
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage stains purple because of the high concentration of glycosaminoglycans in its ground substance; collagen fibrils cannot be resolved with the light microscope. Each chondrocyte, lying in a potential space called a lacuna, can divide to form an isogenous group. No blood vessels are present, so nutrients diffuse through the cartilage to supply the chondrocytes. 400x
Perichondrium: chondrogenic layer
Hyaline cartilage stains purple because of the high concentration of glycosaminoglycans in its ground substance; collagen fibrils cannot be resolved with the light microscope. Each chondrocyte, lying in a potential space called a lacuna, can divide to form an isogenous group. No blood vessels are present, so nutrients diffuse through the cartilage to supply the chondrocytes. 400x
Chondrocytes >
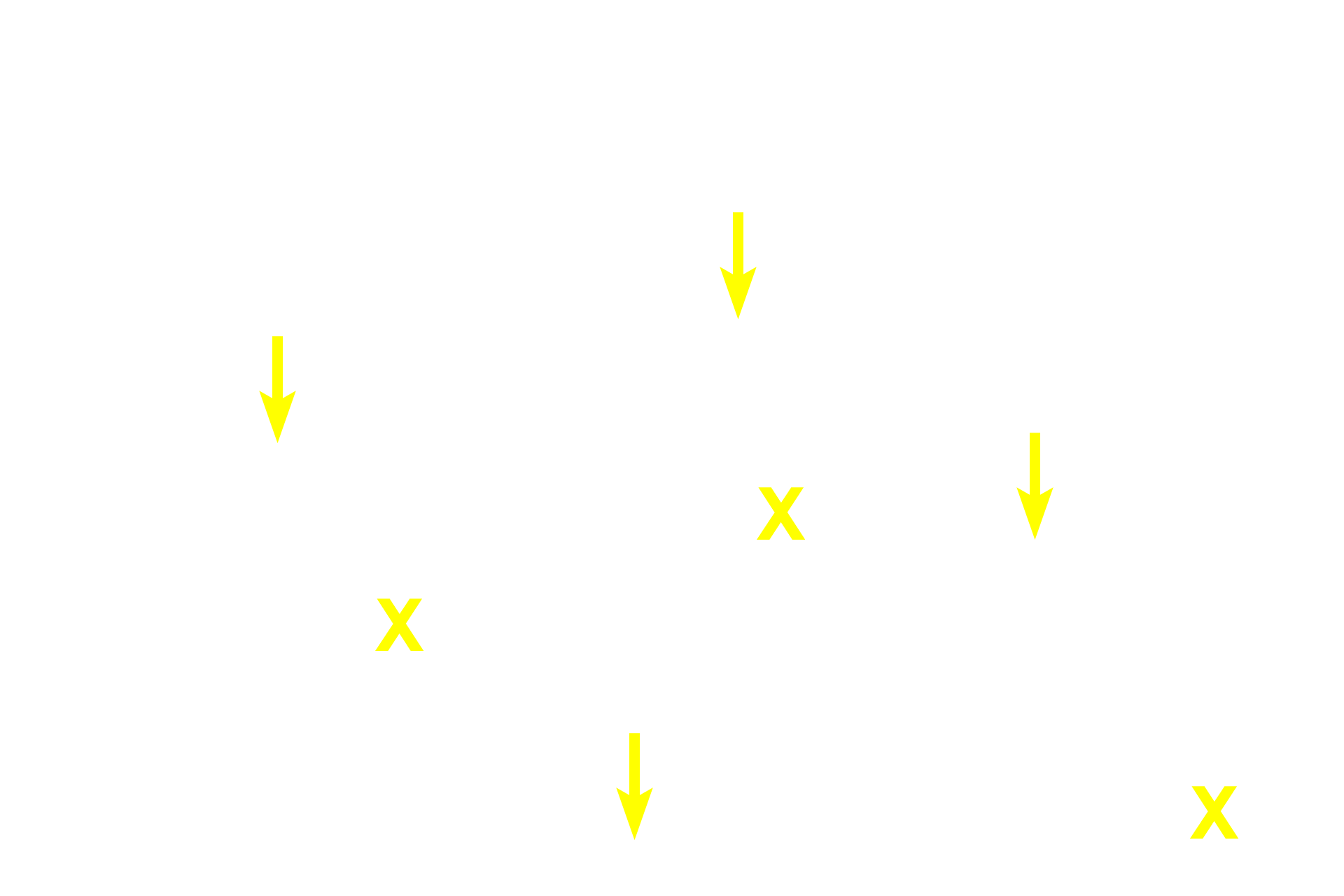
Chondrocytes (yellow arrows) lying in potential spaces called lacunae, are seen singly or in clusters called isogenous groups. These cells retain all the organelles of typical protein-producing cells and secrete matrix and divide throughout life, resulting in interstitial growth. Chondrocytes also contain lipid droplets (white arrows) in their cytoplasm.
Isogenous groups >
Chondrocytes divide and secrete matrix around themselves, resulting in the formation of isogenous groups of cells and increasing the volume of the cartilage by interstitial growth.
Extracellular matrix >
Extracellular matrix is secreted by each chondrocyte and accounts for a majority of the mass of hyaline cartilage. It consists of both Type II collagen fibers and glycosaminoglycans resulting in a rigid but deformable mass. No blood vessels are present, so nutrients must diffuse through the matrix to supply the chondrocytes.
- Territorial matrix >
The darkly staining extracellular matrix immediately surrounding individual chondrocytes and isogenous groups is called territorial matrix and represents an area of high glycosaminoglycan content. These highly sulfated molecules impart intense basophilic staining. Beyond this region of the matrix, glycosaminoglycans are less concentrated and, consequently, stains less blue. This area is termed the interterritorial matrix and stains pink due to the high collagen content.

- Interterritorial matrix
The darkly staining extracellular matrix immediately surrounding individual chondrocytes and isogenous groups is called territorial matrix and represents an area of high glycosaminoglycan content. These highly sulfated molecules impart intense basophilic staining. Beyond this region of the matrix, glycosaminoglycans are less concentrated and, consequently, stains less blue. This area is termed the interterritorial matrix and stains pink due to the high collagen content.