
Structure of compound glands
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x
Lobule
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x
- Acini
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x
- Intralobular ducts
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x
- Intralobular connective tissue
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x

- Interlobular duct
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x

Interlobular connective tissue
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x
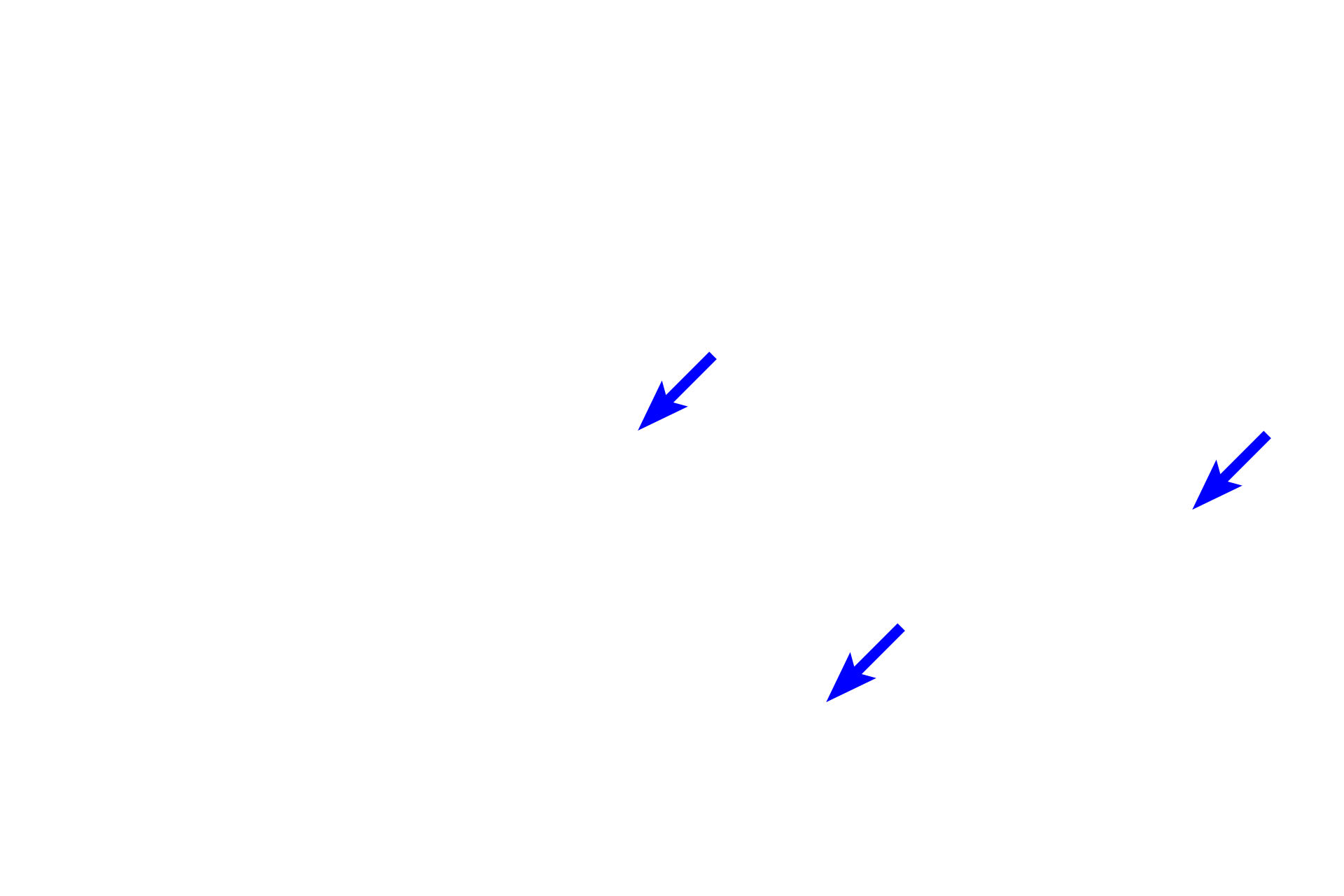

Blood vessels
This portion of a single lobule consists entirely of acini. The ducts draining the acini gradually increase in diameter and their lining epithelia gently transition from low cuboidal to columnar. These ducts, called intralobular, are located within the lobule, surrounded by secretory they units. They join to form interlobular ducts that exit the lobule surrounded by connective tissue and are lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. 100x
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS