
Heart
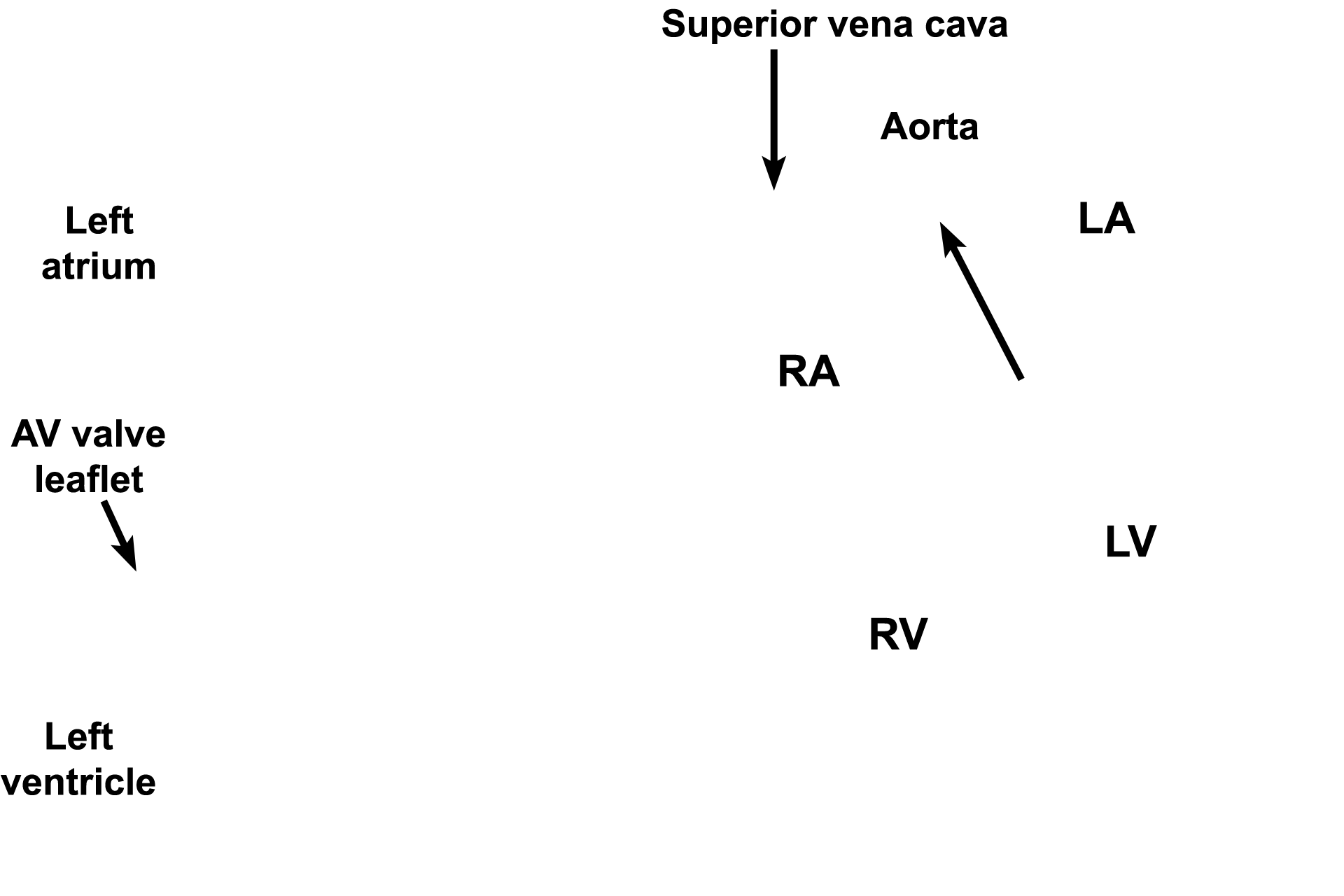
A micrograph and an illustration demonstrate the three layers of the heart; the rectangle on the illustration indicates the region shown in the micrograph. The endocardium, the innermost lining of the heart, contacts the blood. The myocardium is the middle, muscular layer of the heart. The outermost layer of the heart is a serous membrane, the epicardium (visceral pericardium). 10x
Components
A micrograph and an illustration demonstrate the three layers of the heart; the rectangle on the illustration indicates the region shown in the micrograph. The endocardium, the innermost lining of the heart, contacts the blood. The myocardium is the middle, muscular layer of the heart. The outermost layer of the heart is a serous membrane, the epicardium (visceral pericardium). 10x
Endocardium
A micrograph and an illustration demonstrate the three layers of the heart; the rectangle on the illustration indicates the region shown in the micrograph. The endocardium, the innermost lining of the heart, contacts the blood. The myocardium is the middle, muscular layer of the heart. The outermost layer of the heart is a serous membrane, the epicardium (visceral pericardium). 10x
Myocardium
A micrograph and an illustration demonstrate the three layers of the heart; the rectangle on the illustration indicates the region shown in the micrograph. The endocardium, the innermost lining of the heart, contacts the blood. The myocardium is the middle, muscular layer of the heart. The outermost layer of the heart is a serous membrane, the epicardium (visceral pericardium). 10x
Epicardium
A micrograph and an illustration demonstrate the three layers of the heart; the rectangle on the illustration indicates the region shown in the micrograph. The endocardium, the innermost lining of the heart, contacts the blood. The myocardium is the middle, muscular layer of the heart. The outermost layer of the heart is a serous membrane, the epicardium (visceral pericardium). 10x
Cardiac skeleton >
The cardiac skeleton is composed primarily of dense connective tissue, providing a framework for the attachment of cardiac muscle fibers, support for heart valves and electrical insulation between the atria and ventricles. The cardiac skeleton consists of the annuli fibrosi (annular rings, oval) that surround each valve, two fibrous trigons (not shown) that connect the annuli and the membranous portion of the interventricular septum (arrow).

Conducting system >
The conducting system, modified cardiac muscle fibers, coordinates and regulates heartbeat. This system consists of a sinoatrial node (pacemaker), fibers spreading through the atria, AV node located in lower part of the interatrial septum, AV bundle (green arrow) in the interventricular septum, and two bundle branches (black arrows) continuing as Purkinje fibers to innervate ventricular myocardium.
