
Venule (pericytic venule)
Post-capillary venules often possess pericytes, multipotential cells with extensive cytoplasmic extensions that extend around the venule. Pericytes have contractile properties and form gap junctions with endothelial cells, with which they share a basal lamina. Pericytes also have additional roles in vessel growth and maintenance. 2500x
Endothelial cells
Post-capillary venules often possess pericytes, multipotential cells with extensive cytoplasmic extensions that extend around the venule. Pericytes have contractile properties and form gap junctions with endothelial cells, with which they share a basal lamina. Pericytes also have additional roles in vessel growth and maintenance. 2500x
Pericyte nucleus
Post-capillary venules often possess pericytes, multipotential cells with extensive cytoplasmic extensions that extend around the venule. Pericytes have contractile properties and form gap junctions with endothelial cells, with which they share a basal lamina. Pericytes also have additional roles in vessel growth and maintenance. 2500x
Pericyte processes
Post-capillary venules often possess pericytes, multipotential cells with extensive cytoplasmic extensions that extend around the venule. Pericytes have contractile properties and form gap junctions with endothelial cells, with which they share a basal lamina. Pericytes also have additional roles in vessel growth and maintenance. 2500x
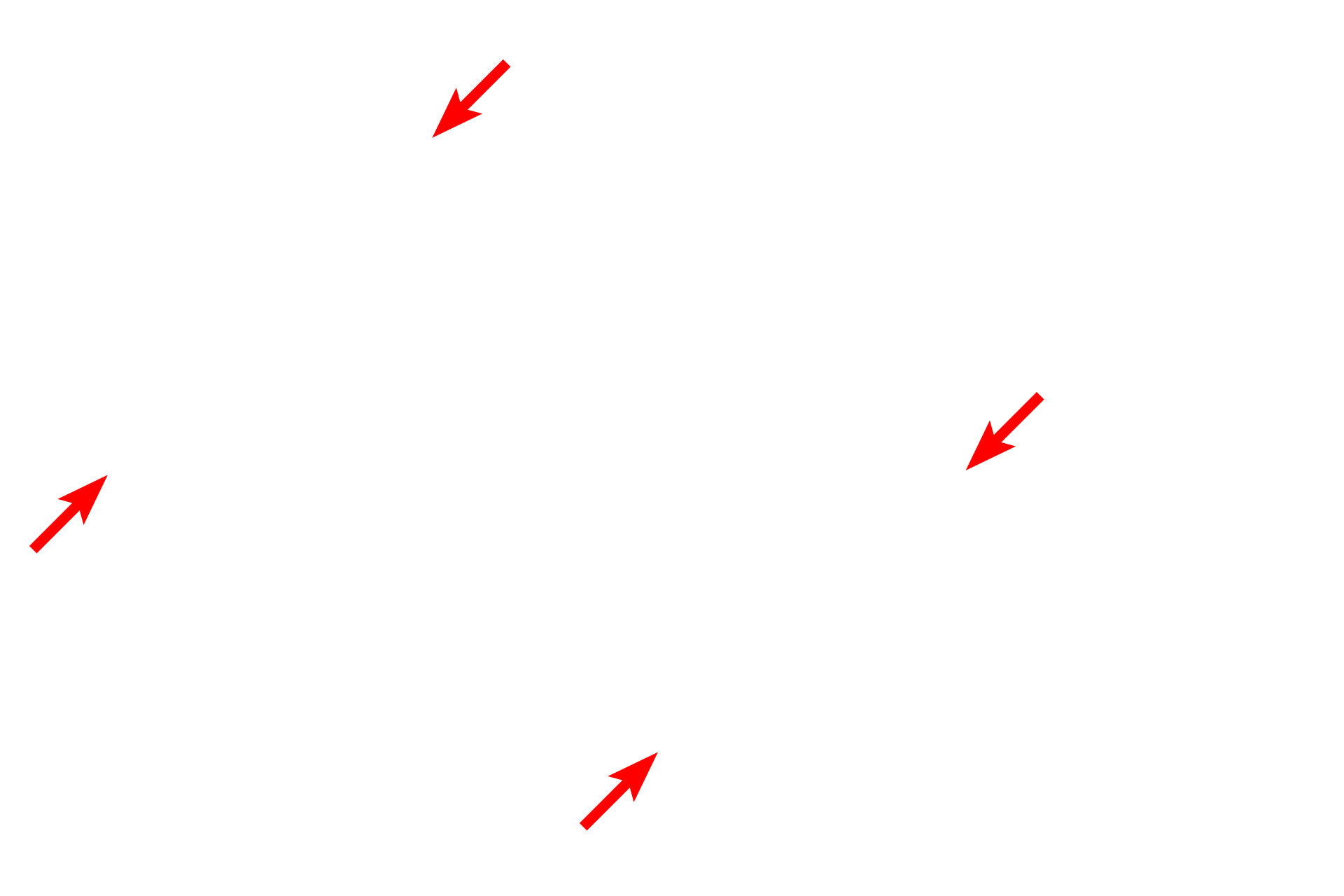

Basal lamina
Post-capillary venules often possess pericytes, multipotential cells with extensive cytoplasmic extensions that extend around the venule. Pericytes have contractile properties and form gap junctions with endothelial cells, with which they share a basal lamina. Pericytes also have additional roles in vessel growth and maintenance. 2500x