
Renal corpuscle
Renal corpuscles are composed of a capillary tuft, the glomerulus, which is surrounded by a double-walled capsule, Bowman’s capsule. The space between the capsular walls, Bowman’s space, receives the fluid passing through the filtration barrier.
Afferent arteriole >
The afferent arteriole supplies a capillary tuft called the glomerulus, which continues as the efferent arteriole to exit the renal corpuscle. The junctions of the glomerulus with the afferent and efferent arterioles is termed the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle.
- Glomerulus
The afferent arteriole supplies a capillary tuft called the glomerulus, which continues as the efferent arteriole to exit the renal corpuscle. The junctions of the glomerulus with the afferent and efferent arterioles is termed the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle.

- Efferent arteriole
The afferent arteriole supplies a capillary tuft called the glomerulus, which continues as the efferent arteriole to exit the renal corpuscle. The junctions of the glomerulus with the afferent and efferent arterioles is termed the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle.
- Vascular pole
The afferent arteriole supplies a capillary tuft called the glomerulus, which continues as the efferent arteriole to exit the renal corpuscle. The junctions of the glomerulus with the afferent and efferent arterioles is termed the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle.
Bowman's capsule >
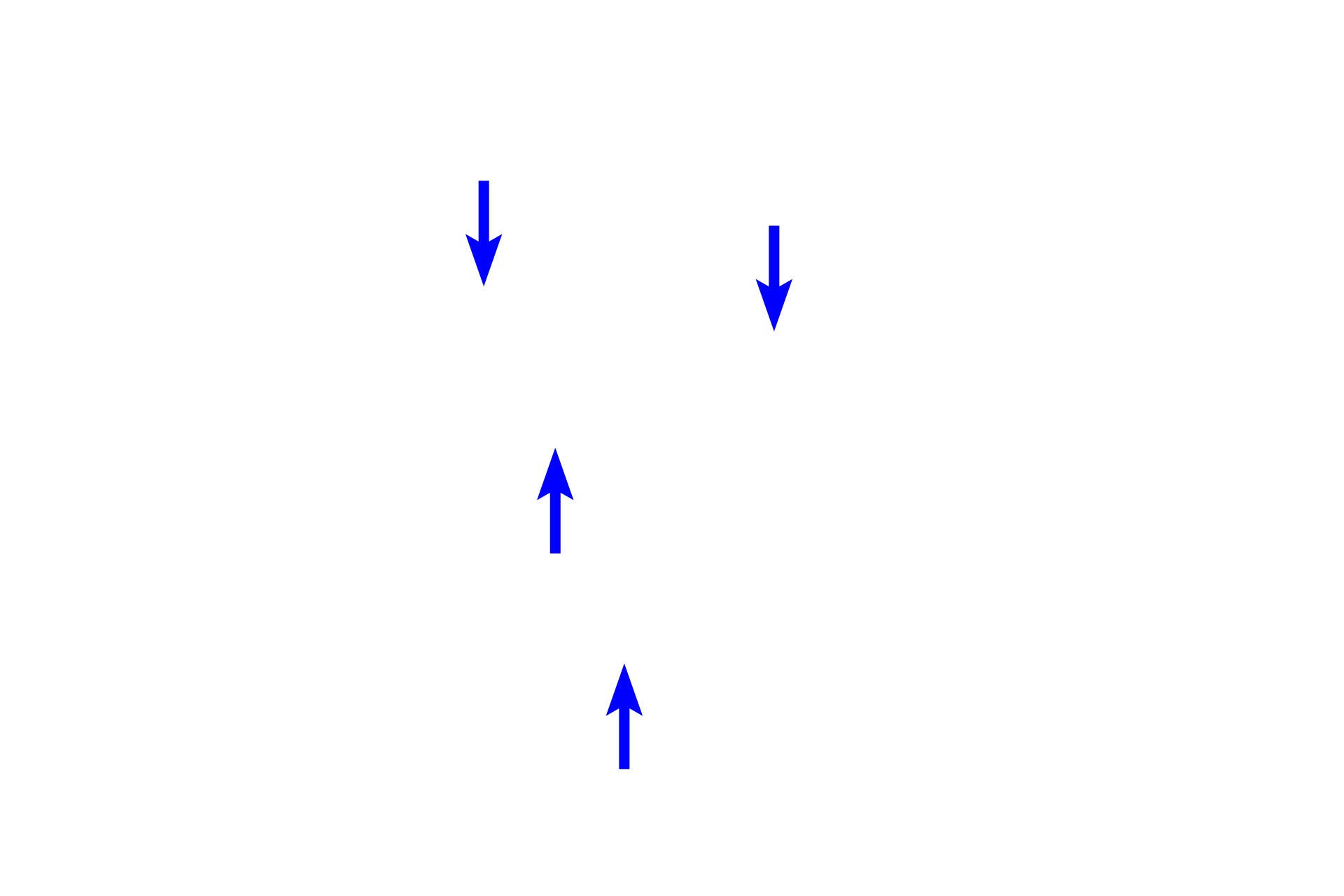
Bowman’s capsule is a double-walled structure enclosing the glomerulus. An inner layer of cells, podocytes (visceral layer, blue arrows), surrounds the glomerular capillary and serves as part of the filtration barrier. The outer, parietal layer of the capsule (black arrows) is