
Cochlear duct
The cochlear duct, part of the membranous labyrinth, is a triangular-shaped wedge located in the cochlea. The cochlear duct, filled with endolymph, lies in the middle of the cochlea, dividing it into thirds, with the scala vestibuli above and the scala tympani below the cochlear duct. The organ of Corti, the receptor for sound, is housed in the cochlear duct.
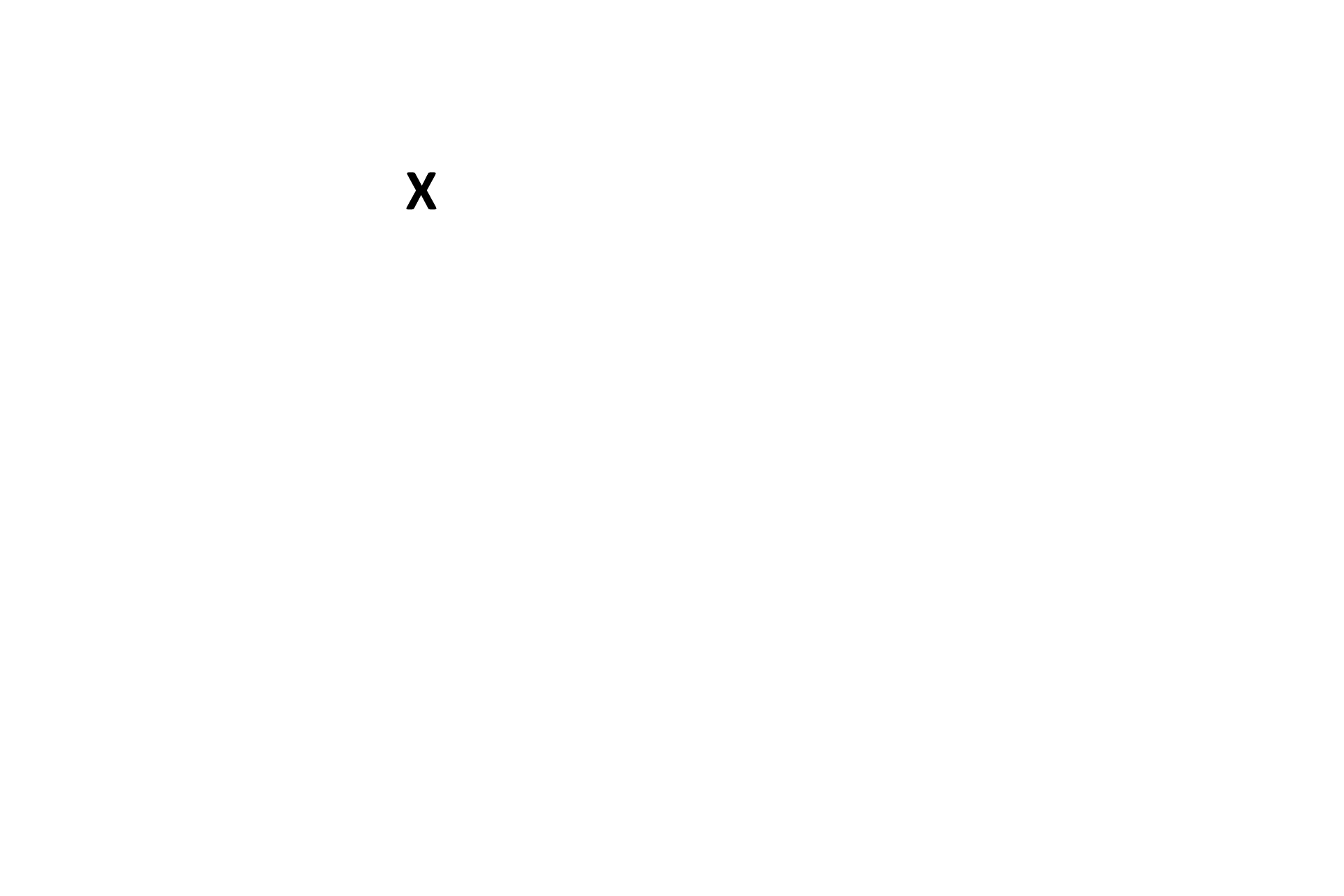
Scala vestibuli
The cochlear duct, part of the membranous labyrinth, is a triangular-shaped wedge located in the cochlea. The cochlear duct, filled with endolymph, lies in the middle of the cochlea, dividing it into thirds, with the scala vestibuli above and the scala tympani below the cochlear duct. The organ of Corti, the receptor for sound, is housed in the cochlear duct.

Vestibular membrane
The cochlear duct, part of the membranous labyrinth, is a triangular-shaped wedge located in the cochlea. The cochlear duct, filled with endolymph, lies in the middle of the cochlea, dividing it into thirds, with the scala vestibuli above and the scala tympani below the cochlear duct. The organ of Corti, the receptor for sound, is housed in the cochlear duct.

Scala tympani
The cochlear duct, part of the membranous labyrinth, is a triangular-shaped wedge located in the cochlea. The cochlear duct, filled with endolymph, lies in the middle of the cochlea, dividing it into thirds, with the scala vestibuli above and the scala tympani below the cochlear duct. The organ of Corti, the receptor for sound, is housed in the cochlear duct.
Basilar membrane
The cochlear duct, part of the membranous labyrinth, is a triangular-shaped wedge located in the cochlea. The cochlear duct, filled with endolymph, lies in the middle of the cochlea, dividing it into thirds, with the scala vestibuli above and the scala tympani below the cochlear duct. The organ of Corti, the receptor for sound, is housed in the cochlear duct.
Cochlear duct
The cochlear duct, part of the membranous labyrinth, is a triangular-shaped wedge located in the cochlea. The cochlear duct, filled with endolymph, lies in the middle of the cochlea, dividing it into thirds, with the scala vestibuli above and the scala tympani below the cochlear duct. The organ of Corti, the receptor for sound, is housed in the cochlear duct.
- Organ of Corti >
The organ of Corti consists of a complex of supportive cells and hair cells with elongated microvilli (stereocilia). Some of the stereocilia are embedded in the tectorial membrane, extending laterally over the organ of Corti. This membrane is frequently displaced during tissue preparation and, therefore, is not always seen in its proper location.
- Hair cells >
Hair cells are the auditory receptors in the organ of Corti. These cells possess stereocilia, the tallest of which are embedded in the gelatinous tectorial membrane. Peripheral processes of CN VIII that innervate the hair cells exit the organ of Corti through the osseous spiral lamina and continue to the spiral ganglia where their bipolar nerve cell bodies are located. Central processes of these neurons form the cochlear division of CN VIII.
- Tectorial membrane
Hair cells are the auditory receptors in the organ of Corti. These cells possess stereocilia, the tallest of which are embedded in the gelatinous tectorial membrane. Peripheral processes of CN VIII that innervate the hair cells exit the organ of Corti through the osseous spiral lamina and continue to the spiral ganglia where their bipolar nerve cell bodies are located. Central processes of these neurons form the cochlear division of CN VIII.
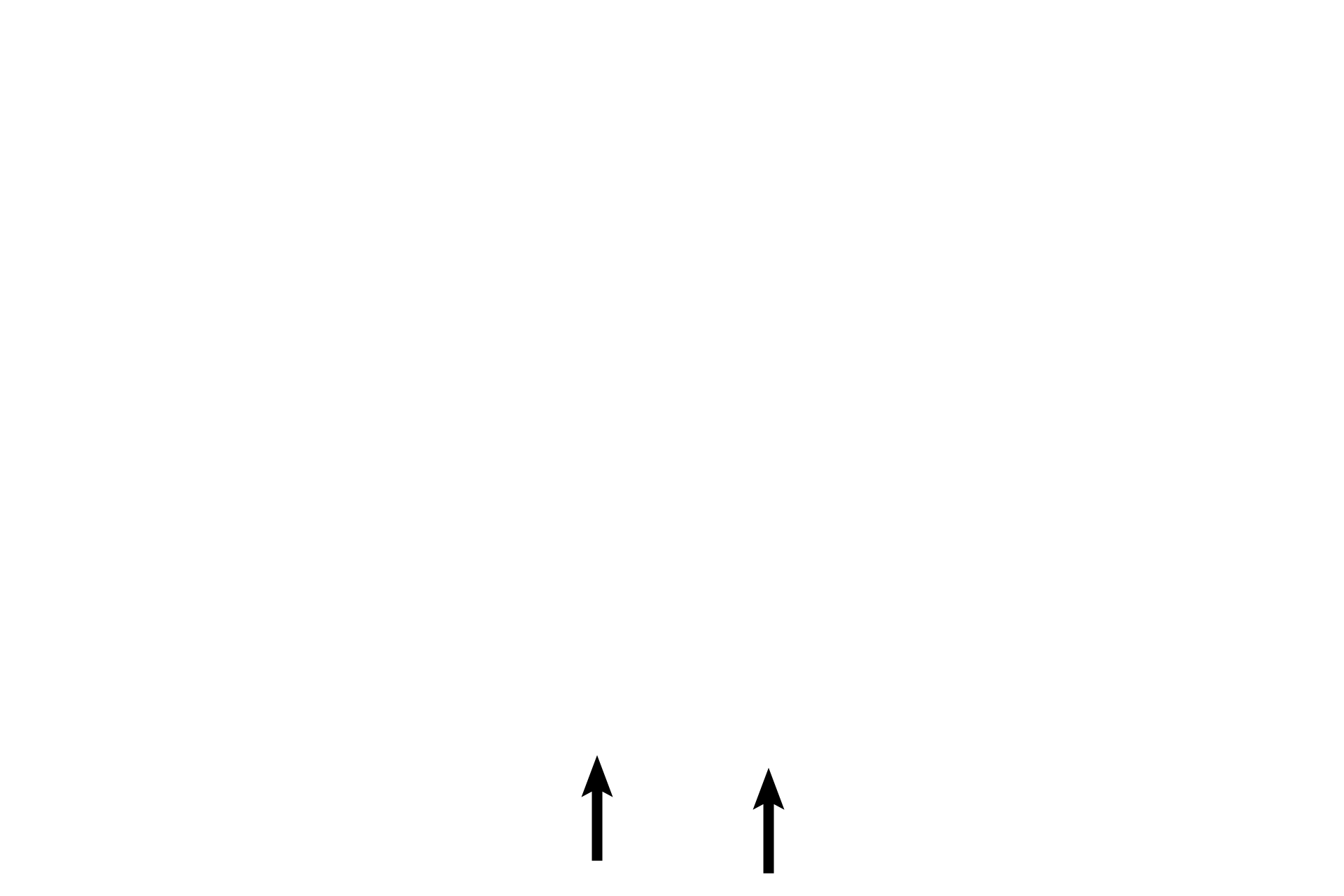
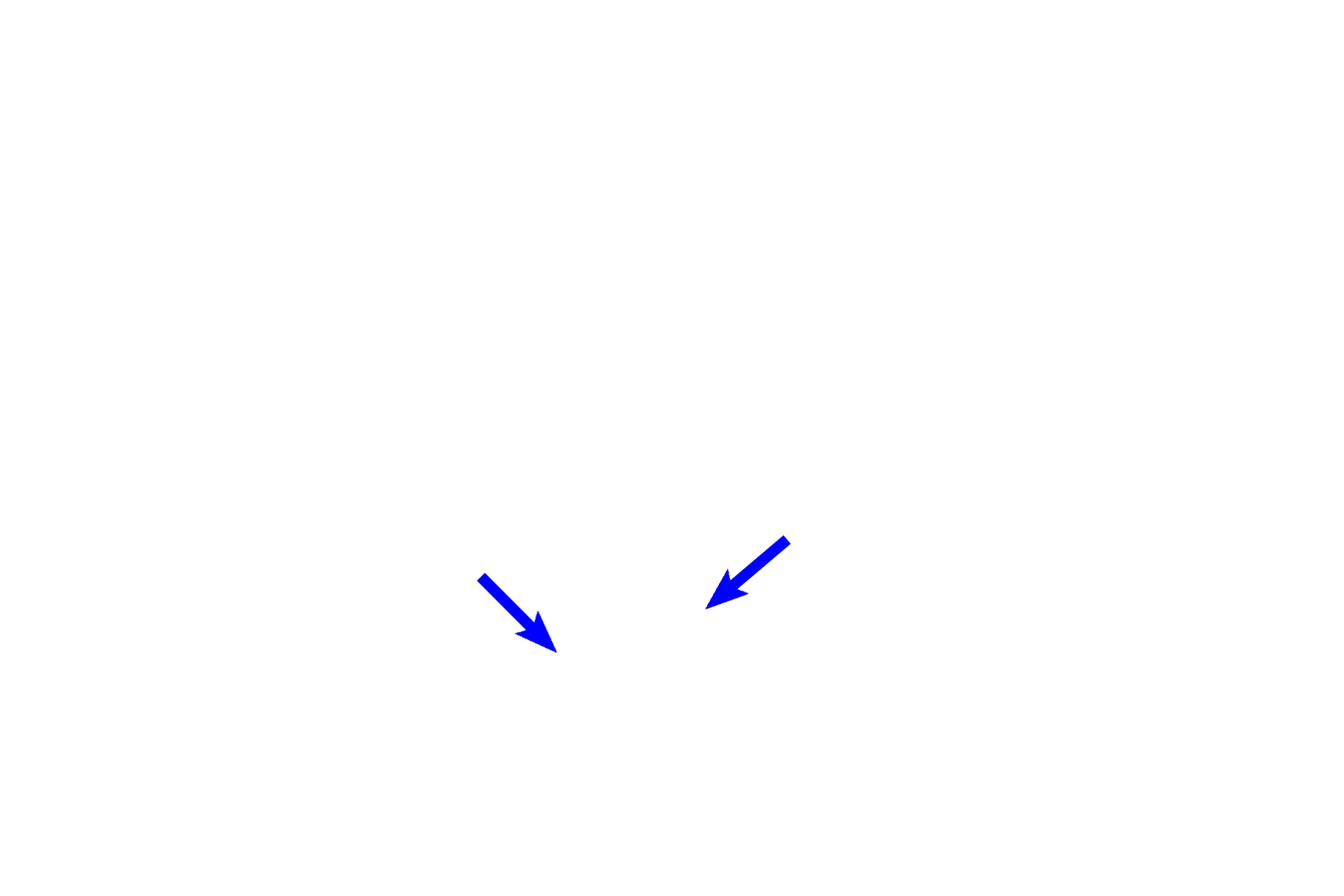
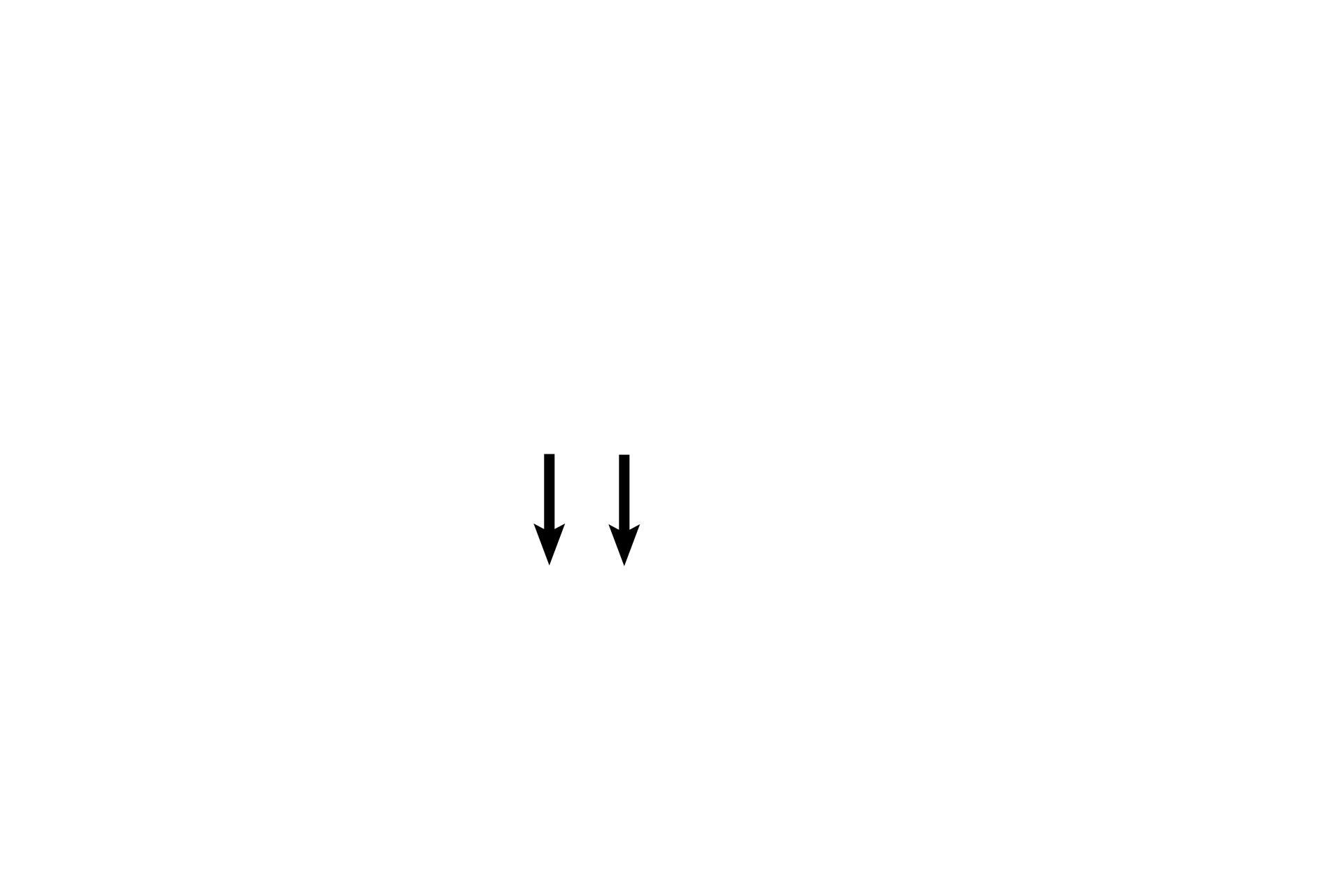
CN VIII >
Cranial nerve VIII innervates the hair cells. Peripheral axons (blue arrows) of this nerve pass medially from the hair cells through the osseous spiral lamina (black arrows) to the spiral ganglion, where their bipolar nerve cell bodies are located. Central processes of these neurons form the cochlear division of the nerve.
Stria vascularis >
The stria vascularis, an epithelium located on the outer wall of the cochlear duct, is unique in that it is the only vascularized epithelium in mammals. The stria vascularis, along with related cells in the maculae and cristae ampullares, produces endolymph.