
Connective tissue proper classification overview
Connective tissue proper is subdivided into two major categories, loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue. These designations are based on two features: (1) the arrangement and size of the collagen fibers; and (2) the number and types of cells present. 400x
Loose connective tissue >
Loose connective tissue consists of thin, interlacing and relatively sparse collagen fibers. Additionally, this tissue has a large number and a great variety of cell types surrounded by an abundant, gelatinous ground substance. Loose connective tissue is also called areolar connective tissue, referring to the many holes or spaces between the collagen fibers that allow for diffusion and cell migration. Loose connective tissue also provides delicate padding between tissues and around organs.
Dense connective tissue >
Dense connective tissue consist of thicker, more robust and densely arranged collagen fibers. This tissue has few cells, almost all of which are fibroblasts, and a sparse amount of ground substance. Dense connective tissue provides great strength because of its abundant collagen fiber content and is further subdivided into regular and irregular subdivisions based on the arrangement of its collagen fibers.
Collagen fibers >
Collagen fibers assemble from individual collagen fibrils and stain with eosin.
Collagen bundles >
Collagen bundles, also eosinophilic, consist of larger aggregation of collagen fibers.
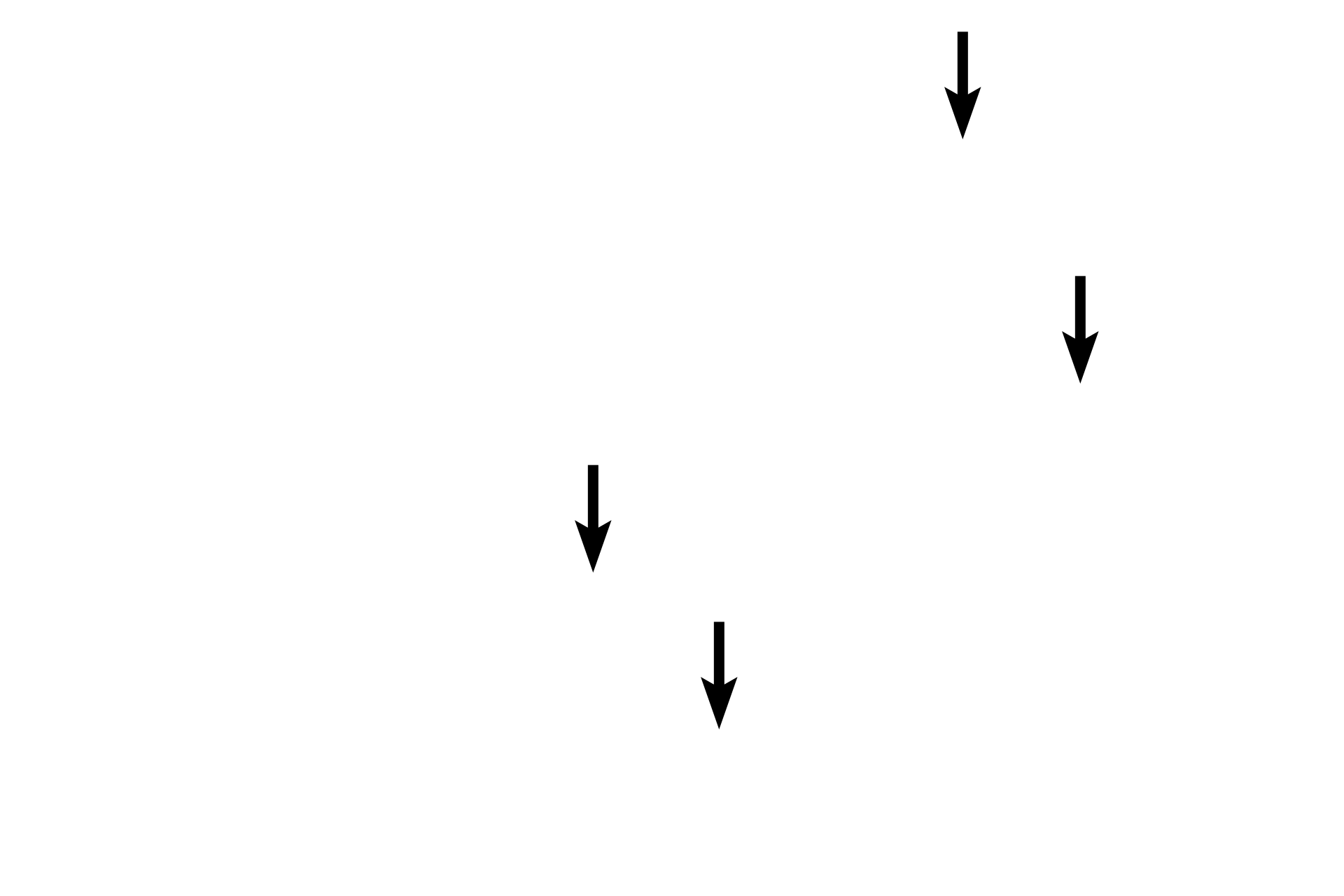
Active fibroblast nuclei >
In most cases, the fibroblast cytoplasm is not well differentiated from the surrounding extracellular matrix. Thus, identification is based on nuclear morphology. These fibroblasts are active, indicated by their large, euchromatic nuclei.
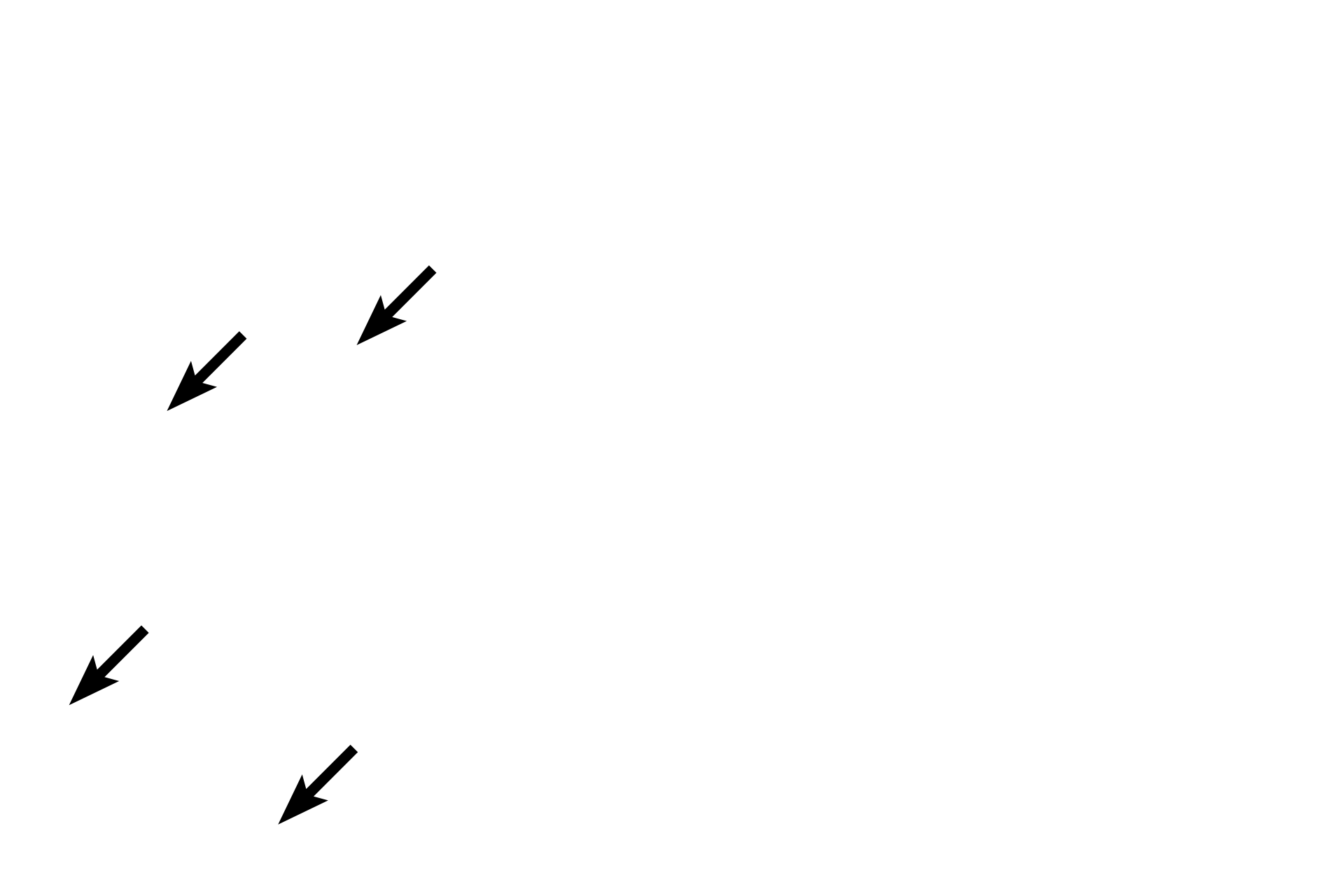

Inactive fibroblast nuclei >
Compared with active fibroblasts, inactive fibroblasts have smaller, more heterochromatic nuclei.
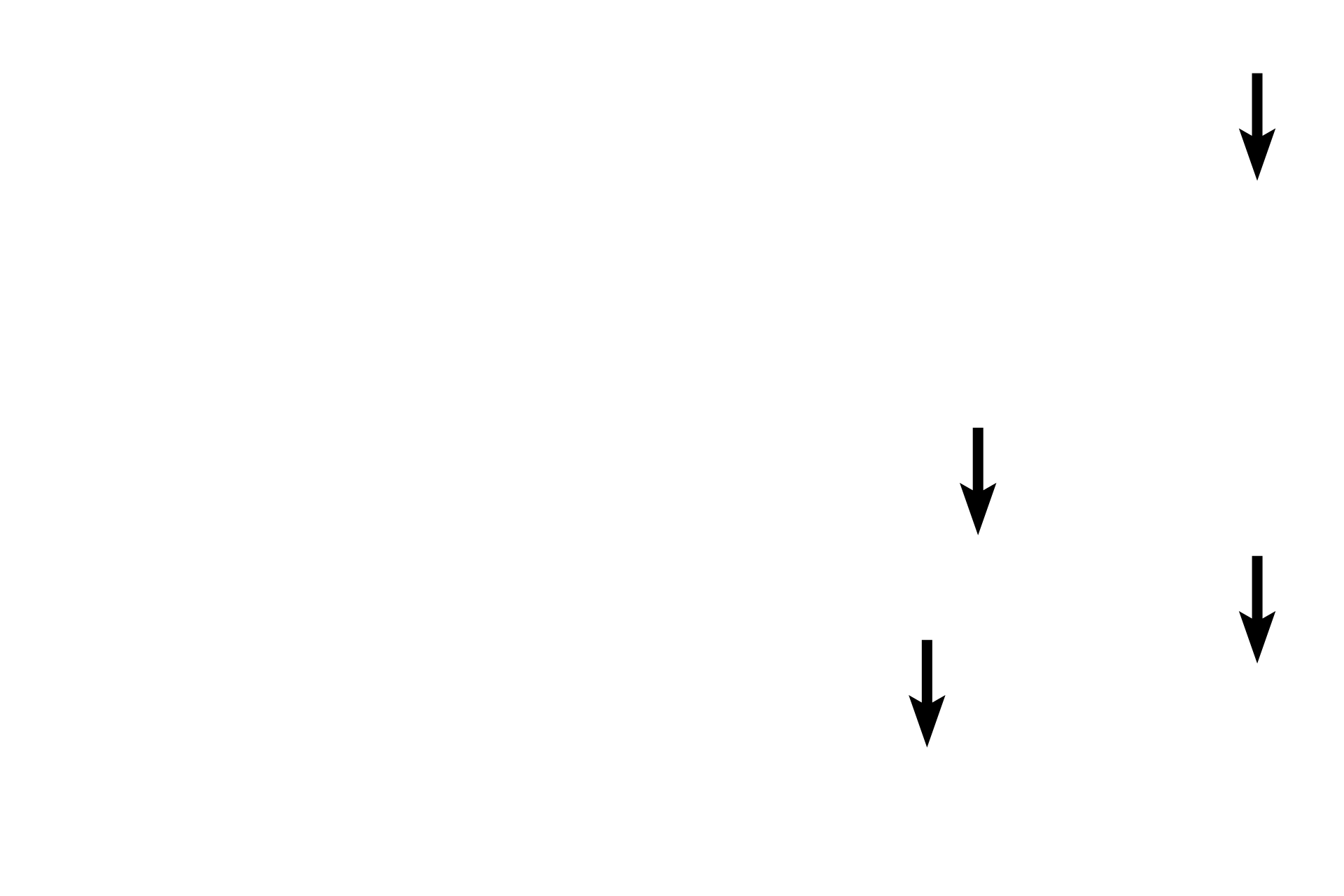
Adipocytes >
Adipocytes are found individually or in small clusters in loose connective tissue. Adipocytes contain a single large lipid droplet that compresses the nucleus and cytoplasm to the periphery. The lipid is extracted during tissue processing and, therefore, the cells appear empty.
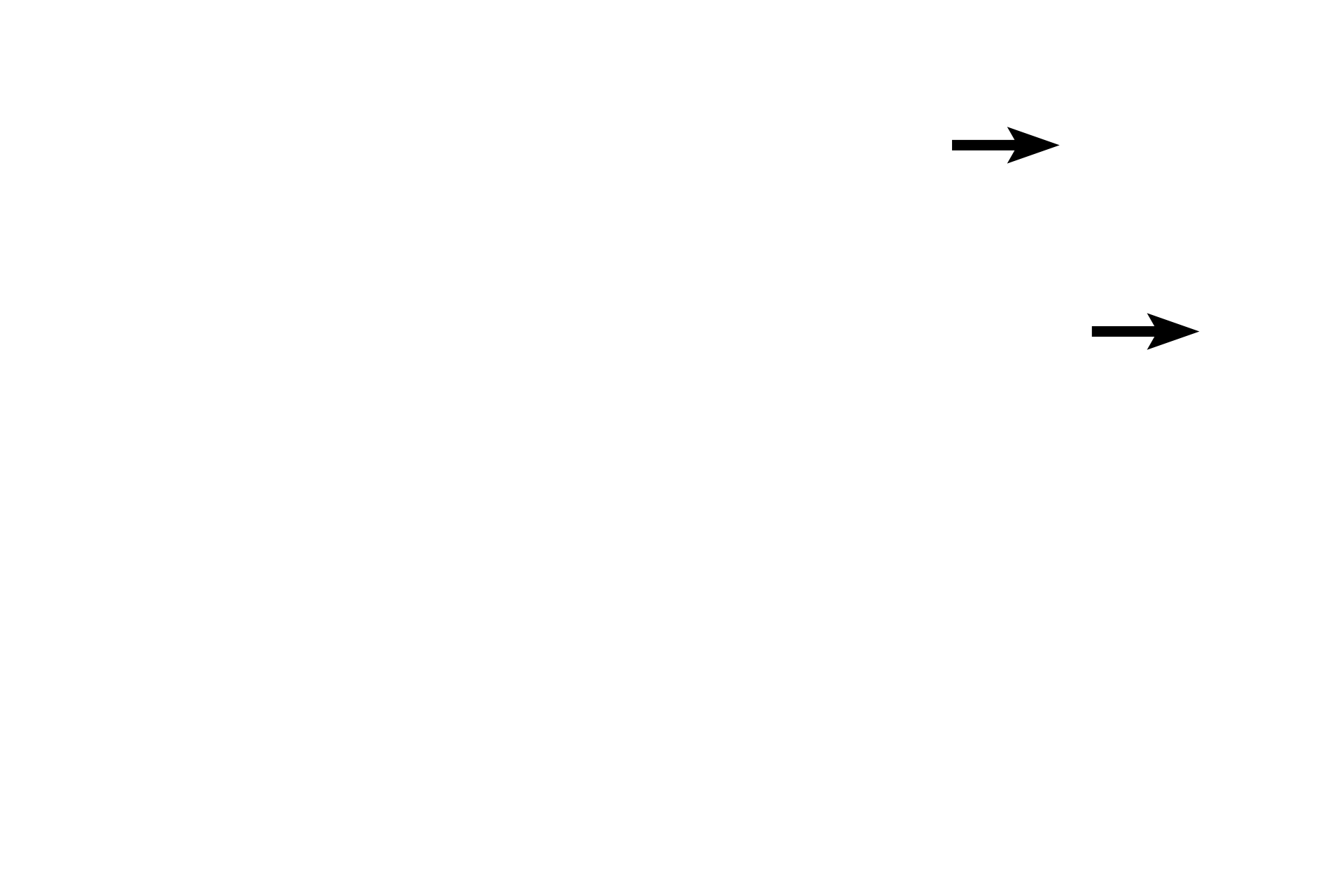
Mast cells >
Mast cells are spherical to oval-shaped with a centrally-located, spherical nucleus. The cytoplasm of mast cells is filled with numerous granules that contain mediators of the inflammatory response.
