae) below them.

Intestinal lumen
Simple tubular glands resemble test tubes. Each gland forms a single, unbranched tubule that is directly connected to the overlying epithelium. Tubular glands in which a duct is absent, as in this case, or is unbranched, are both classified as simple. These glands, named intestinal glands, are composed primarily of goblet and absorptive cells and are located in the small and large intestines. Colon 200x