
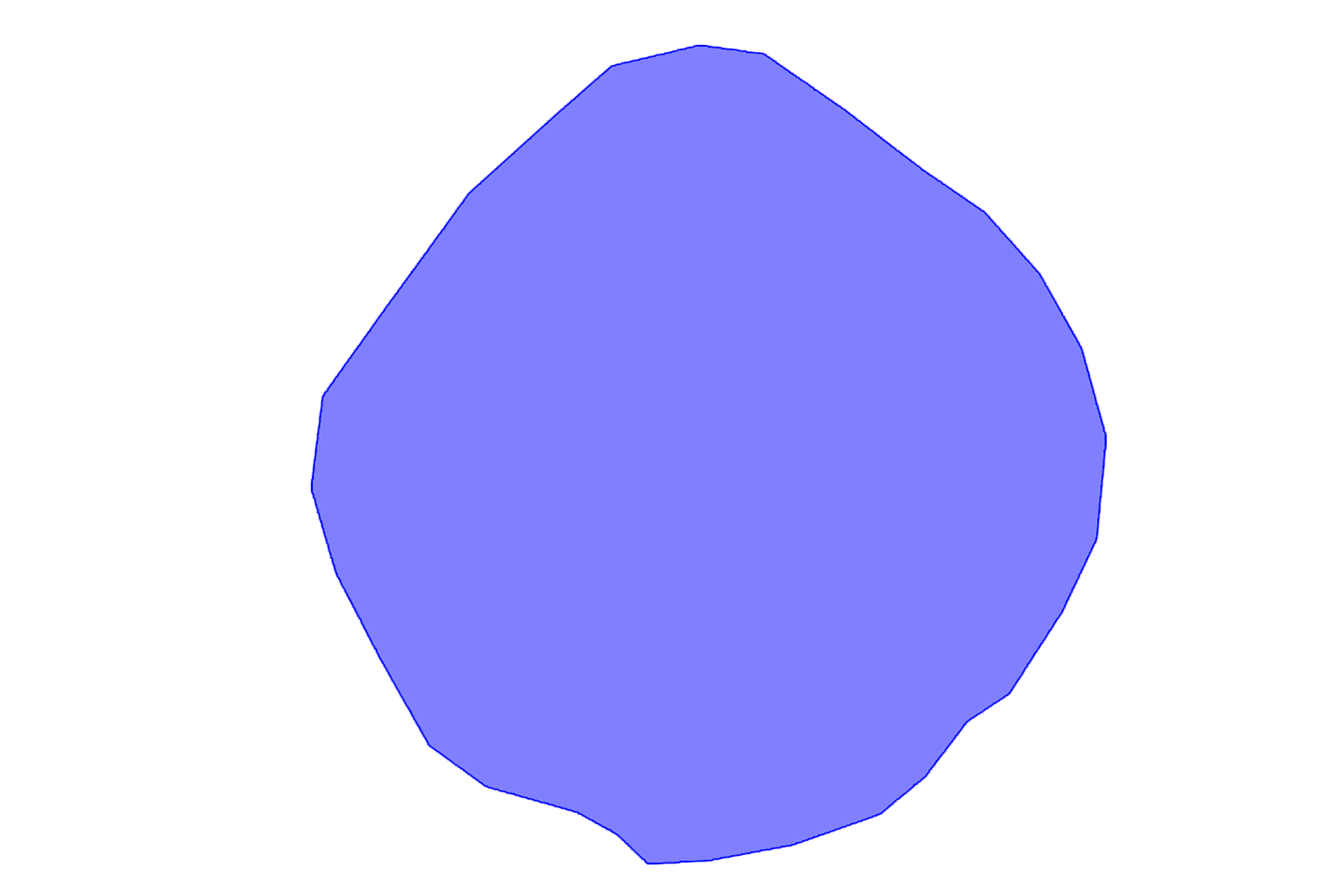
Cap stage of tooth development
This image shows the cap stage of tooth development, during which the concavity of the enamel organ deepens as histodifferentiation progresses. The central region of the enamel organ contains ectodermal cells that will eventually form the stellate reticulum during the bell stage. 100x
Tooth germ >
The tooth germ is first identifiable at the cap stage of tooth development (histodifferentiation). The tooth germ consists of all the identifiable ectoderm and ectomesenchyme tissues that form the tooth: inner and outer enamel epithelia, (ectoderm), dental papillae and the dental follicle (ectomesenchyme).
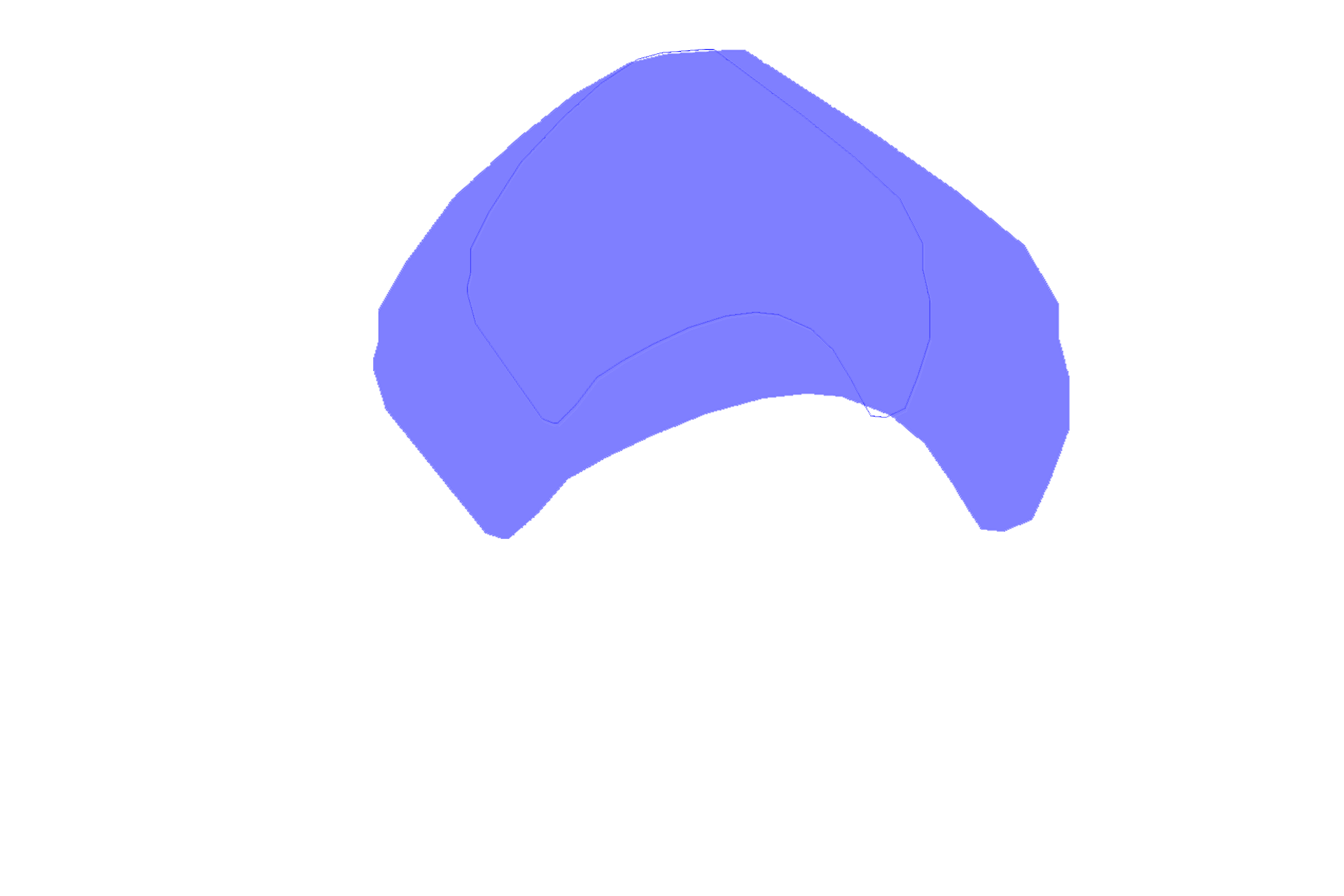

Enamel organ >
The enamel organ is the structure formed from ectoderm during the cap stage of tooth development. The enamel organ contains both the inner enamel epithelium and the outer enamel epithelium.
- Inner enamel epithelium >
The columnar ectodermal cells on the inner aspect of the enamel organ are the inner enamel epithelium. These cells will differentiate into ameloblasts that deposit enamel.
- Outer enamel epithelium >
The cuboidal ectodermal cells on the outer aspect of the enamel organ are the outer enamel epithelium.
- Cervical loop >
The location where the inner enamel epithelium and outer enamel epithelium meet is the cervical loop. This structure will elongate during tooth development to form the Hertwig’s epithelium root sheath.
Dental papilla >
The dental papilla is formed of ectomesenchymal cells beneath the enamel organ and will form the majority of the dental pulp.
Dental follicle >
The dental follicle, also called the dental sac, surrounds the enamel organ and dental papilla in the apical regions of the tooth germ. The follicle differentiates into cementoblasts that deposit cementum, fibroblasts that deposit collagen fibers as part of the periodontal ligament, and osteoblasts that deposit alveolar bone.

Developing alveolar bone >
Alveolar bone > Alveolar bone lines the tooth socket (alveolus) and anchors the tooth via the periodontal ligament.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS