
Trachea and primary bronchus
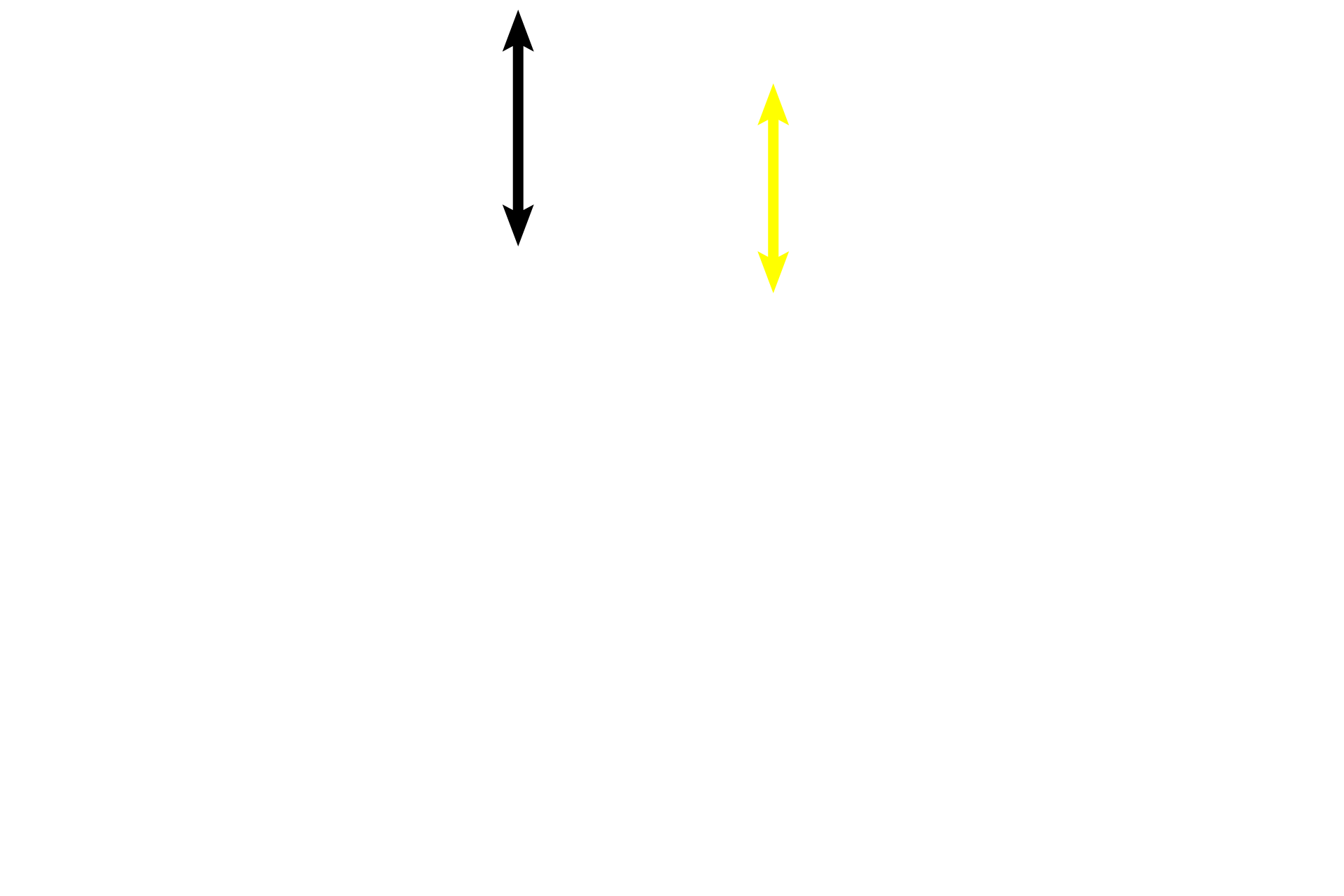
The epithelium lining the trachea and primary bronchi is respiratory epithelium, pseudostratified columnar with cilia and goblet cells. The basement membrane is frequently prominent beneath this epithelium. Elastic fibers/lamella are obvious in the lamina propria, while only the left image shows scattered smooth muscle nuclei in narrows bands. 1000x
Epithelium
The epithelium lining the trachea and primary bronchi is respiratory epithelium, pseudostratified columnar with cilia and goblet cells. The basement membrane is frequently prominent beneath this epithelium. Elastic fibers/lamella are obvious in the lamina propria, while only the left image shows scattered smooth muscle nuclei in narrows bands. 1000x

- Basement membrane
The epithelium lining the trachea and primary bronchi is respiratory epithelium, pseudostratified columnar with cilia and goblet cells. The basement membrane is frequently prominent beneath this epithelium. Elastic fibers/lamella are obvious in the lamina propria, while only the left image shows scattered smooth muscle nuclei in narrows bands. 1000x
Lamina propria >
The epithelium lining the trachea and primary bronchi is respiratory epithelium, pseudostratified columnar with cilia and goblet cells. The basement membrane is frequently prominent beneath this epithelium. Elastic fibers/lamella are obvious in the lamina propria, while only the left image shows scattered smooth muscle nuclei in narrows bands. 1000x
- Elastic lamina
In the left image, longitudinally oriented elastic fibers, typical for the respiratory system, are dispersed in the lamina propria.
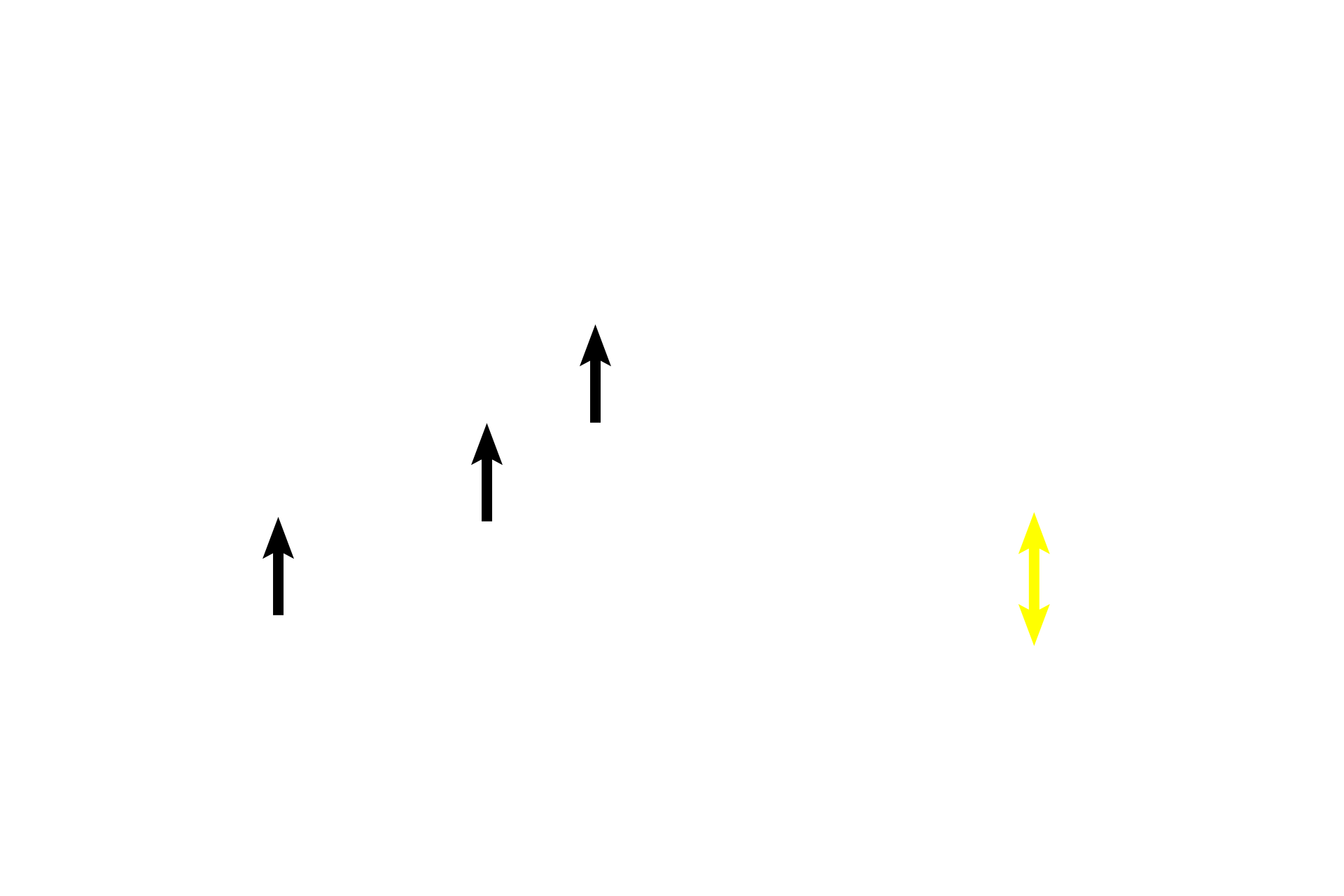
- Smooth muscle >
Smooth muscle bands (red arrows) are indistinct, while only two smooth muscle nuclei (black arrows) are obvious.
- Blood vessels >
Numerous blood vessels are still present to modulate incoming air temperature.

Image source >
This image was taken of a slide from the University of Mississippi collection.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS