
Loose connective tissue
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x
Region of right image
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x

Intestinal lumen
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x
Epithelium
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x
Glands
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x
Loose connective tissue
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x
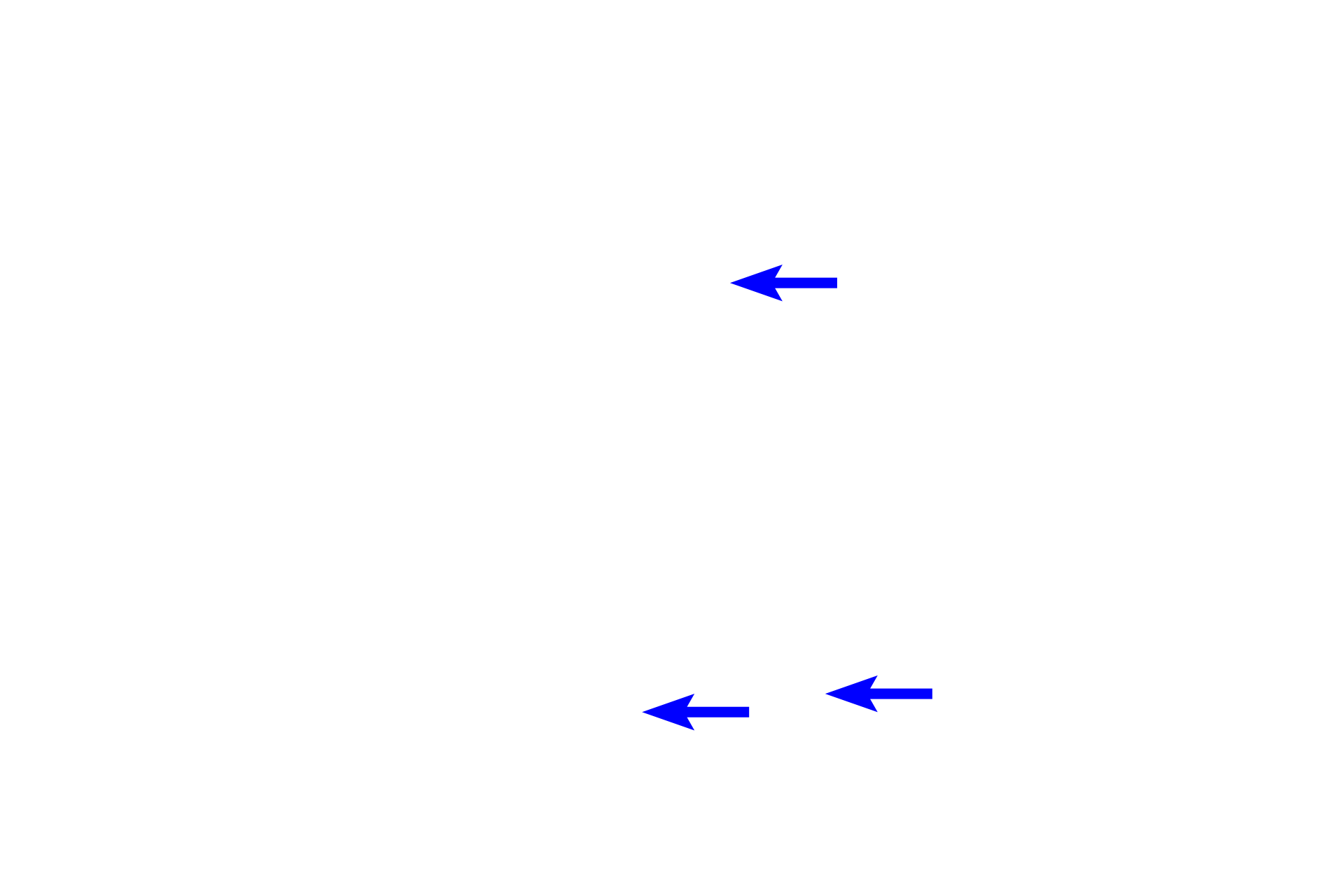
Eosinophils
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x

Plasma cells
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x
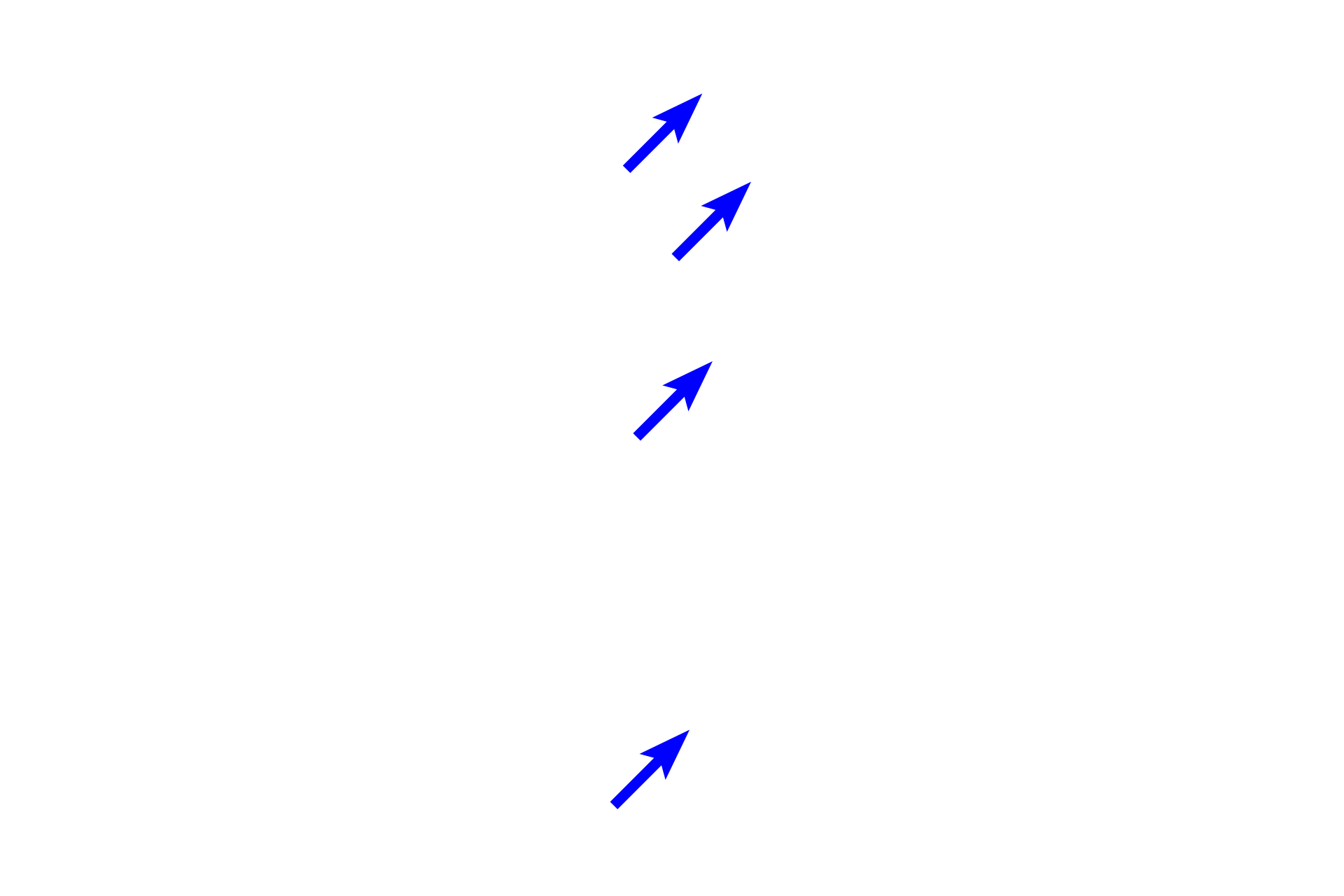
Fibroblasts
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x
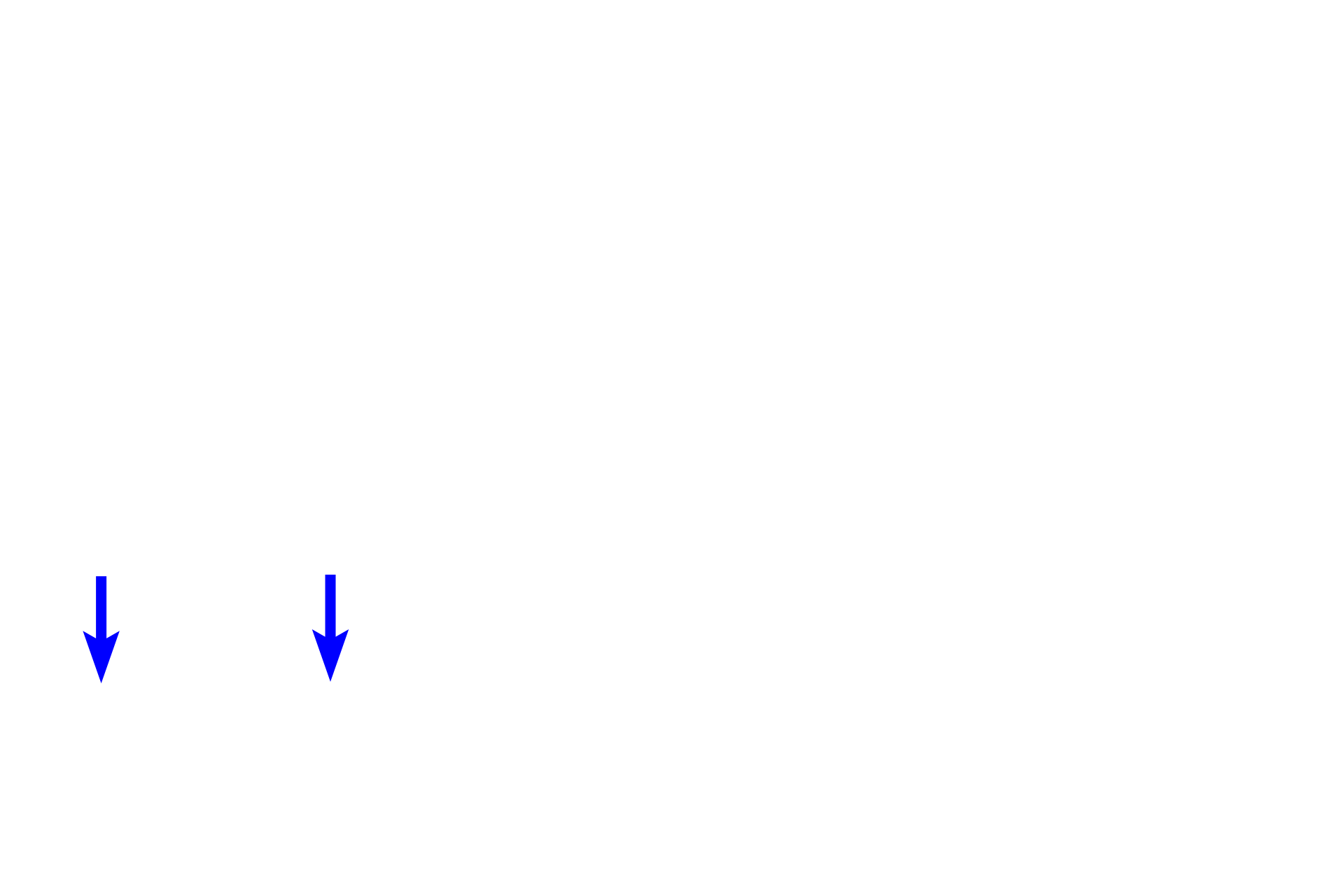
Smooth muscle
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x

Dense irregular connective tissue
In the small intestine, a loose connective tissue lies beneath the epithelium and surrounds many glands associated with the epithelium. In this position, loose connective tissue allows for cell migration and diffusion and provides cushioning and support for the epithelium and glands. Loose connective tissue also contains phagocytic and immunoresponsive cells. 100x, 400x

Image source >
Images taken of a slide in the University of Michigan collection.