
Serosal membrane
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x
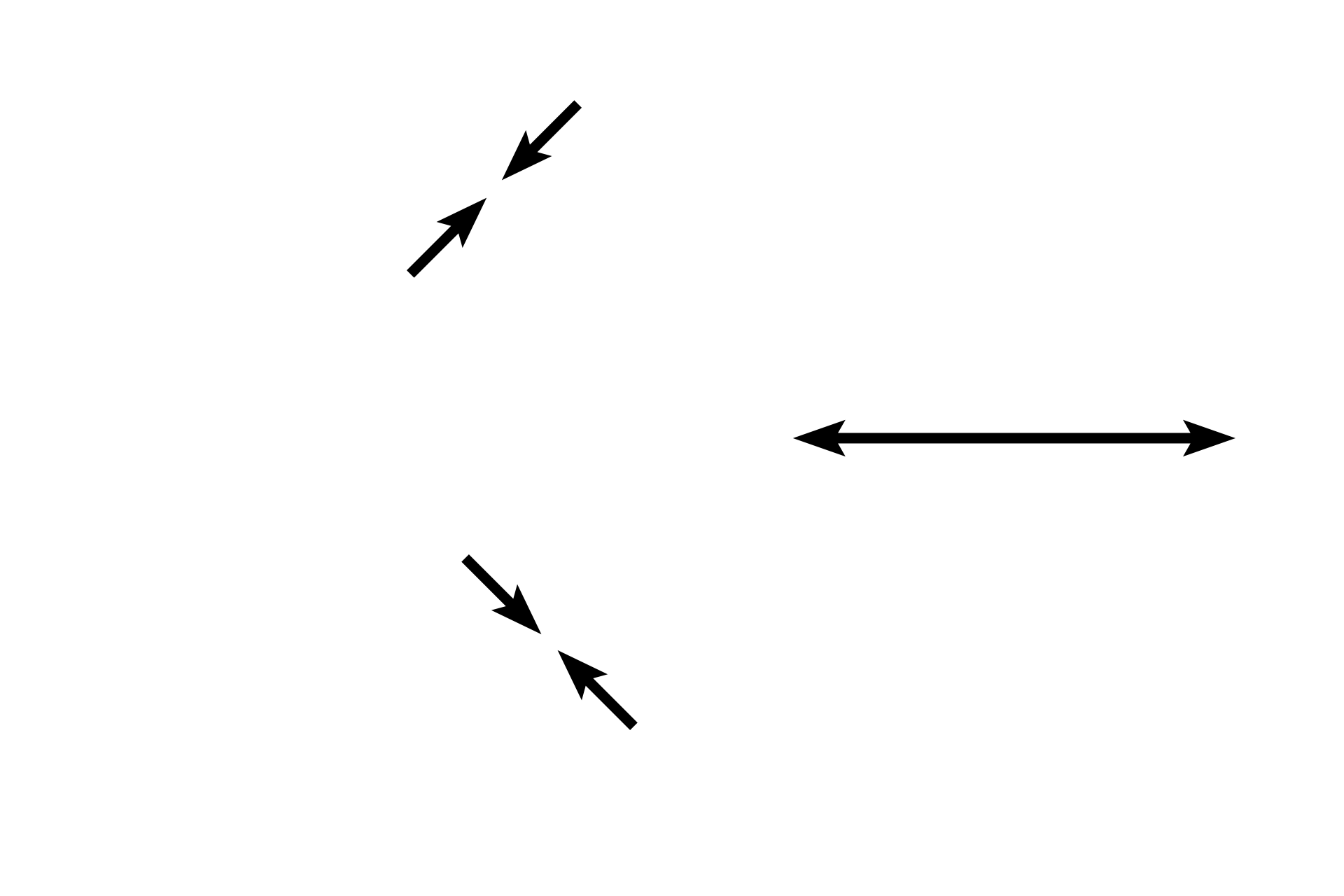
Serosa
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x
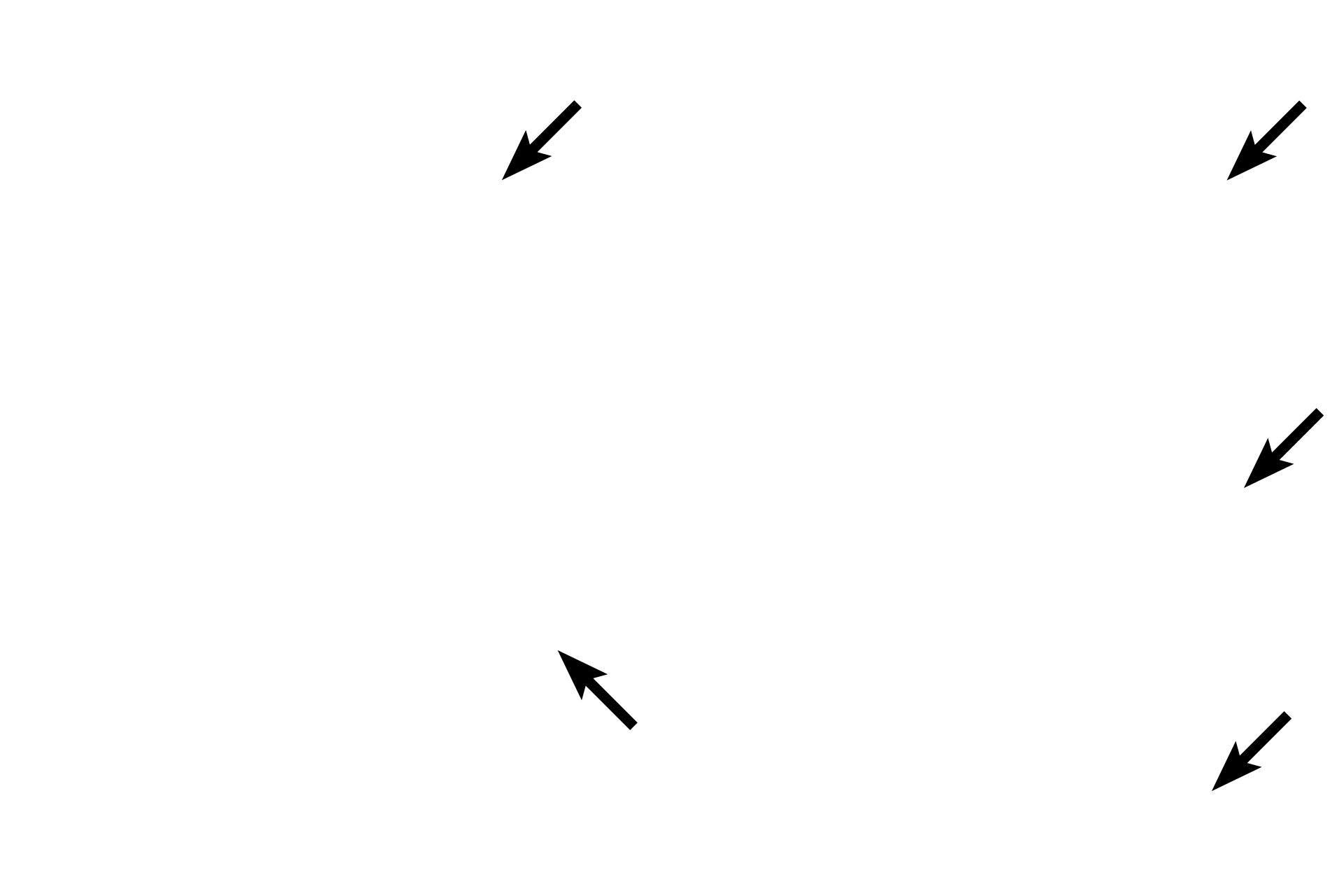
- Epithelium (mesothelium)
