
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage is frequently seen as a transition from dense connective tissue when greater strength is needed, as in this section of pubic symphysis. Observing differences in the cells and the appearance of the surrounding ground substance is key to distinguishing these two tissues. 400x
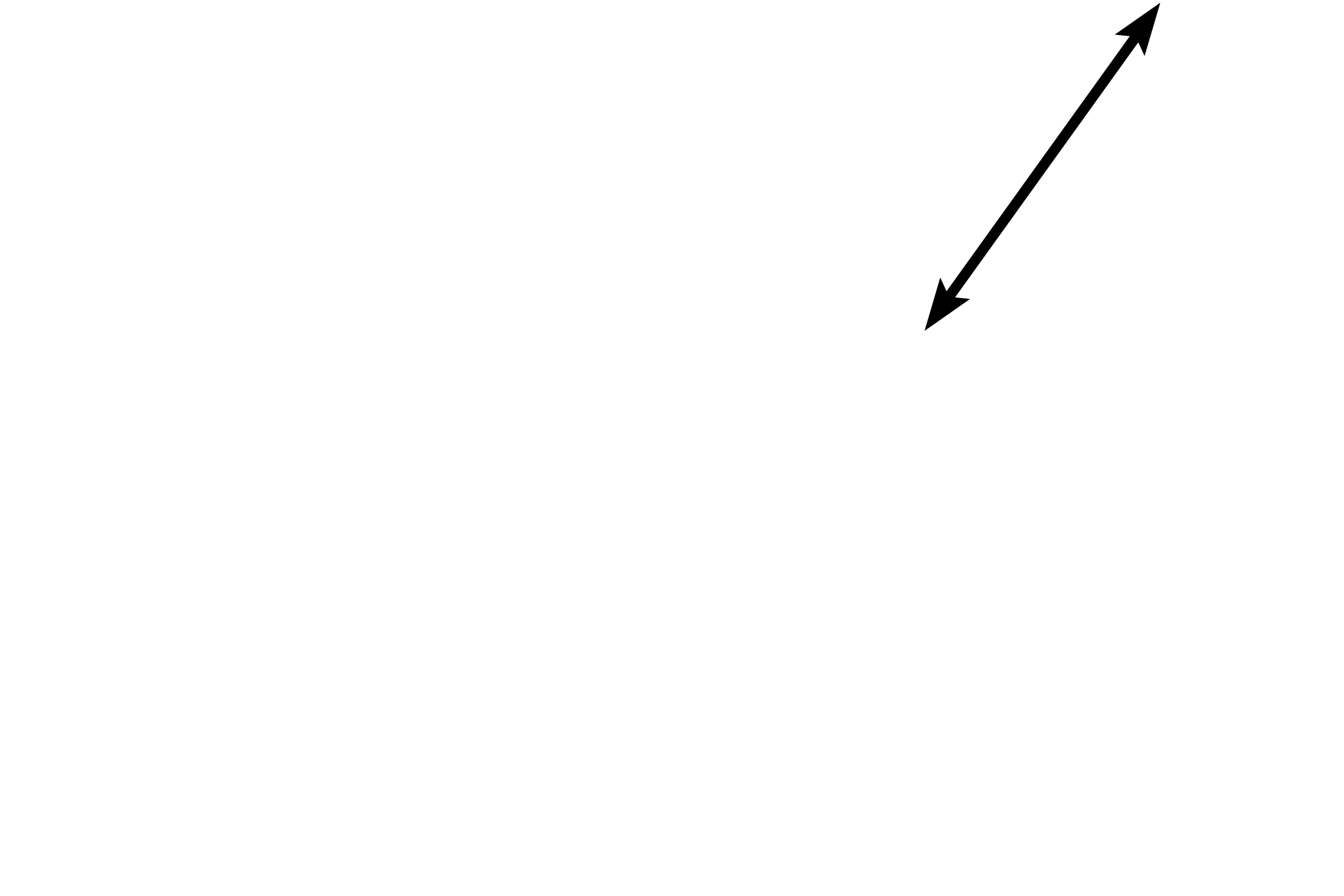
Dense irregular connective tissue >
In dense connective tissue, fibroblast nuclei are oval to flattened and their cytoplasmic extensions are difficult to discern from the surrounding collagen fibers. Collagen fibers are highly interlaced.
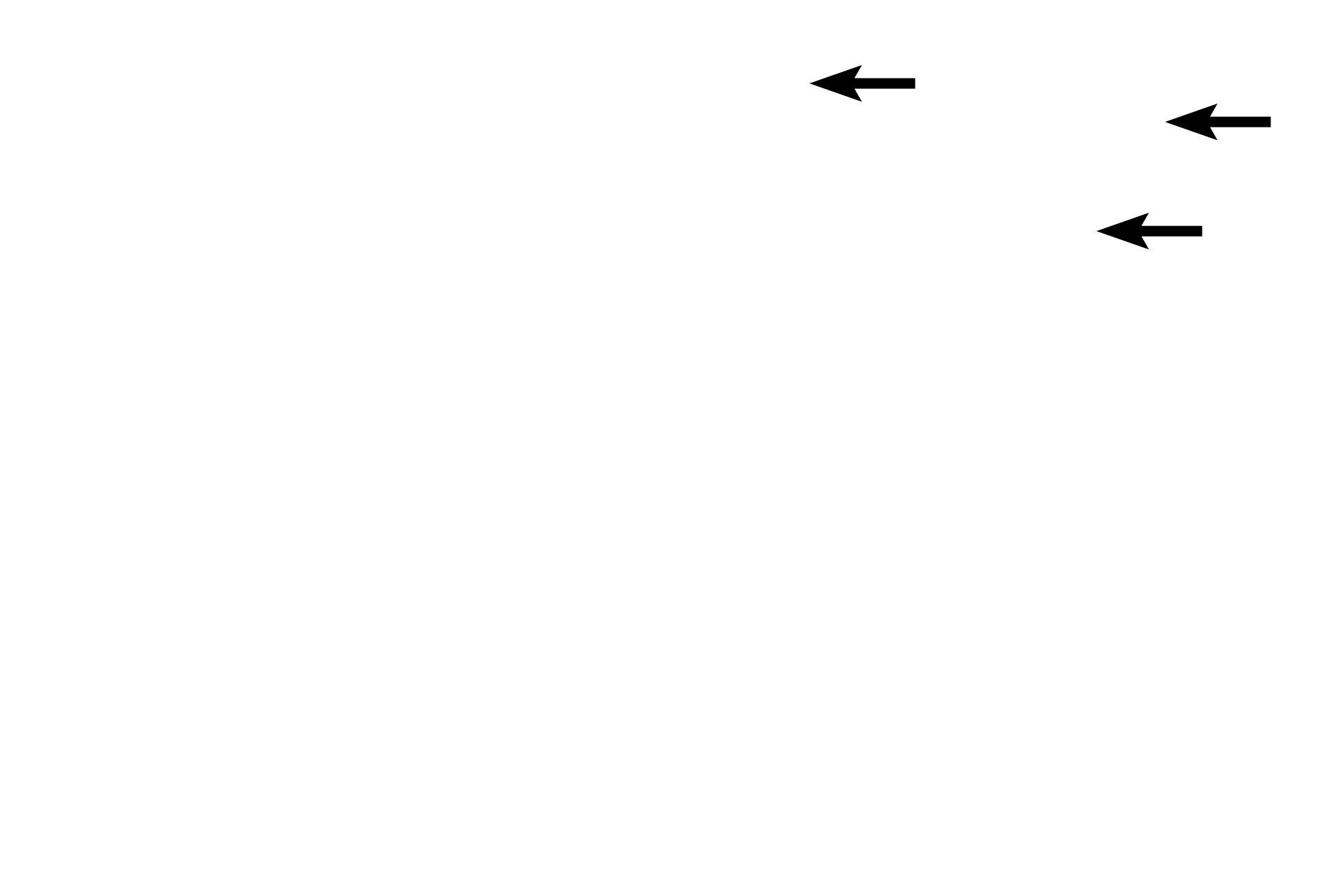
- Fibroblasts
In dense connective tissue, fibroblast nuclei are oval to flattened and their cytoplasmic extensions are difficult to discern from the surrounding collagen fibers. Collagen fibers are highly interlaced.
