
Globe: Iris
A higher magnification image shows details of the iris musculature and stroma. The image is rotated 90 degrees clockwise from the previous image; the aperture of the pupil would be to the left.

Lens
This higher magnification image shows details of the iris musculature and stroma. The image rotated 90 degrees from the previous image, the aperture of the pupil would be to the left.
Posterior iris epithelium >
The epithelium covering the posterior surface is a continuation of the non-sensory retina and consists of two layers. The anterior surface of the iris is not lined by an epithelium.

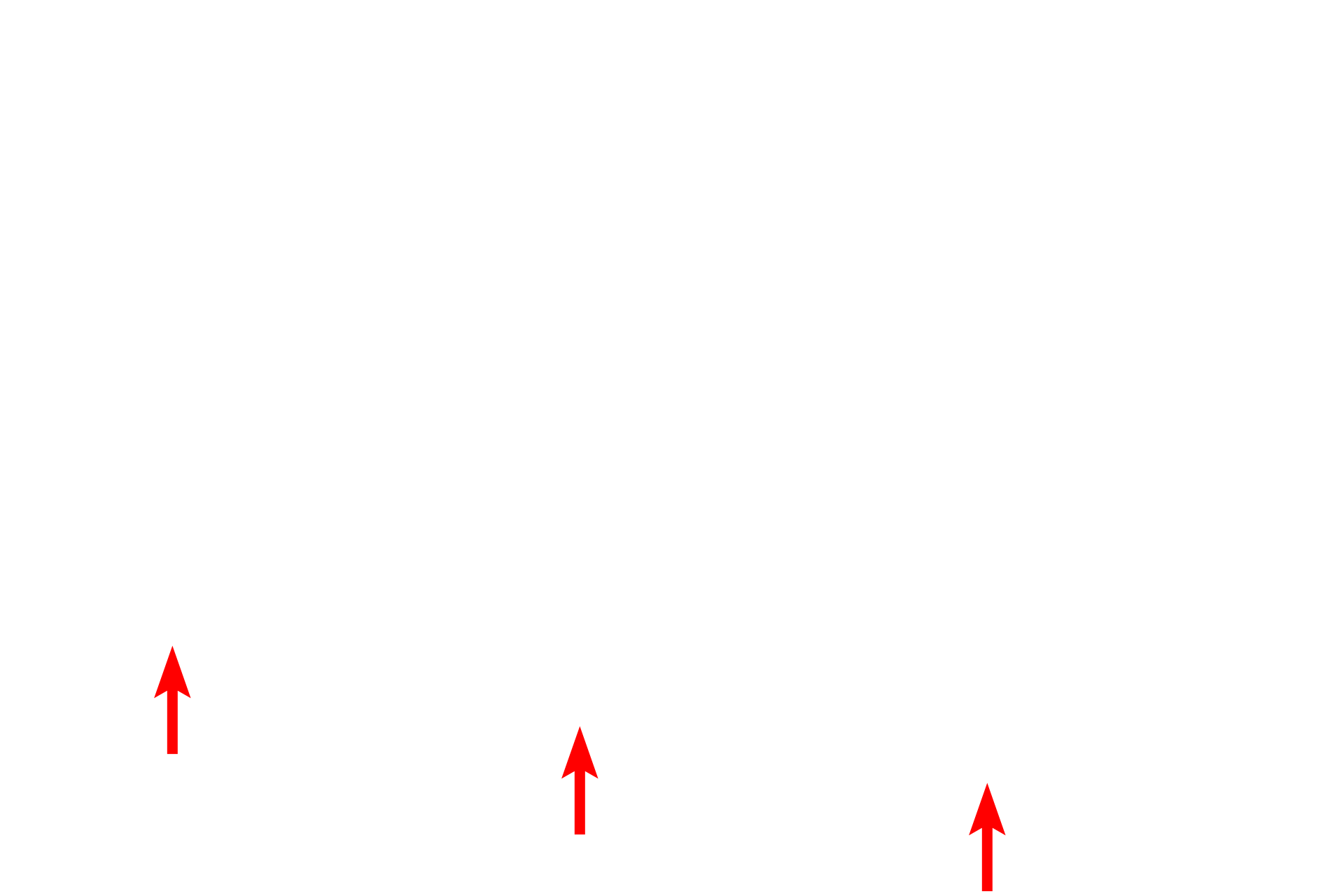
Constrictor pupillae muscle >
The constrictor pupillae muscle consists of smooth muscle fibers located at the internal perimeter of the iris. These muscle fibers are oriented circumferentially around the pupillary rim of the iris and contraction, controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system, decreases the aperture of the pupil.

Dilator pupillae muscle >
The thin dilator pupillae muscle is the antagonist of the constrictor. Contraction of this muscle, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, results in an increase in pupillary diameter. The dilator muscle consists of myoepithelial cells derived from the epithelial layer adjacent to the stroma. The individual layers of the epithelium cannot be distinguished in this image.
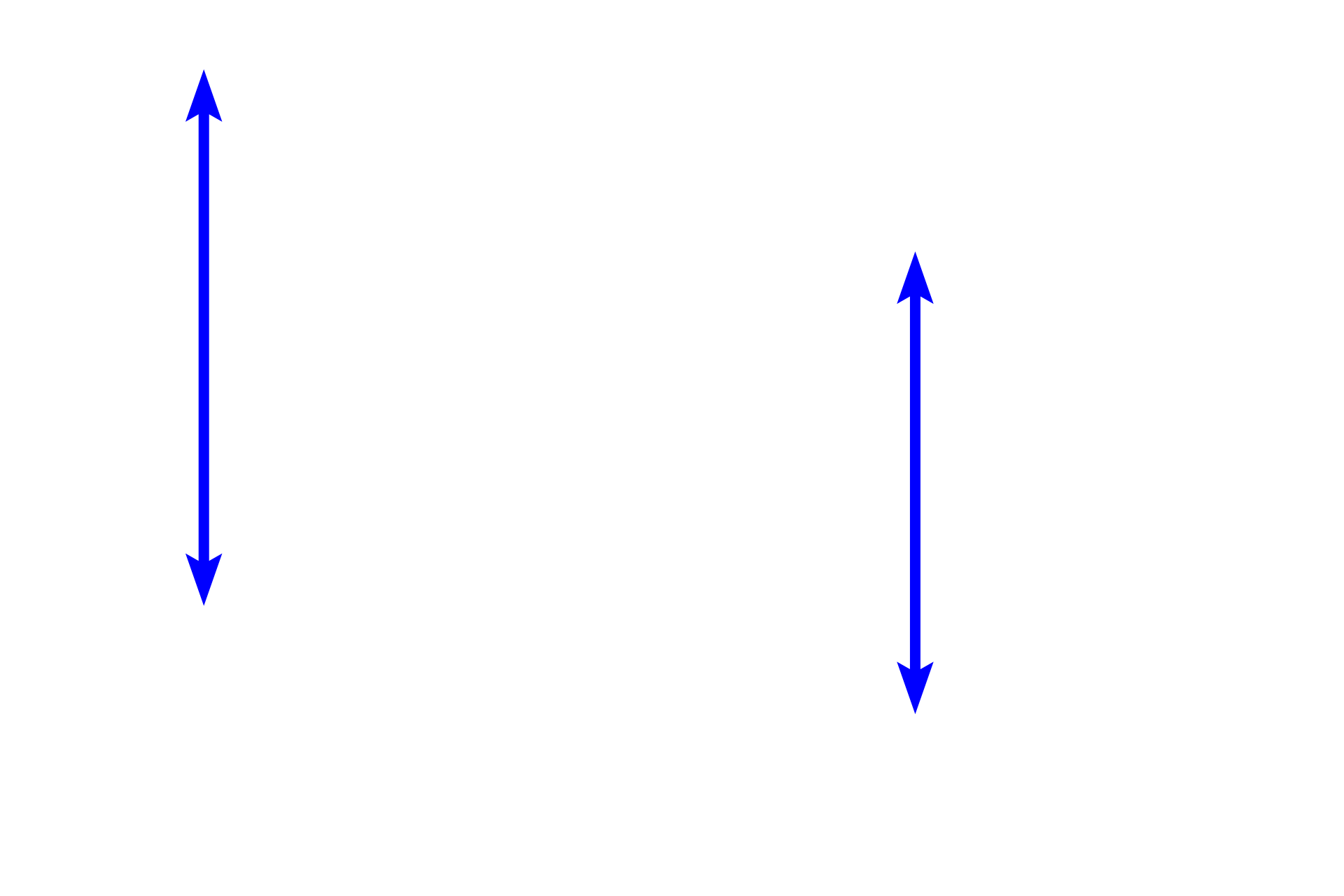
Stroma >
Stroma forms the bulk of the iris and is composed of loose connective tissue, containing fibroblasts and melanocytes. The stroma is highly vascular. The anterior surface of the iris has numerous grooves and ridges and is not covered by an epithelium.

Image source >
Image taken of a slide from the University of Iowa collection.