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x
- Connective tissue of serosa
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x
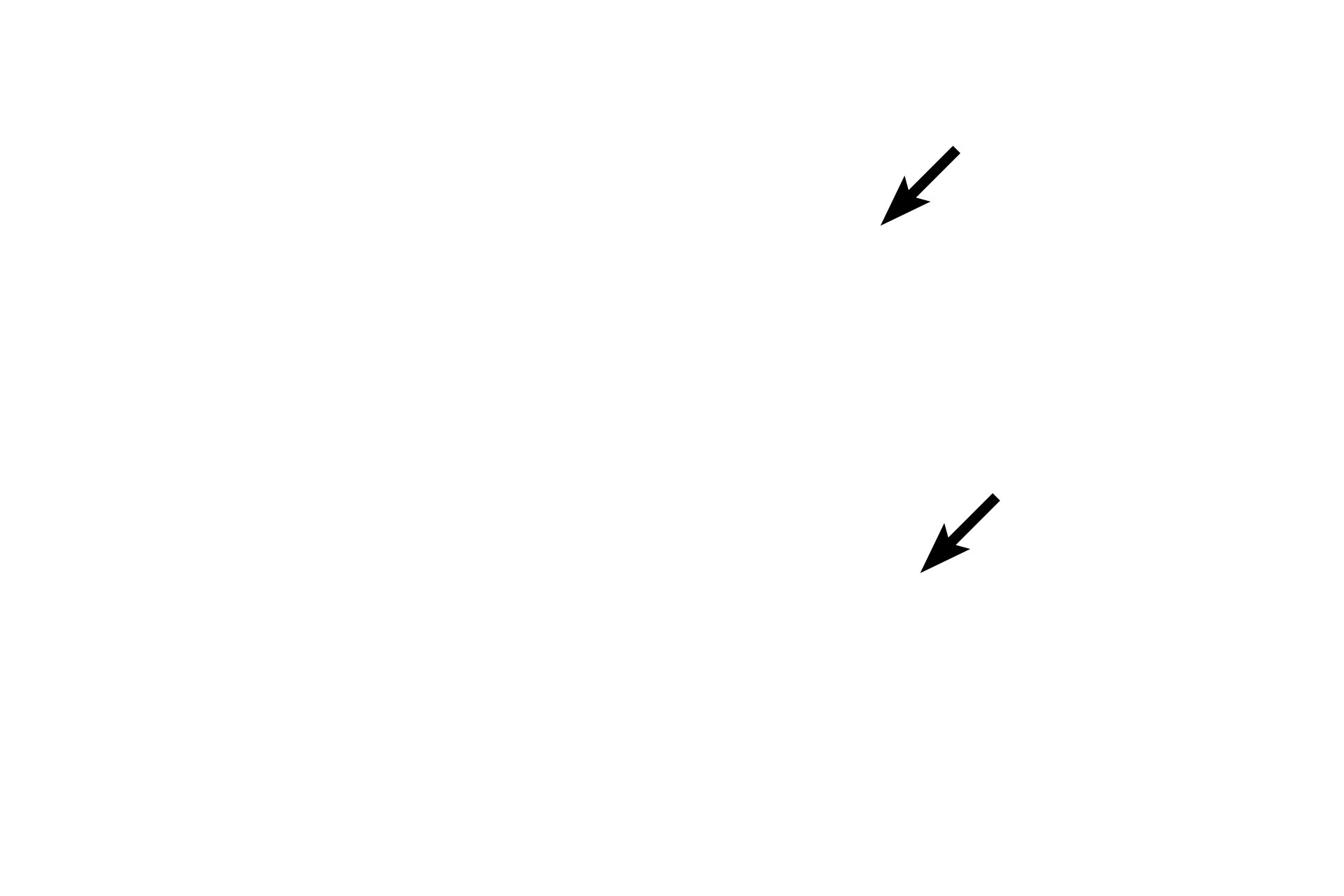

- Blood vessels
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x

Peritoneal space
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x
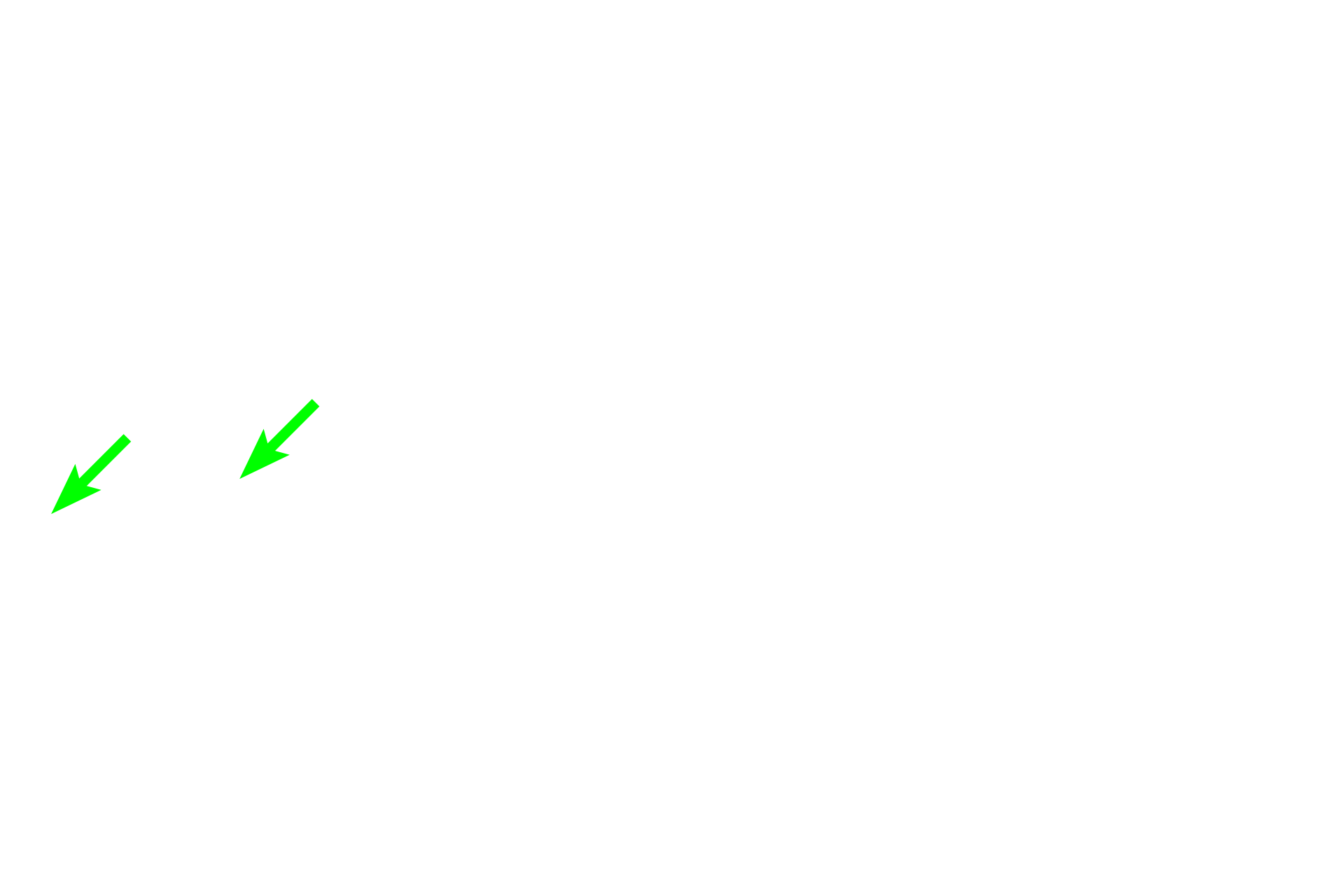

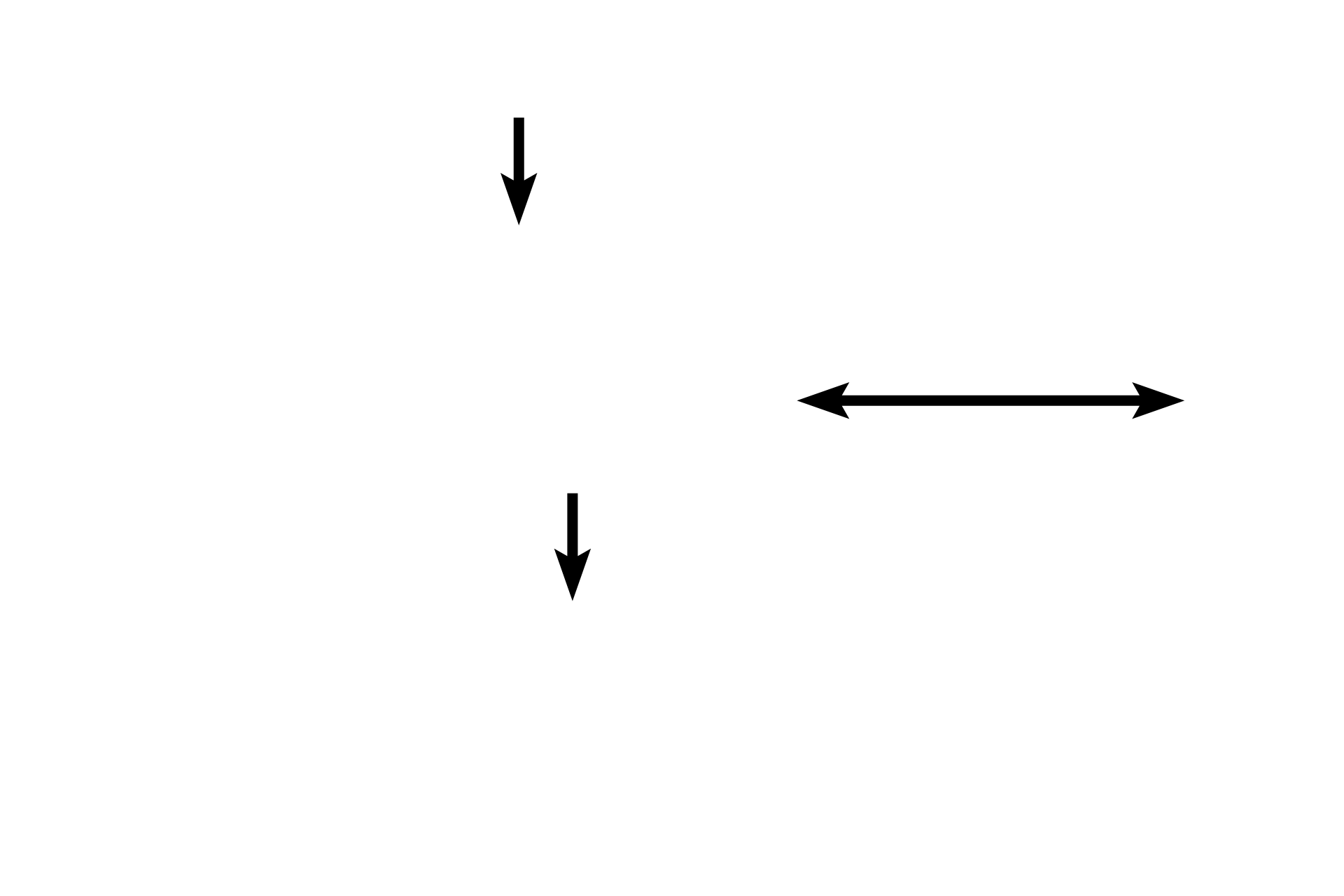
Mucosa of the intestine
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x

Lumen of the intestine
A serosal membrane (serosa) lines internal body cavities, forming a parietal layer around the cavity’s inner wall and a visceral layer over organs protruding into the cavity. A serosa is composed of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) overlying a layer of connective tissue. Examples of serosal membranes are pleural, pericardial and peritoneal membranes identified in gross anatomy. 200x, 1000x

Image source >
These images were taken of a slide from the University of Michigan collection.