
Tongue
The dorsum of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium with filiform, fungiform, and circumvallate (not seen here) papillae. The ventral surface of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous moist epithelium (lining mucosa). The core of the tongue contains intrinsic and extrinsic skeletal muscles and connective tissue. 10x
Dorsum of the tongue
The dorsum of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium with filiform, fungiform, and circumvallate (not seen here) papillae. The ventral surface of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous moist epithelium (lining mucosa). The core of the tongue contains intrinsic and extrinsic skeletal muscles and connective tissue. 10x
Ventral surface
The dorsum of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium with filiform, fungiform, and circumvallate (not seen here) papillae. The ventral surface of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous moist epithelium (lining mucosa). The core of the tongue contains intrinsic and extrinsic skeletal muscles and connective tissue. 10x

Filiform papillae
The dorsum of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium with filiform, fungiform, and circumvallate (not seen here) papillae. The ventral surface of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous moist epithelium (lining mucosa). The core of the tongue contains intrinsic and extrinsic skeletal muscles and connective tissue. 10x
Fungiform papillae
The dorsum of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium with filiform, fungiform, and circumvallate (not seen here) papillae. The ventral surface of the tongue is covered by a stratified squamous moist epithelium (lining mucosa). The core of the tongue contains intrinsic and extrinsic skeletal muscles and connective tissue. 10x
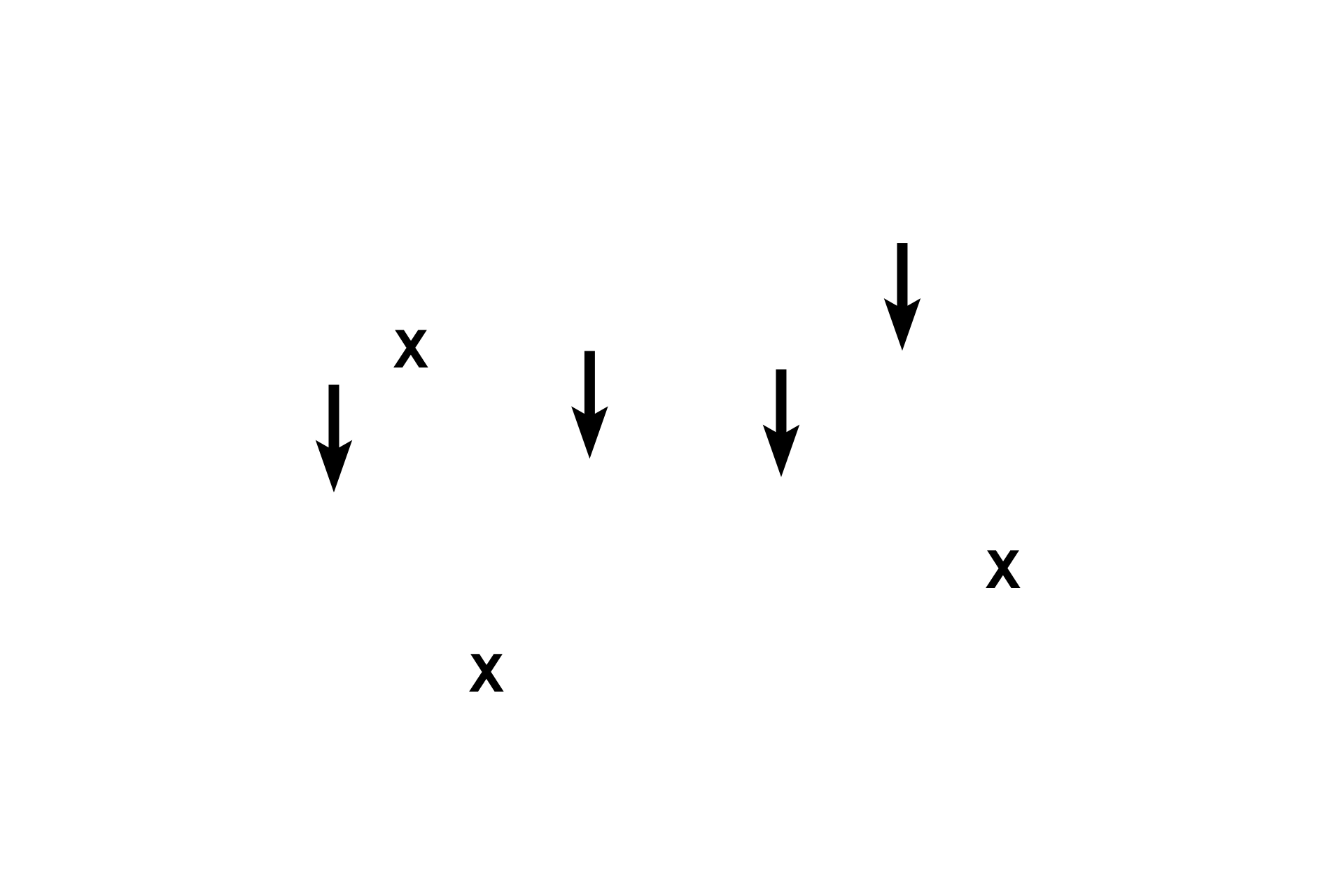
Skeletal muscle >
Motility of the tongue is controlled by extrinsic and intrinsic skeletal muscles. The intrinsic muscles, seen here, originate within and insert into the tongue; they change the shape of the tongue. Muscle fibers are arranged in criss-crossing fascicles, seen in longitudinal (arrows) and cross section (X’s).