
Renal corpuscle
A higher magnification demonstrates the components of the renal corpuscle. 1000x
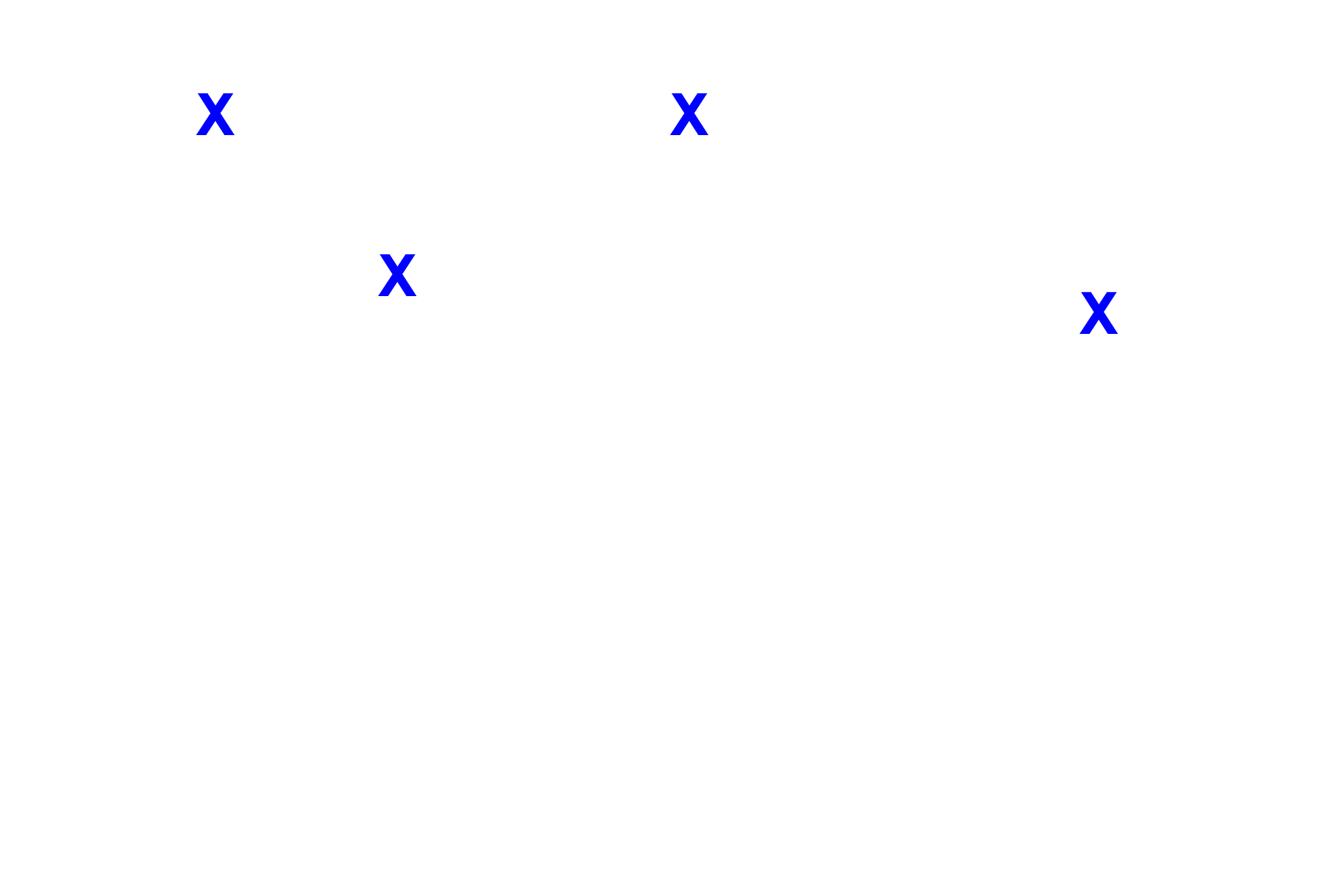
Capillary lumens >
Endothelial cells line the glomerular capillaries, which are fenestrated capillaries, lacking diaphragms.
Endothelial cells
Endothelial cells line the glomerular capillaries, which are fenestrated capillaries, lacking diaphragms.

Podocytes >
The visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule is composed of specialized cells called podocytes, which possess numerous foot processes that wrap around the glomerular capillaries. These cells, along with the fenestrated endothelium of the glomerular capillaries and their fused basal laminae, form the glomerular filtration barrier.
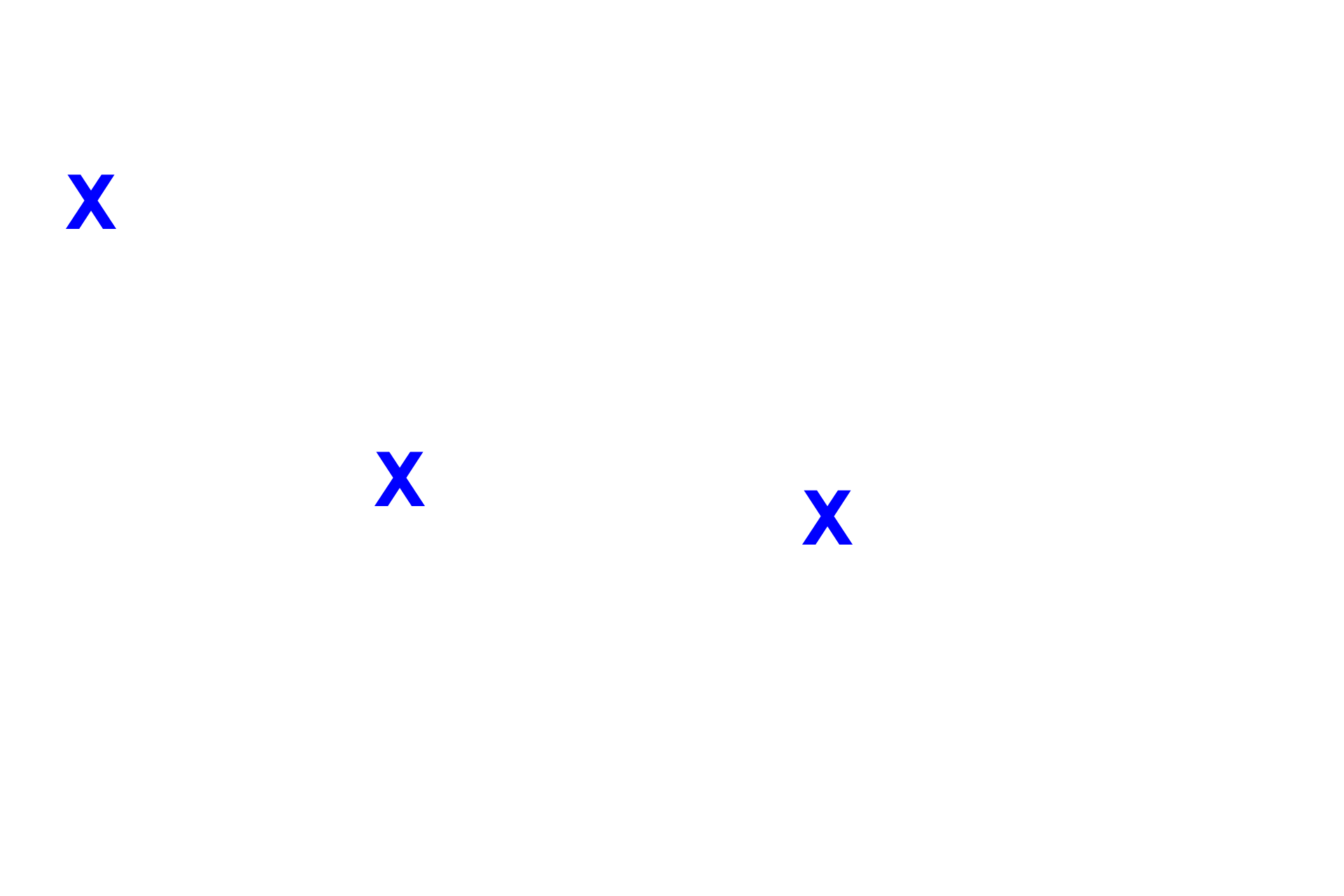
Mesangial cells >
Mesangial cells are wedged between the endothelial cells and the podocytes. They add support to the walls of the capillaries and are also phagocytic.
Bowman's space >
Bowman’s space receives the filtrate passing through the glomerular filtration barrier.
Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule >
The parietal layer of Bowman’s capsule lines the perimeter of the capsule and is composed of simple squamous epithelial cells.

Proximal convoluted tubule >
The proximal convoluted tubule is lined by a tall cuboidal epithelium with a brush border. The numerous vacuole-appearing structures in the cytoplasm are artifactually-disrupted mitochondria. This distal convoluted tubule shows the characteristic low cuboidal epithelial lining with irregularly spaced nuclei.

Distal convoluted tubule
The proximal convoluted tubule is lined by a tall cuboidal epithelium with a brush border. The numerous vacuole-appearing structures in the cytoplasm are artifactually-disrupted mitochondria. This distal convoluted tubule shows the characteristic low cuboidal epithelial lining with irregularly spaced nuclei.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS