
Parotid gland
The coalescing interlobular ducts seen here exit into the surrounding interlobular connective tissue. These larger interlobular ducts are lined by a stratified epithelium, initially stratified cuboidal, that eventually transitions into stratified columnar. 300x
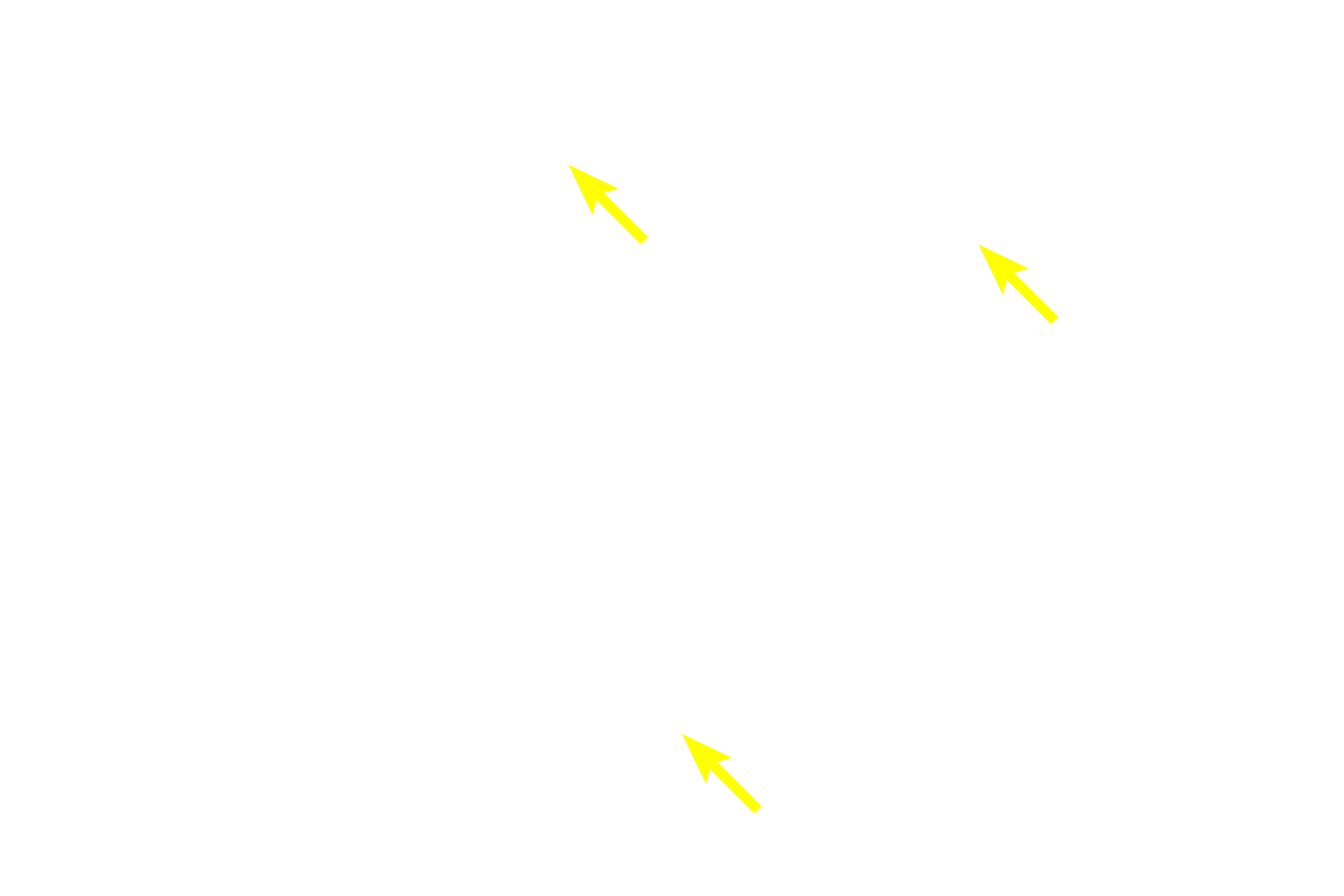
Serous acini
The coalescing interlobular ducts seen here exit into the surrounding interlobular connective tissue. These larger interlobular ducts are lined by a stratified epithelium, initially stratified cuboidal, that eventually transitions into stratified columnar. 300x

Intercalated duct
The coalescing interlobular ducts seen here exit into the surrounding interlobular connective tissue. These larger interlobular ducts are lined by a stratified epithelium, initially stratified cuboidal, that eventually transitions into stratified columnar. 300x

Intralobular (striated) ducts
The coalescing interlobular ducts seen here exit into the surrounding interlobular connective tissue. These larger interlobular ducts are lined by a stratified epithelium, initially stratified cuboidal, that eventually transitions into stratified columnar. 300x
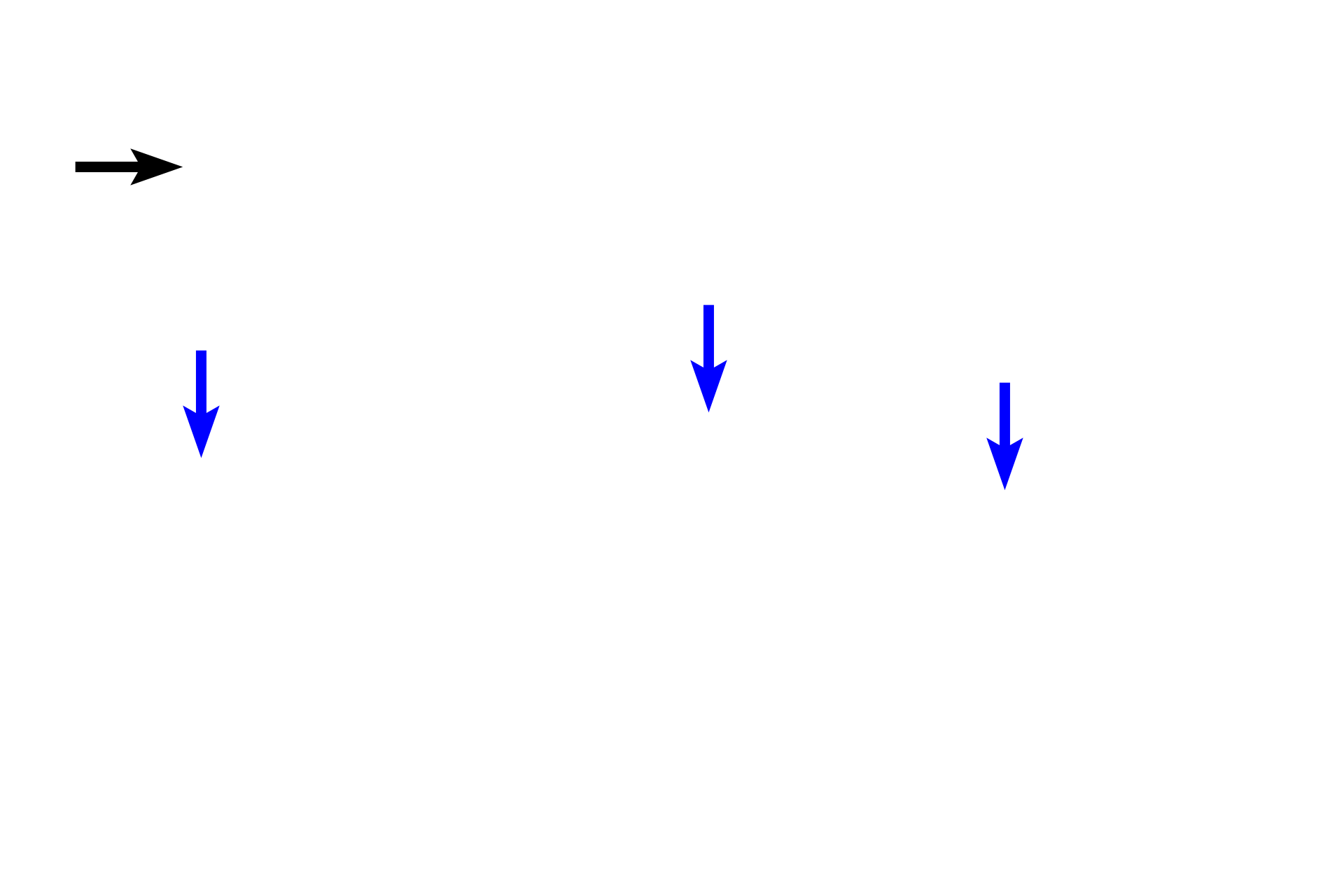
Interlobular ducts >
The smaller interlobular ducts are lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium (blue arrows), which becomes stratified columnar as the duct enlarges (black arrow).

Interlobular connective tissue
The smaller interlobular ducts are lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium (blue arrows), which becomes stratified columnar as the duct enlarges (black arrow).
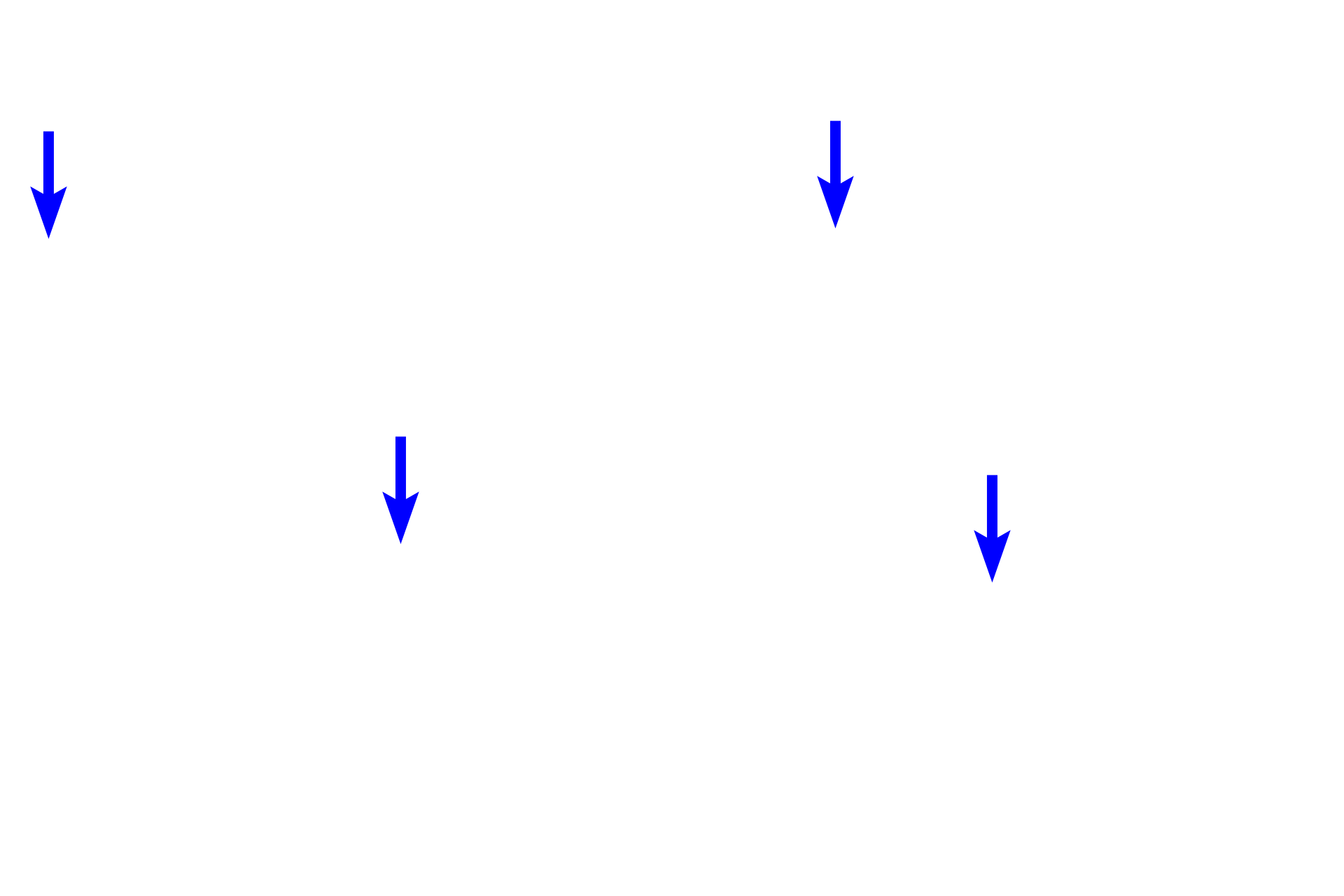
Blood vessels
The smaller interlobular ducts are lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium (blue arrows), which becomes stratified columnar as the duct enlarges (black arrow).
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS