
Middle ear: mucosa
Bone of the middle ear cavity is lined by a mucosa that is composed predominately of a simple squamous epithelium overlying a thin, vascular connective tissue. 40x, 40x, 40x
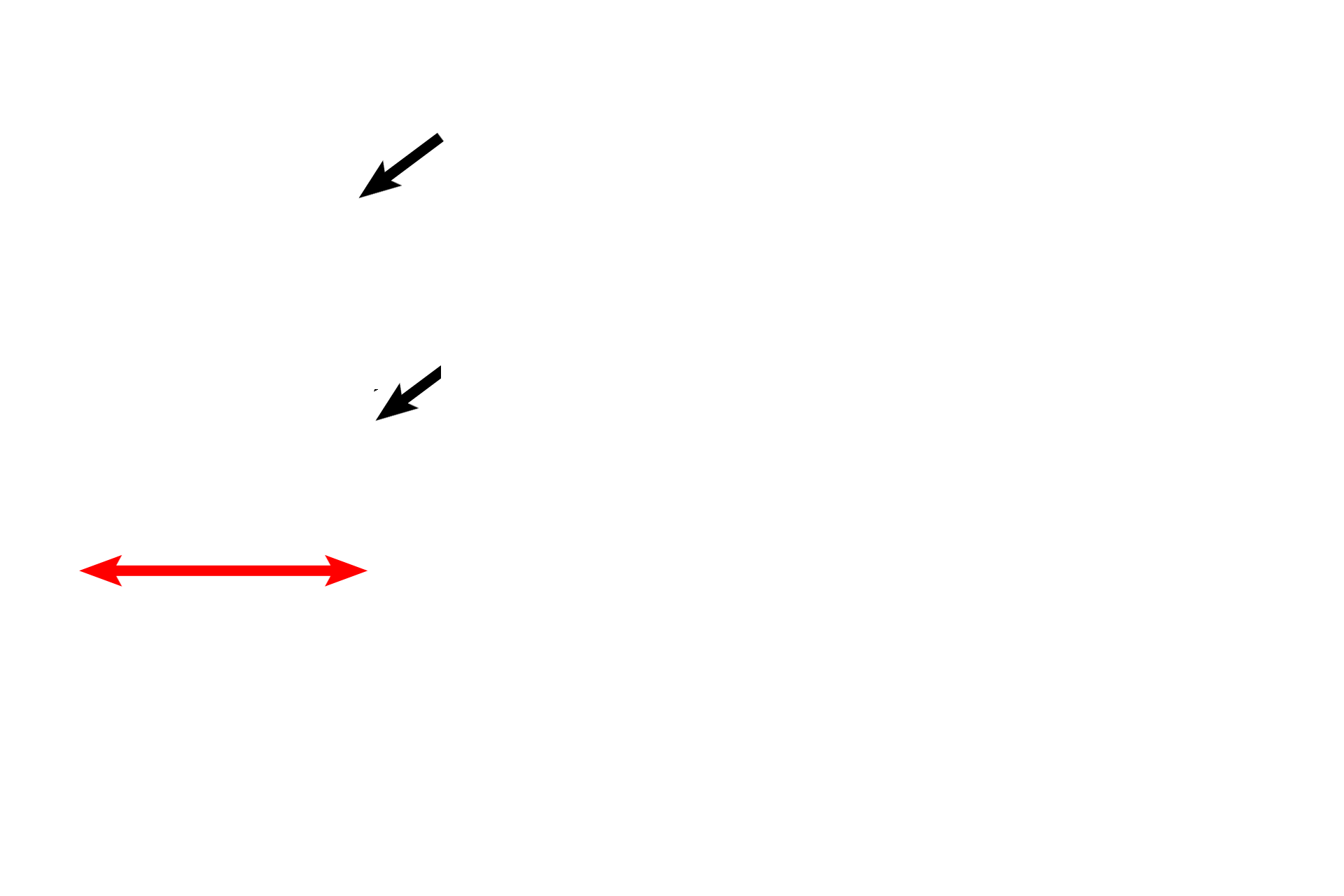
Left panel >
A region of middle ear mucosa and its supporting temporal bone (red arrow) are shown. As in most of the middle ear, the epithelium (black arrows) is simple squamous with a thin underlying, vascular connective tissue.
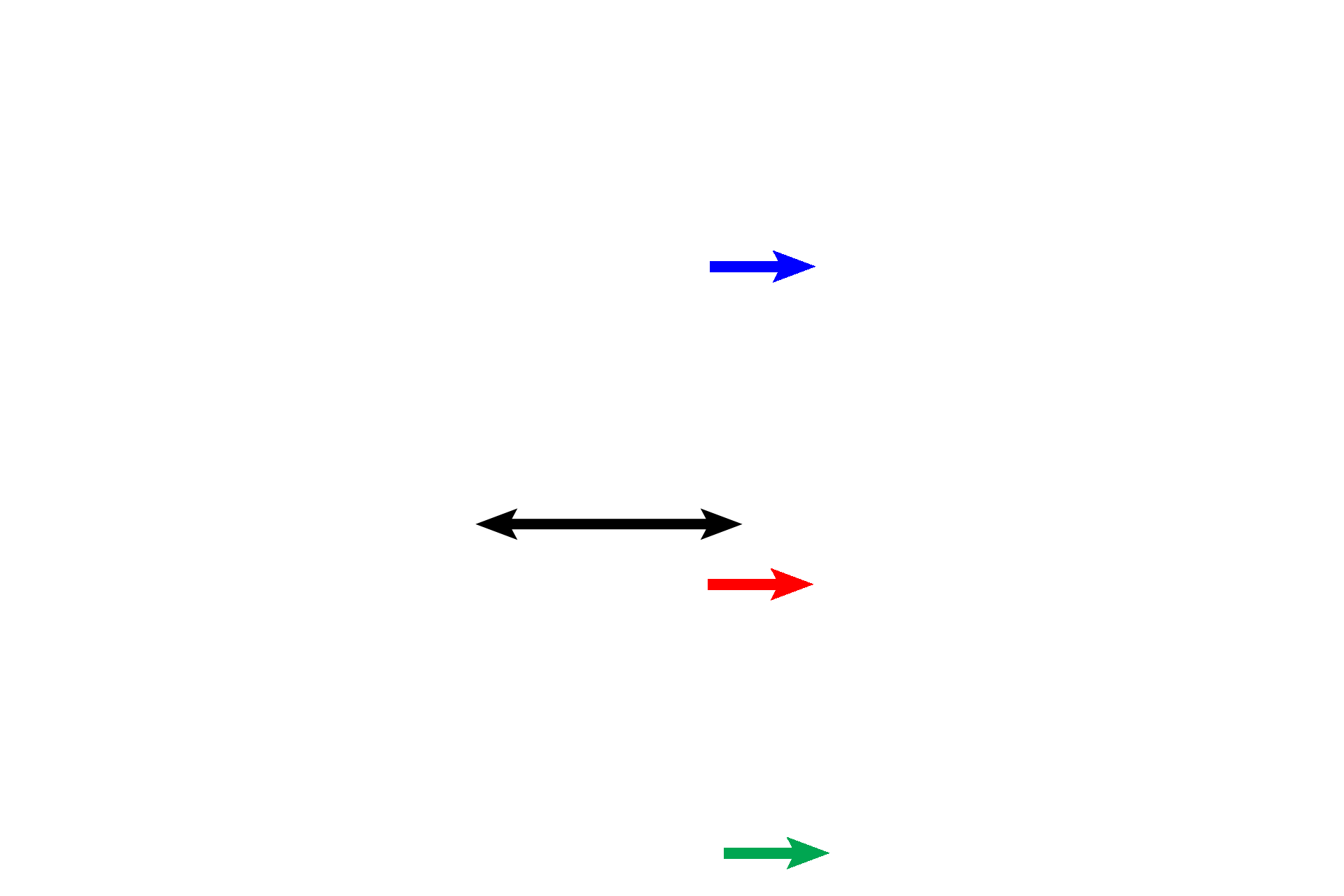
Middle panel >
The epithelial lining of the middle ear gradually increases in height as it approaches the opening of the Eustachian tube. Squamous (green arrow), cuboidal (red arrow), and columnar cells (blue arrow) are indicated. Temporal bone is indicated by the black arrow.
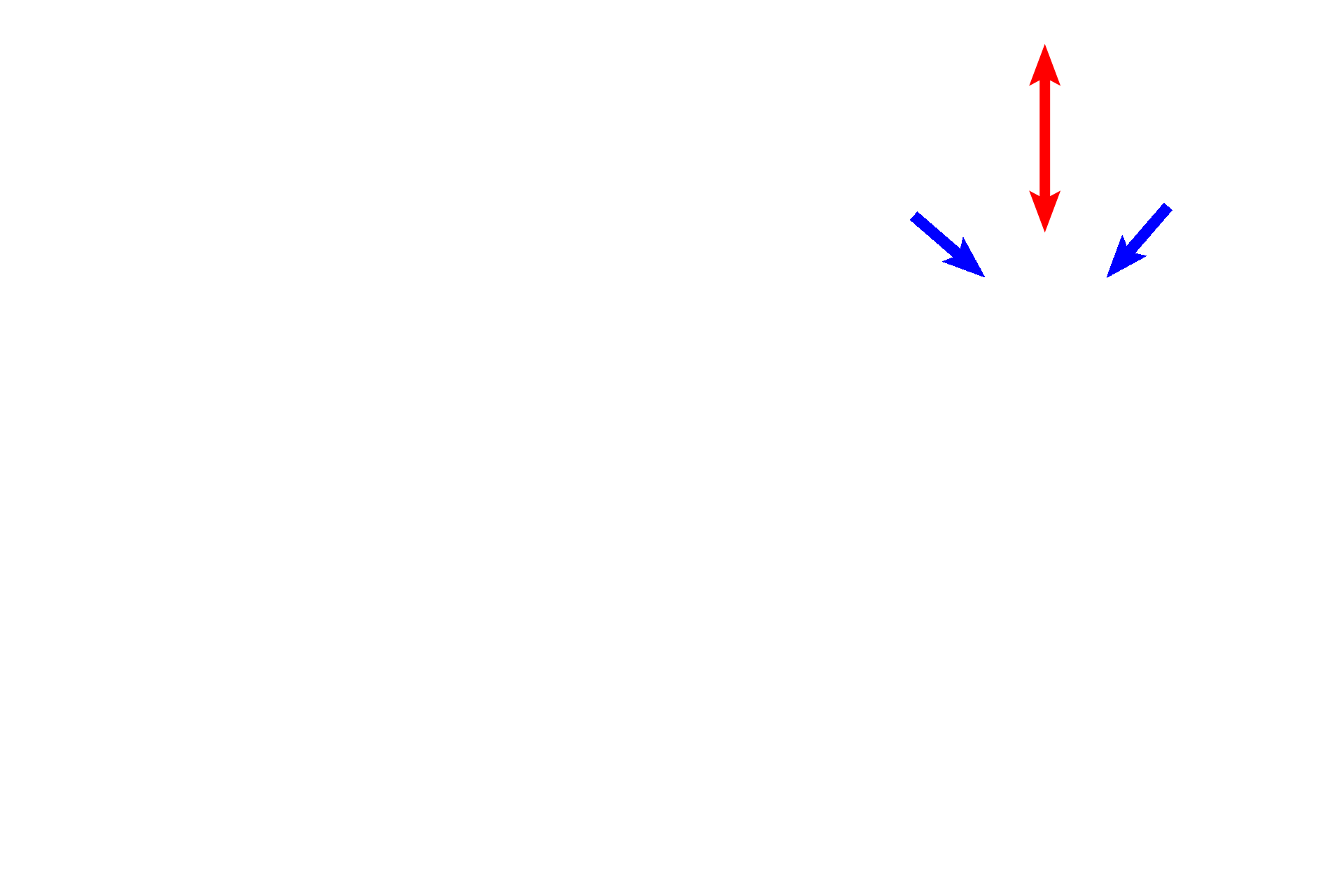
Right panel >
The Eustachian tube opening is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium (blue arrows), which becomes pseudostratified columnar with cilia and goblet cells closer to the junction of the Eustachian tube with the nasopharynx. Cilia of this epithelium beat toward the nasopharynx. Supporting cartilage is indicated by a red arrow.