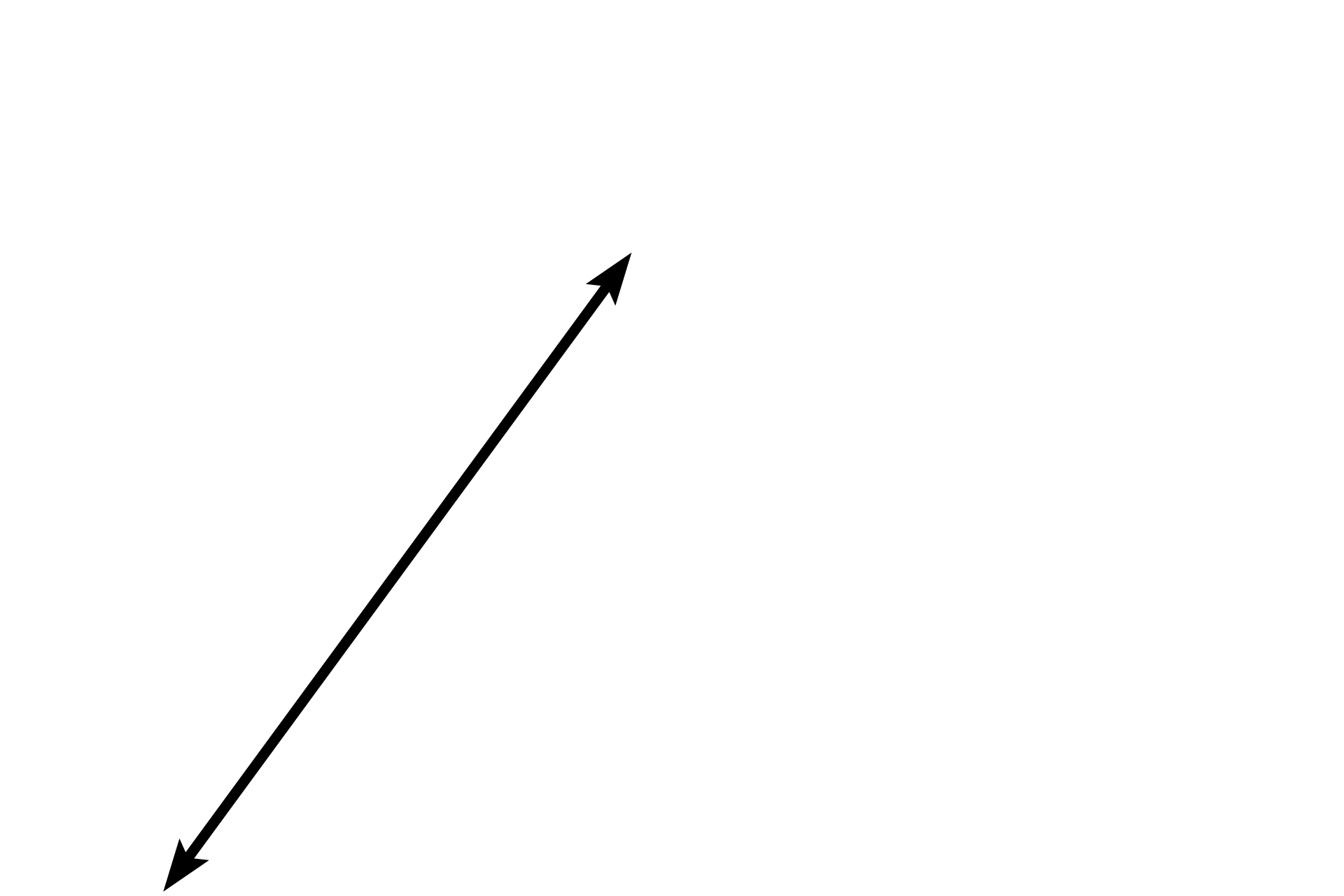
Fibrocartilage >
In fibrocartilage, chondrocytes are protected from compression by the rubbery cartilage ground substance. Therefore, these cells display rounder nuclei and visible, basophilic cytoplasm. Collagen fibers extend between the chondrocytes and tend to run more parallel to each other than in dense irregular connective tissue.

- Chondrocytes
In fibrocartilage, chondrocytes are protected from compression by the rubbery cartilage ground substance. Therefore, these cells display rounder nuclei and visible, basophilic cytoplasm. Collagen fibers extend between the chondrocytes and tend to run more parallel to each other than in dense irregular connective tissue.
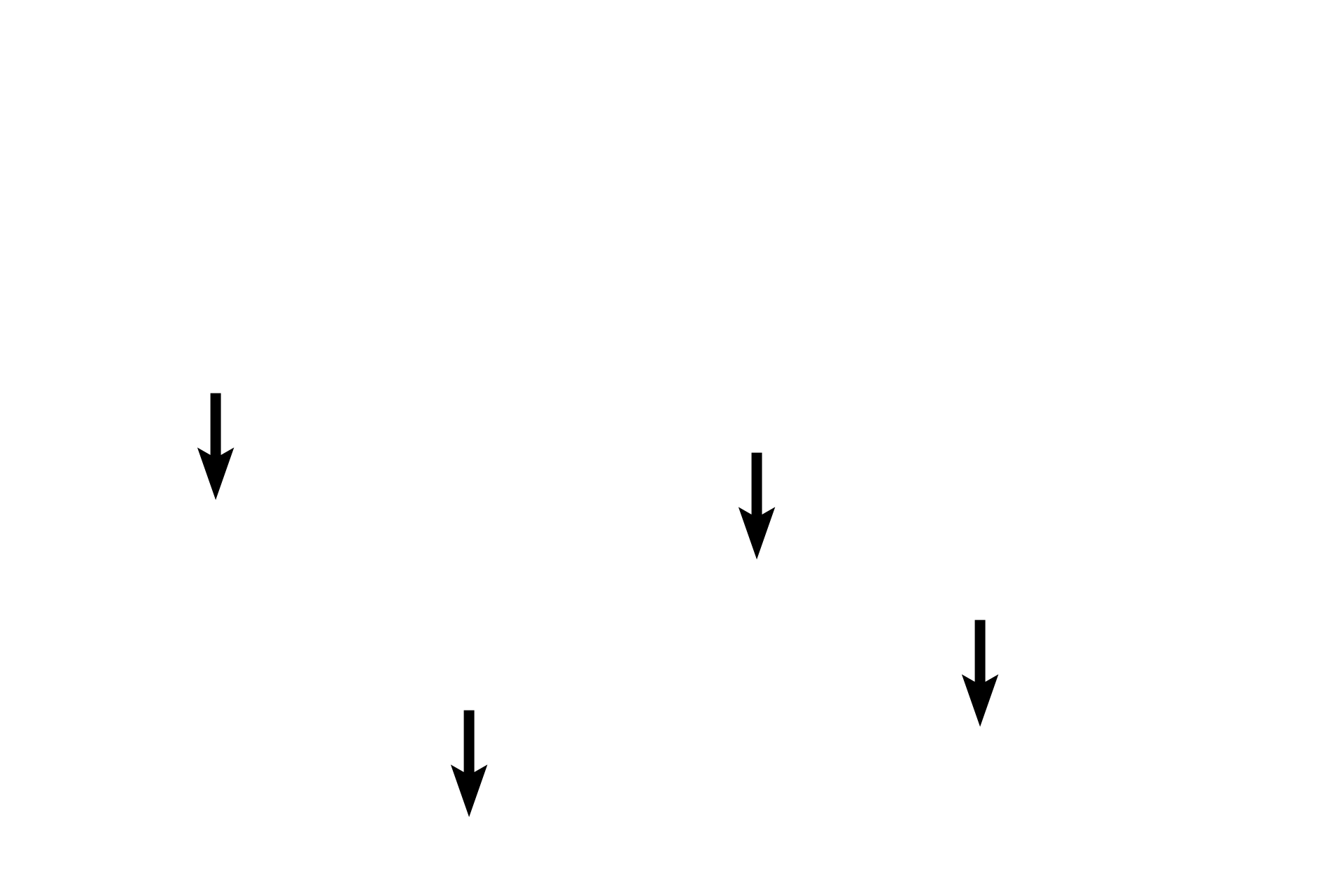
- Cartilage matrix
The chondrocytes produce matrix around themselves and between the fibers. It appears more palely stained than the collagen fibers.
Collagen fibers
In fibrocartilage, chondrocytes are protected from compression by the rubbery cartilage ground substance. Therefore, these cells display rounder nuclei and visible, basophilic cytoplasm. Collagen fibers extend between the chondrocytes and tend to run more parallel to each other than in dense irregular connective tissue.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS