
Nephron
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. In order, structures included in a nephron are Bowman’s capsule (surrounding the glomerulus), proximal tubule (convoluted and straight portions), thin limb, and distal tubule (straight and convoluted portions). The term uriniferous tubule includes both nephron and the collecting ducts into which the nephron drains. 20x
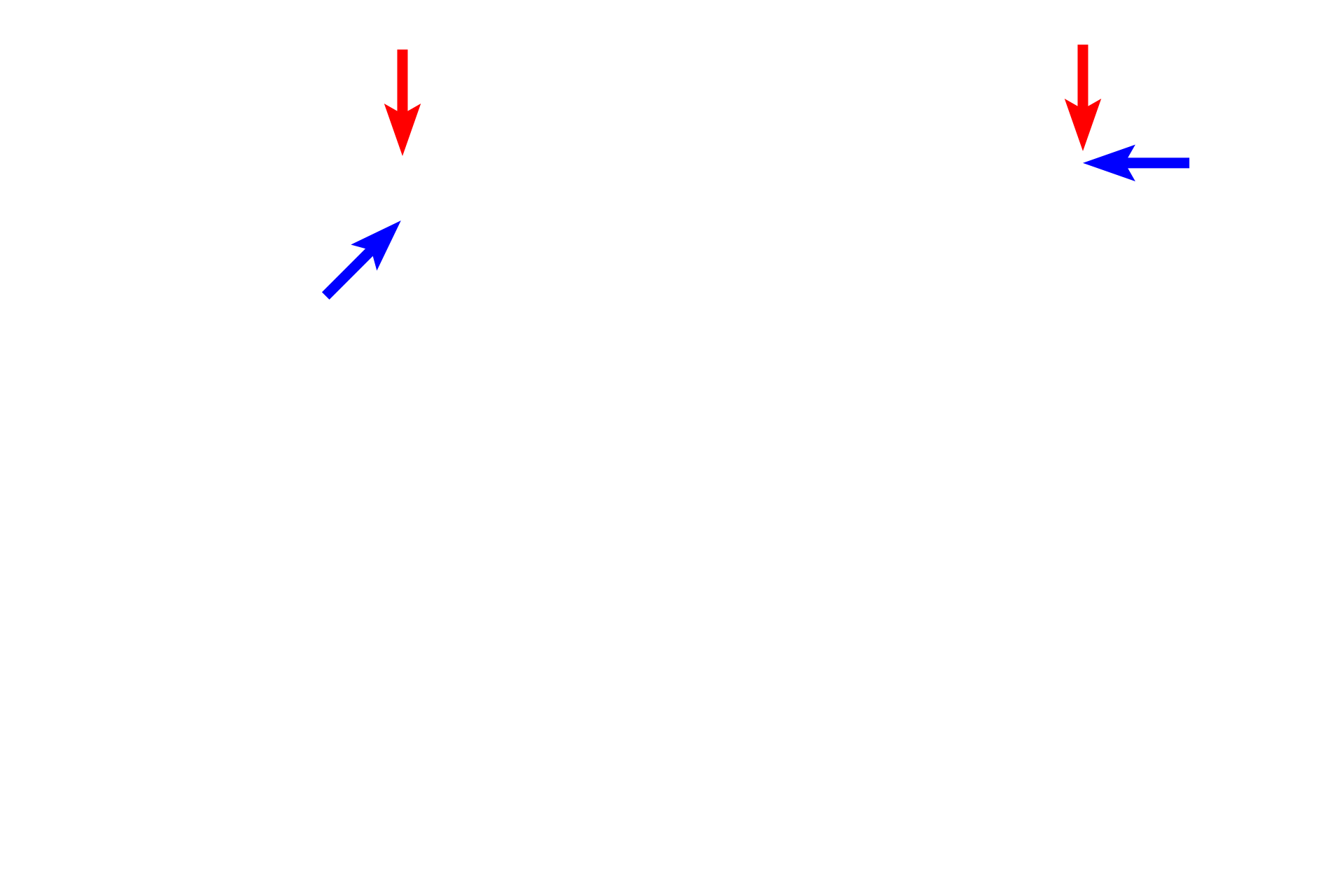
Renal corpuscle >
The renal corpuscle is composed of a tuft of capillaries called the glomerulus (blue arrows) which is surrounded by the double-walled Bowman’s capsule (red arrows). The space of Bowman’s capsule receives the glomerular filtrate of blood.
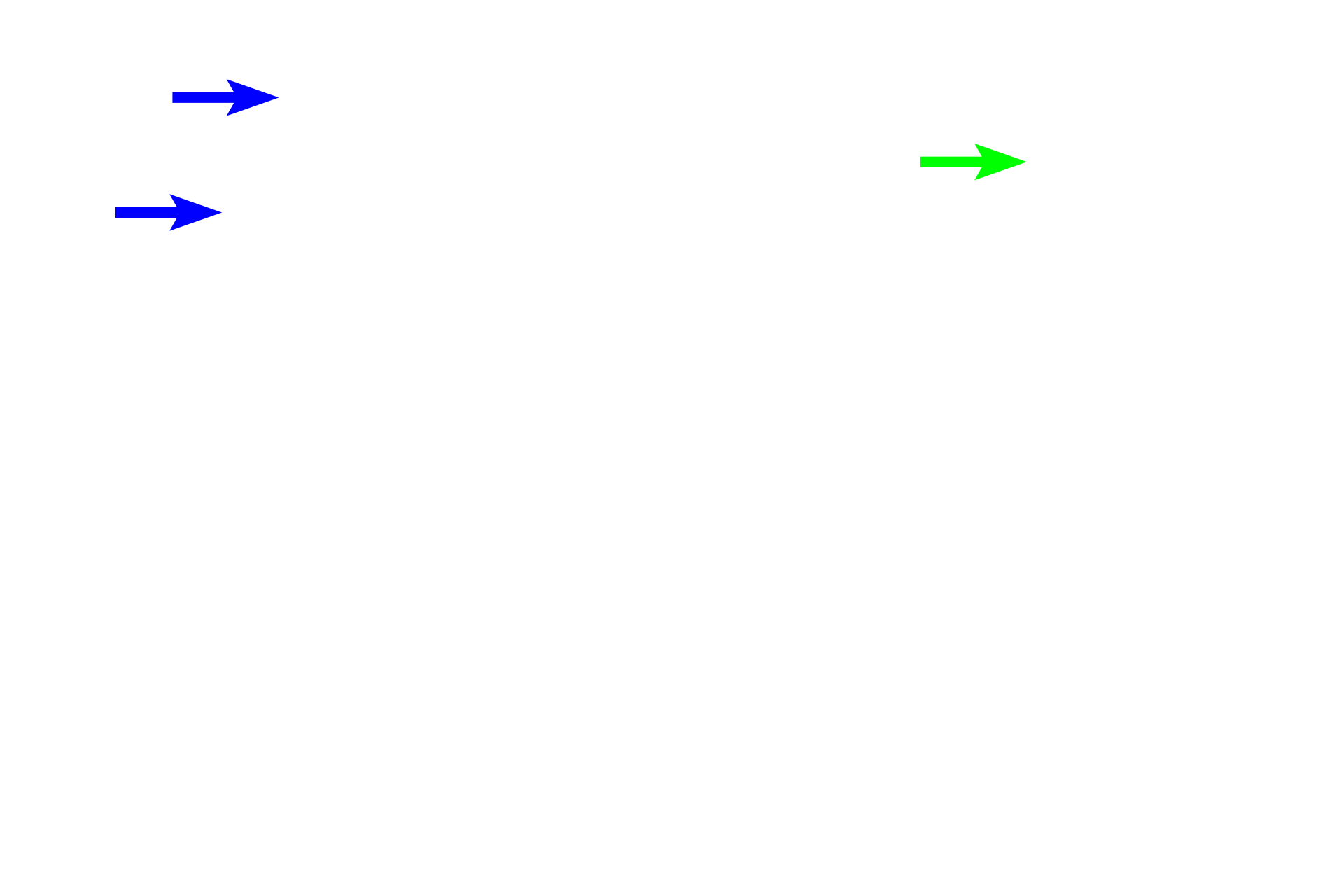
Proximal convoluted tubule >
The proximal convoluted tubule is continuous with and drains the filtrate from Bowman’s capsule. This segment of the nephron is located in the convoluted portion of the renal cortex.
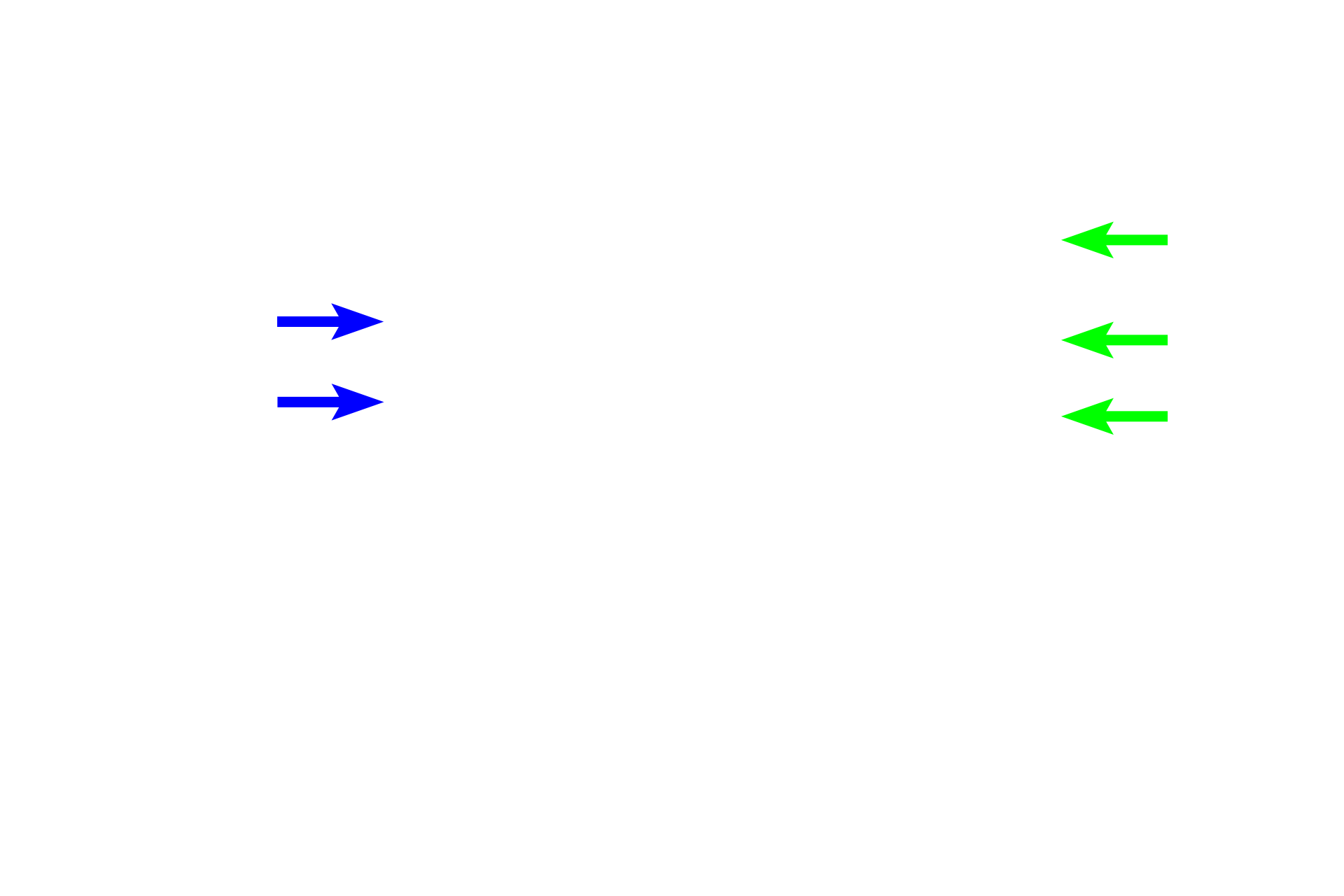
Proximal straight tubule >
The proximal tubule enters the medullary ray, where it is then called the proximal straight tubule. This segment can also be called the thick descending limb of the loop of Henle. The thick descending limb travels in the medullary ray of the cortex to enter the medulla.
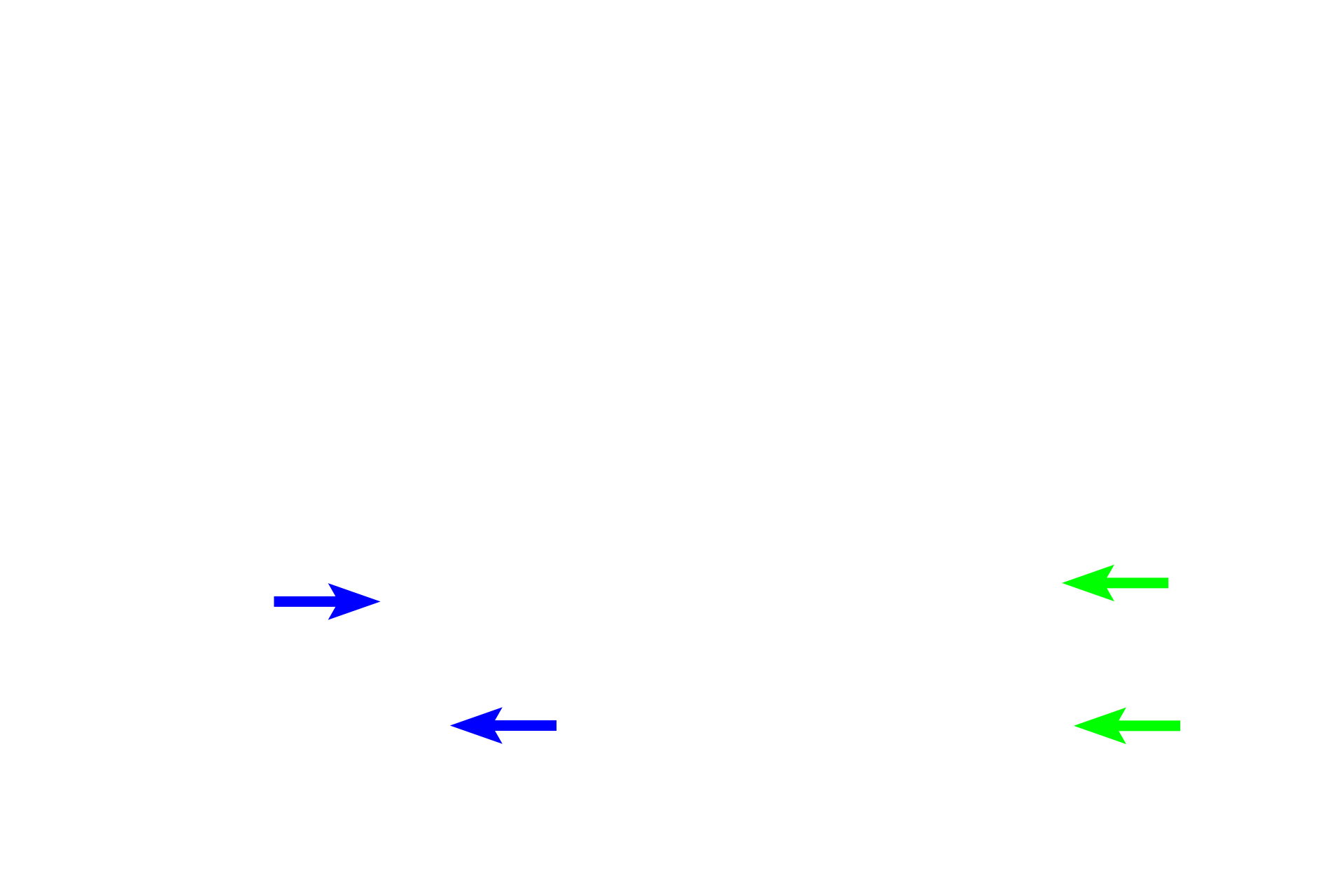
Thin limb >
The thin limb of Henle’s loop continues from the proximal straight tubule. It is usually located in the medulla, where it forms the bend in the loop of Henle.
Ascending thick limb >
The ascending thick limb (sometimes called the distal straight tubule) continues from the thin limb and ascends through the medulla to enter a medullary ray of the cortex. At the level of its parent renal corpuscle, the thick limb leaves the ray and moves into the convoluted region and contacts the afferent arteriole at the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle (black arrow). Here, its cells are modified to form the macula densa of the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
Loop of Henle >
The loop of Henle consists of a thick descending limb (proximal straight tubule), a thick ascending limb (distal straight tubule) and a thin, looped segment (thin limb) that interconnects the two.

Distal convoluted tubule >
The continuation of the ascending thick limb beyond the juxtaglomerular apparatus is distal convoluted tubule. It is much shorter than the proximal convoluted tubule and eventually joins with the collecting passageways.
Collecting passageways >
Urine passes out of the nephron into a series of collecting tubules, which consist of connecting tubules, collecting ducts and papillary ducts.

- Connecting tubule >
The connecting tubule is a continuation of the distal convoluted tubule in the convoluted region. This tubule continues as a collecting duct.
- Collecting duct >
The connecting tubule continues as a collecting duct in the medullary ray and proceeds into the medulla. Epithelial cells forming collecting ducts increase in height as they near the apex of the pyramid.

- Papillary duct >
Epithelial cells forming collecting ducts increase in height as they near the apex of the pyramid. The largest ducts, papillary ducts of Bellini, open into a minor calyx.
Medullary ray >
The medullary ray contains the straight portions of the proximal and distal tubules, as well as the collecting ducts.
Interlobular artery >
Interlobular arteries branch from arcuate arteries and travel through the convoluted portions of the cortex where they give off afferent arterioles supplying the glomerular capillaries.
Afferent arteriole
Interlobular arteries branch from arcuate arteries and travel through the convoluted portions of the cortex, where they give off afferent arterioles supplying the glomerular capillaries.