
Overview: Innervation
The myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus lies between the layers of the muscularis externa throughout the tubular digestive system, providing autonomic innervation to the smooth muscle of muscularis externa. The plexus is a network of unmyelinated axons and ganglia, whose large neuronal cell bodies give rise to the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the plexus. Trichrome stain, 1000x
Muscularis externa
The myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus lies between the layers of the muscularis externa throughout the tubular digestive system, providing autonomic innervation to the smooth muscle of muscularis externa. The plexus is a network of unmyelinated axons and ganglia, whose large neuronal cell bodies give rise to the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the plexus. Trichrome stain, 1000x
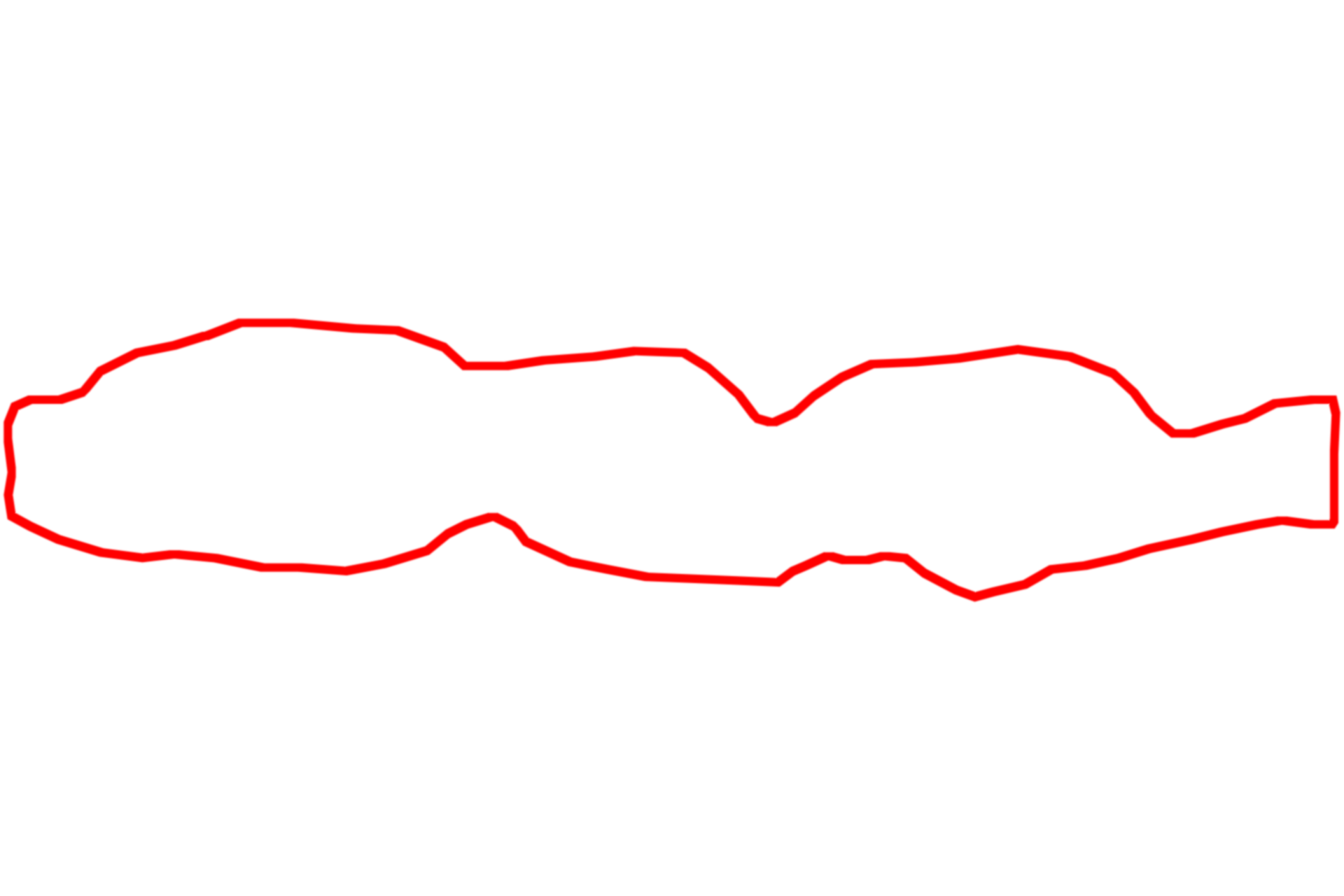
- Myenteric (Auerbach's) plexus
The myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus lies between the layers of the muscularis externa throughout the tubular digestive system, providing autonomic innervation to the smooth muscle of muscularis externa. The plexus is a network of unmyelinated axons and ganglia, whose large neuronal cell bodies give rise to the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the plexus. Trichrome stain, 1000x
- Neuronal cell bodies
The myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus lies between the layers of the muscularis externa throughout the tubular digestive system, providing autonomic innervation to the smooth muscle of muscularis externa. The plexus is a network of unmyelinated axons and ganglia, whose large neuronal cell bodies give rise to the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the plexus. Trichrome stain, 1000x
- Peripheral nerves
The myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus lies between the layers of the muscularis externa throughout the tubular digestive system, providing autonomic innervation to the smooth muscle of muscularis externa. The plexus is a network of unmyelinated axons and ganglia, whose large neuronal cell bodies give rise to the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the plexus. Trichrome stain, 1000x
- Supporting cells
The myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus lies between the layers of the muscularis externa throughout the tubular digestive system, providing autonomic innervation to the smooth muscle of muscularis externa. The plexus is a network of unmyelinated axons and ganglia, whose large neuronal cell bodies give rise to the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the plexus. Trichrome stain, 1000x