a simple squamous epithelium, which is continuous with the proximal convoluted tubule. Separating the layers is Bowman’s space, where the filtrate accumulates.
- Podocytes
Bowman’s capsule is a double-walled structure enclosing the glomerulus. An inner layer of cells, podocytes (visceral layer, blue arrows), surrounds the glomerular capillary and serves as part of the filtration barrier. The outer, parietal layer of the capsule (black arrows) is a simple squamous epithelium, which is continuous with the proximal convoluted tubule. Separating the layers is Bowman’s space, where the filtrate accumulates.
- Bowman's space
Bowman’s capsule is a double-walled structure enclosing the glomerulus. An inner layer of cells, podocytes (visceral layer, blue arrows), surrounds the glomerular capillary and serves as part of the filtration barrier. The outer, parietal layer of the capsule (black arrows) is a simple squamous epithelium, which is continuous with the proximal convoluted tubule. Separating the layers is Bowman’s space, where the filtrate accumulates.
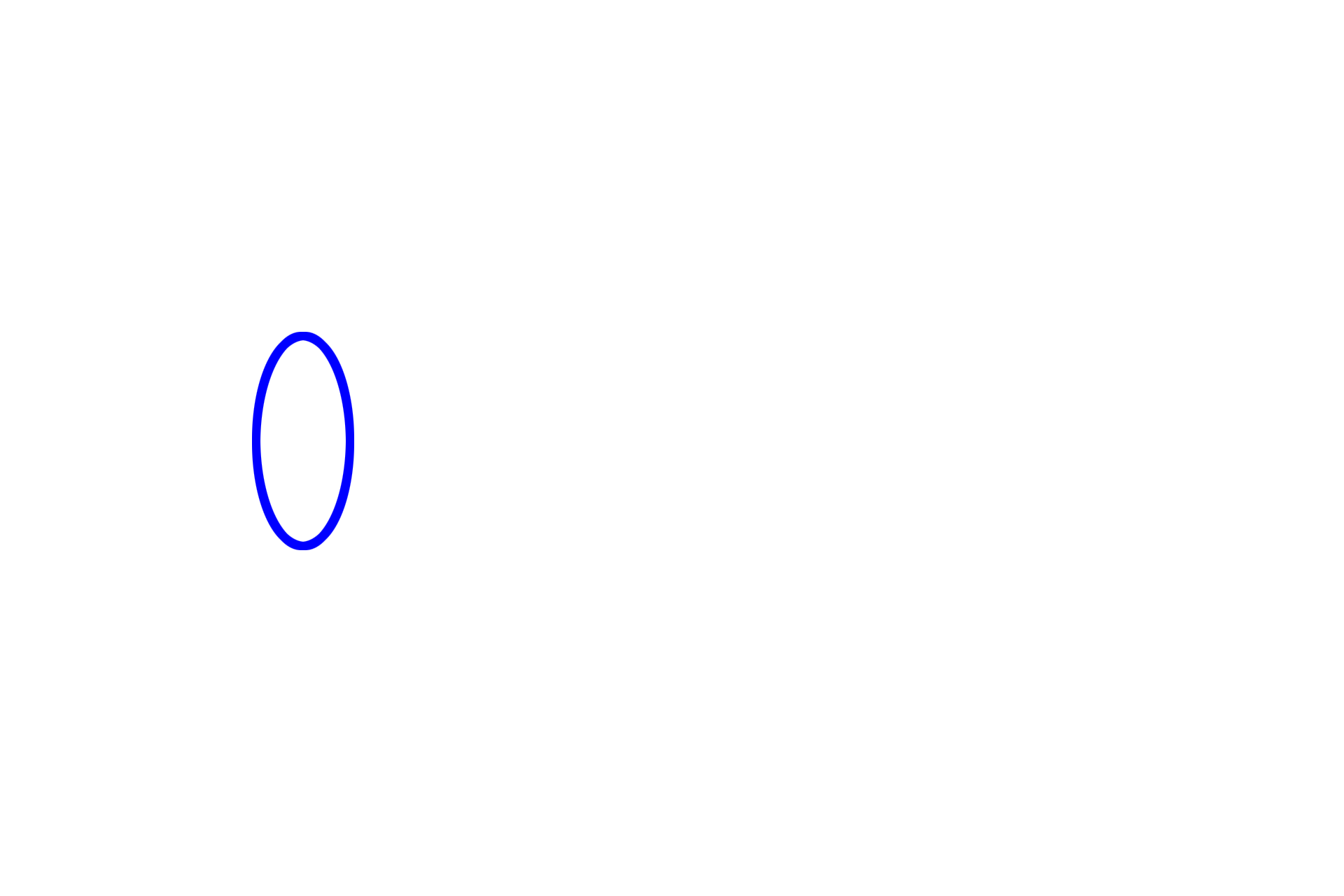
Urinary pole >
The urinary pole is the continuation of the simple squamous epithelium of the parietal layer of Bowman’s capsule with the epithelium forming the proximal convoluted tubule. At the urinary pole, the filtrate accumulating in Bowman’s space enters the first tubular part of the nephron, the proximal convoluted tubule.
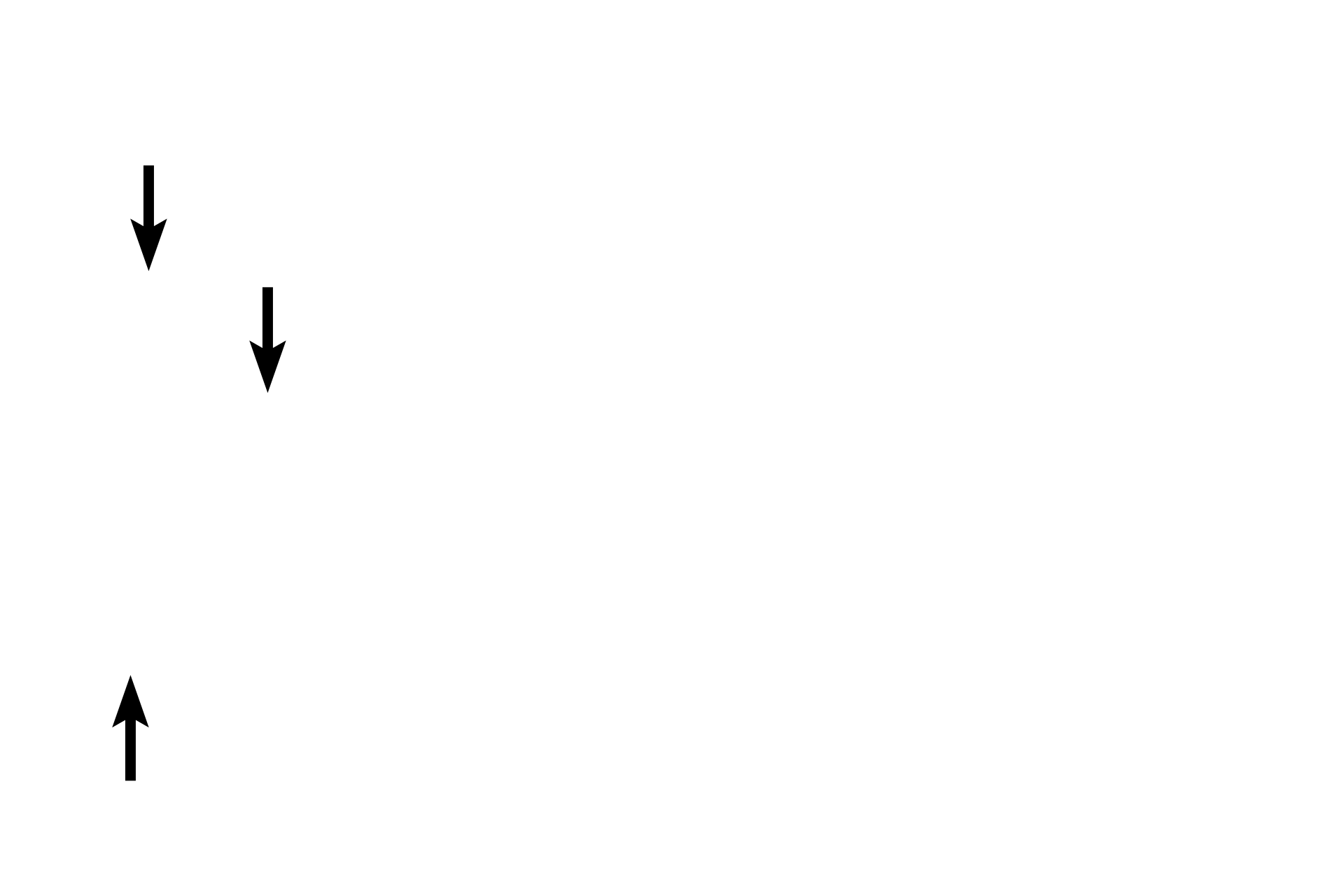
Proximal convoluted tubule
The urinary pole is the continuation of the simple squamous epithelium of the parietal layer of Bowman’s capsule with the epithelium forming the proximal convoluted tubule. At the urinary pole, the filtrate accumulating in Bowman’s space enters the first tubular part of the nephron, the proximal convoluted tubule.
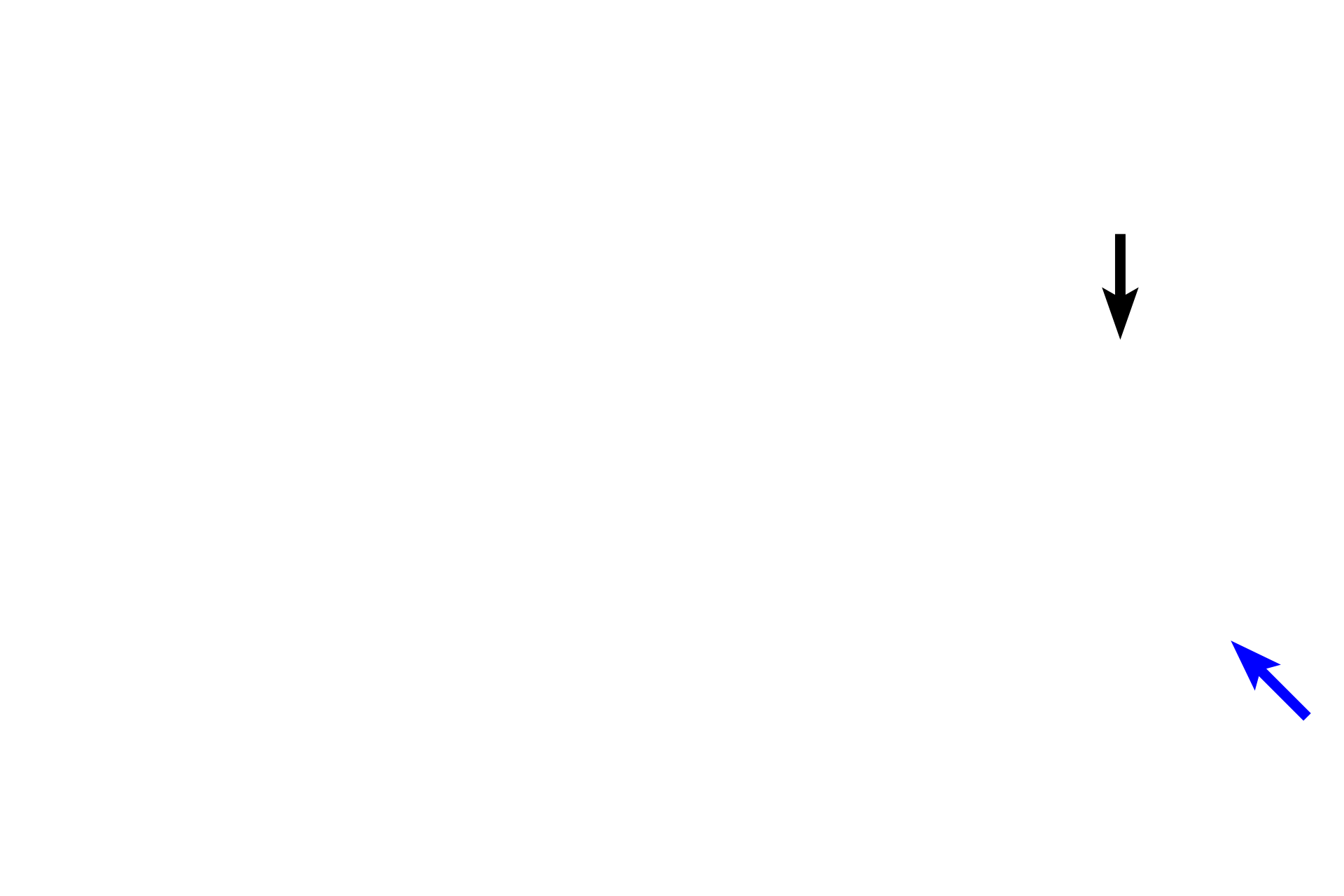
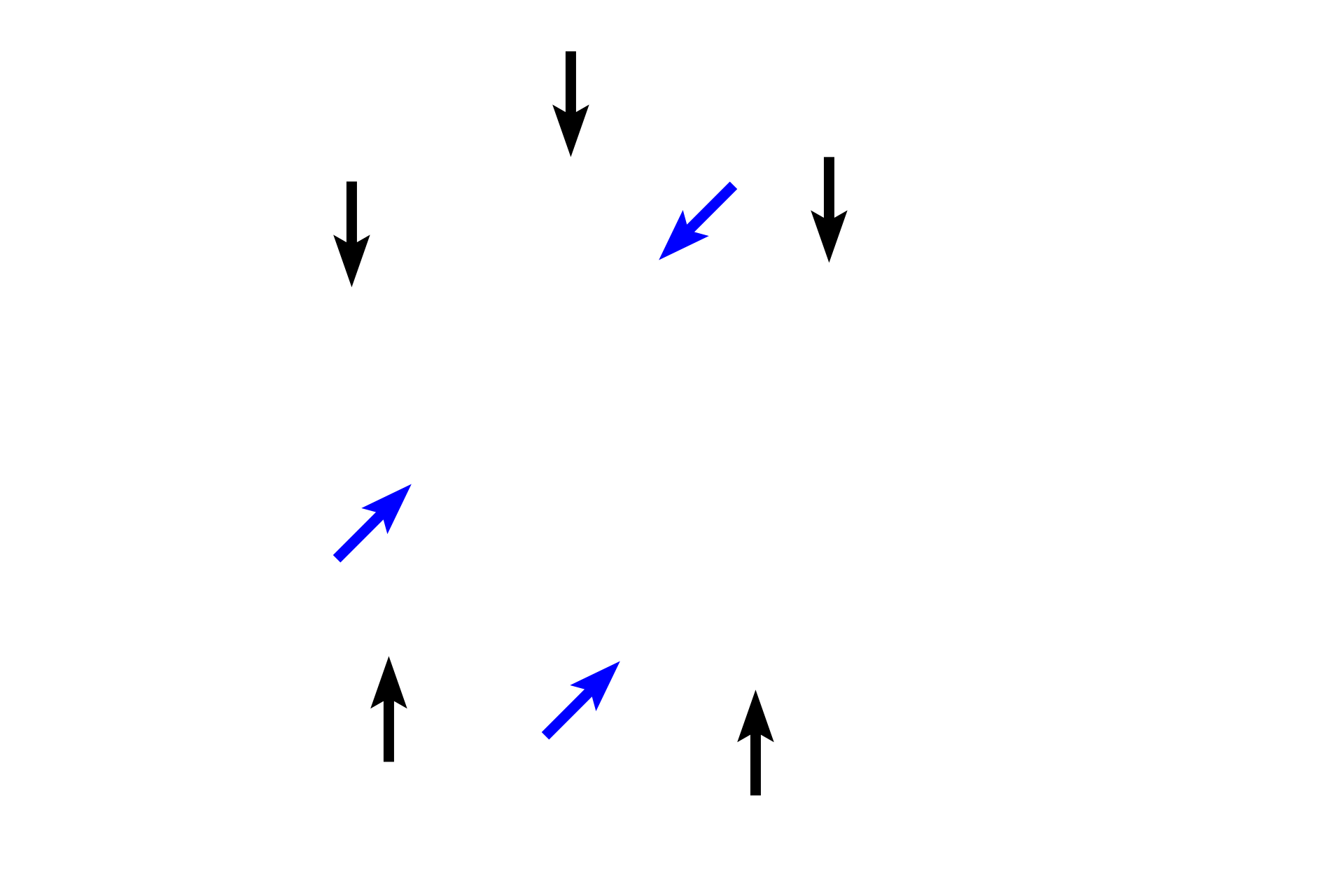
Ascending thick limb >
The ascending thick limb (black arrow) associated with this renal corpuscle loops back to its own vascular pole, where it lies adjacent to the afferent arteriole. Modified cells in the wall of the tubule, the macula densa, and cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole, juxtaglomerular cells, comprise the juxtaglomerular apparatus, which regulates blood pressure and blood volume. The tubule continues as the distal convoluted tubule (blue arrow).

- Macula densa
The ascending thick limb associated with this renal corpuscle loops back to its own vascular pole, where it lies adjacent to the afferent arteriole. Modified cells in the wall of the tubule, the macula densa, and cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole, juxtaglomerular cells, comprise the juxtaglomerular apparatus, which regulates blood pressure and blood volume.

Juxtaglomerular cells
The ascending thick limb associated with this renal corpuscle loops back to its own vascular pole, where it lies adjacent to the afferent arteriole. Modified cells in the wall of the tubule, the macula densa, and cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole, juxtaglomerular cells, comprise the juxtaglomerular apparatus, which regulates blood pressure and blood volume.