
Transition of terminal to respiratory bronchiole
This passageway shows the transition of a terminal bronchiole as it branches into two respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchiole possesses alveoli as components of its wall and thus is the initial passageway of the respiratory portion of the respiratory system. 100x
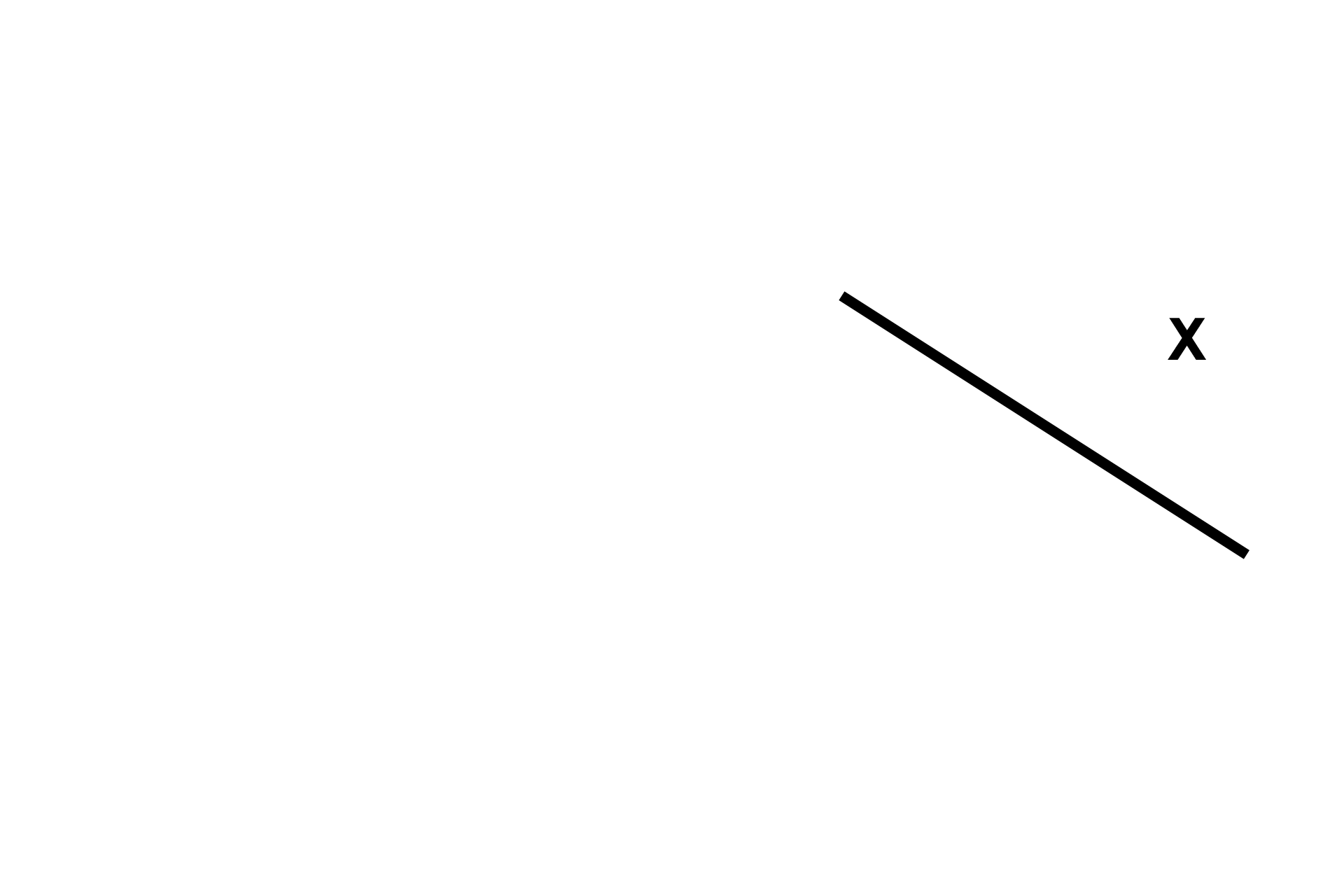
Terminal bronchiole >
A terminal bronchiole is the terminal part of the conducting portion of the respiratory system. It is lined by simple, ciliated columnar epithelium. No alveolar lumens are continuous with the lumen of a respiratory bronchiole.
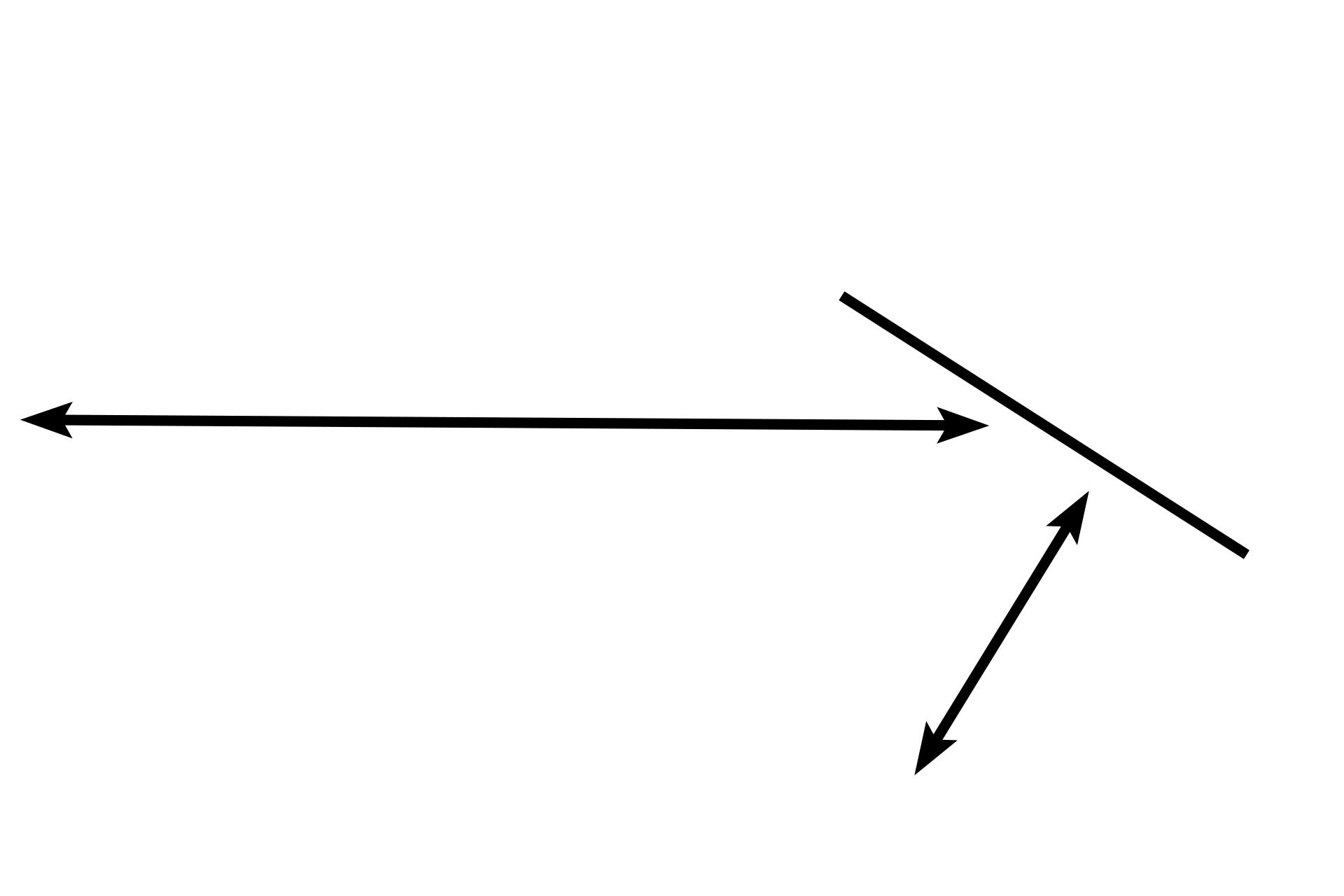
Respiratory bronchioles >
The respiratory bronchiole possesses alveoli as part of its wall. The lumens of the alveoli are directly continuous with that of the respiratory bronchiole and thus the respiratory bronchiole is capable of gaseous exchange. This bronchiole is lined by a cuboidal epithelium with scattered cilia.
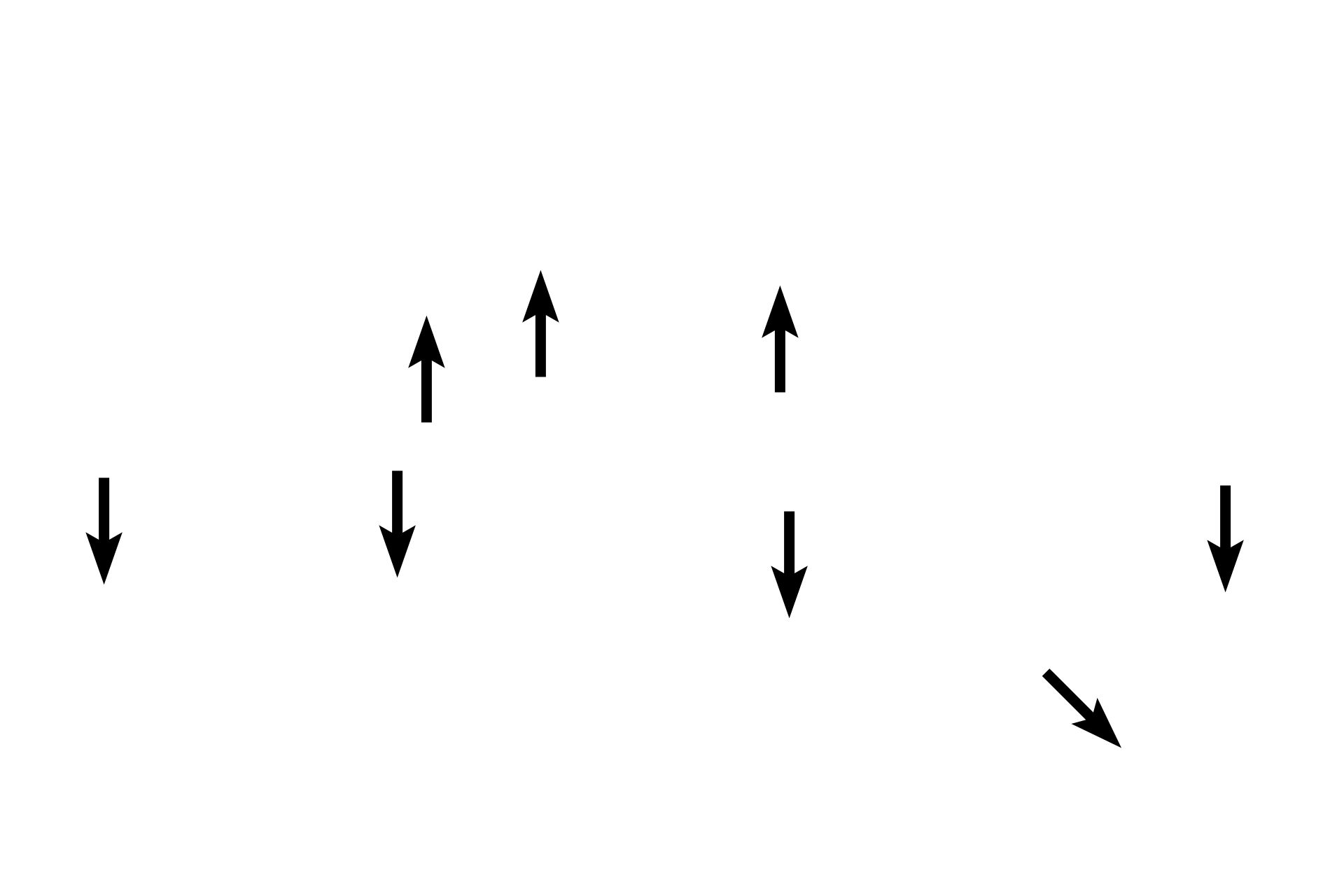
Associated alveoli >
These alveoli are components of the wall of the respiratory bronchiole. The lumen of the bronchiole is continuous with that of the alveoli.
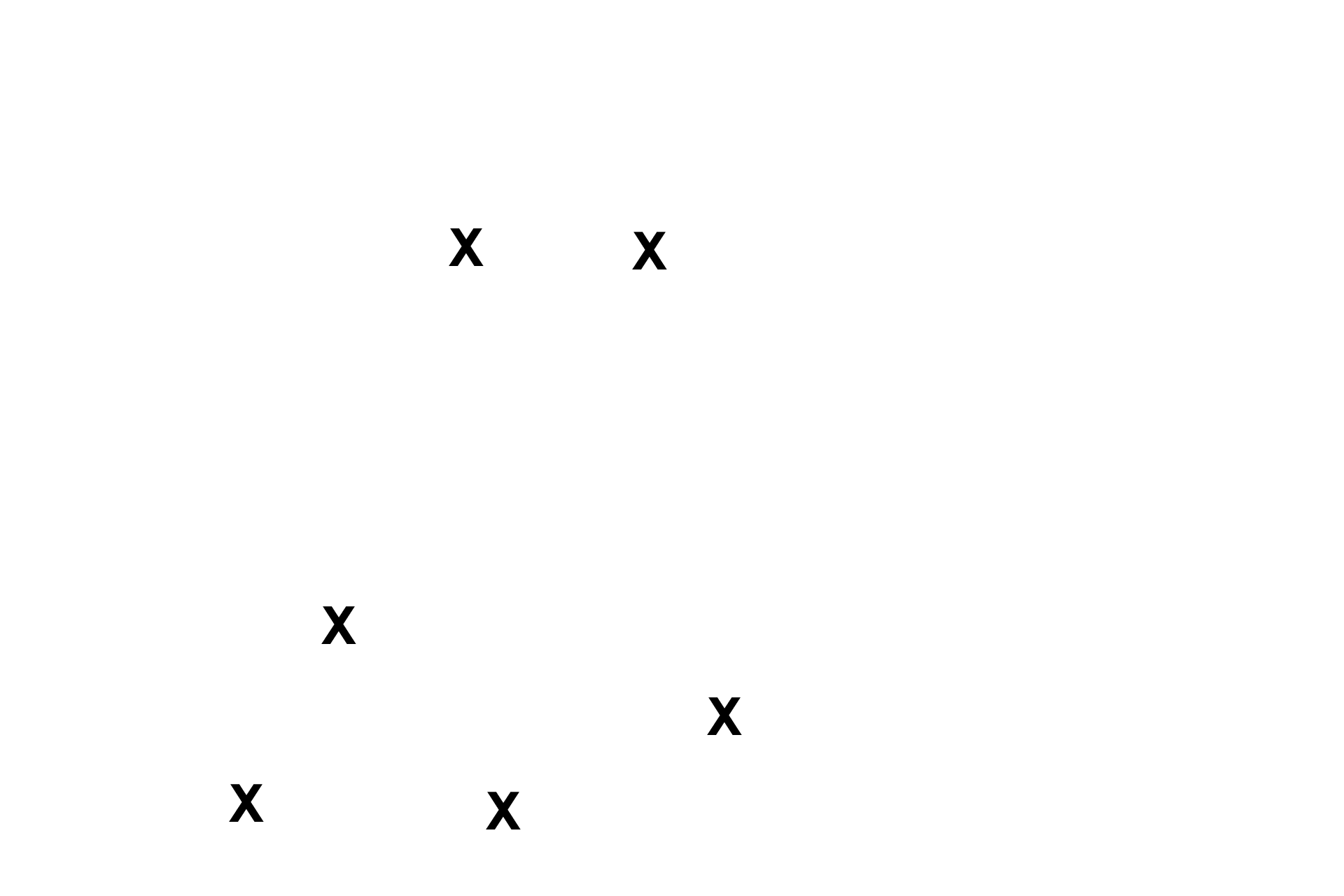
Non-associated alveoli >
Numerous alveoli surround the respiratory bronchiole, however, they belong to other respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts or alveolar sacs.

Pulmonary artery >
This vessel accompanies the bronchiole and eventually carries deoxygenated blood to the alveoli.

Image source >
This image was taken of a slide from University of Iowa collection.