
Section planes
Histological sections are two-dimensional slices of a three-dimensional piece of tissue. Thus, in the microscope, the appearance of a tissue and its component structures will depend on the angle of the section plane. This image shows skeletal muscle cells, which are long, uniformly cylindrical structures, sectioned in cross and longitudinal planes. 400x
Cross sections >
Cross sections, also called transverse sections, pass in a plane that is perpendicular to the long axis of a structure. Examples of skeletal muscle fibers cut in cross section are indicated.
Longitudinal sections >
Longitudinal sections pass in a plane that is parallel to the long axis of a structure. Examples of skeletal muscle fibers cut in longitudinal section are indicated.
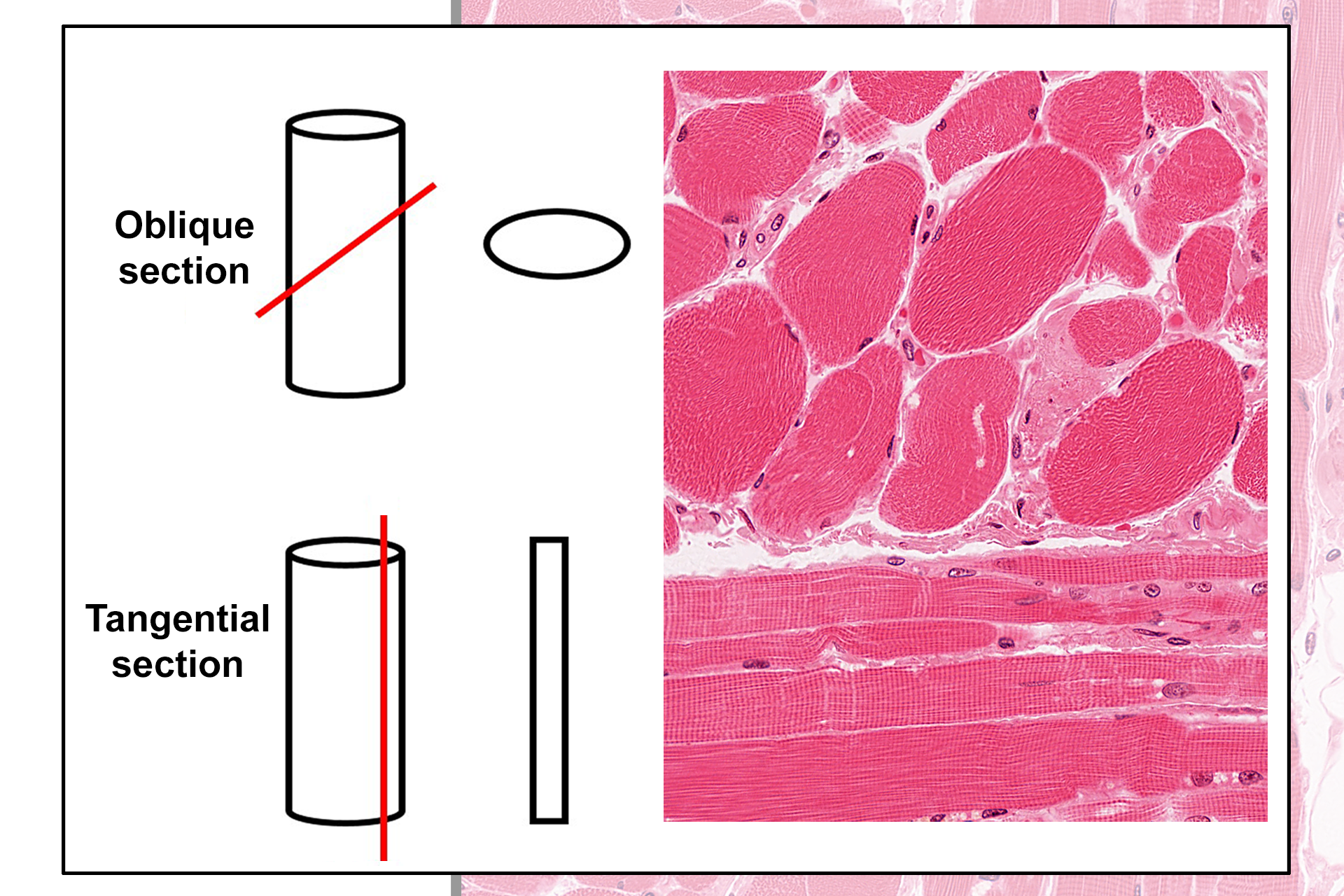
Additional section planes >
While structures are often depicted in either cross or longitudinal section, most tissue components are sectioned either obliquely or tangentially, thus complicating the interpretation of their three-dimensional shape.
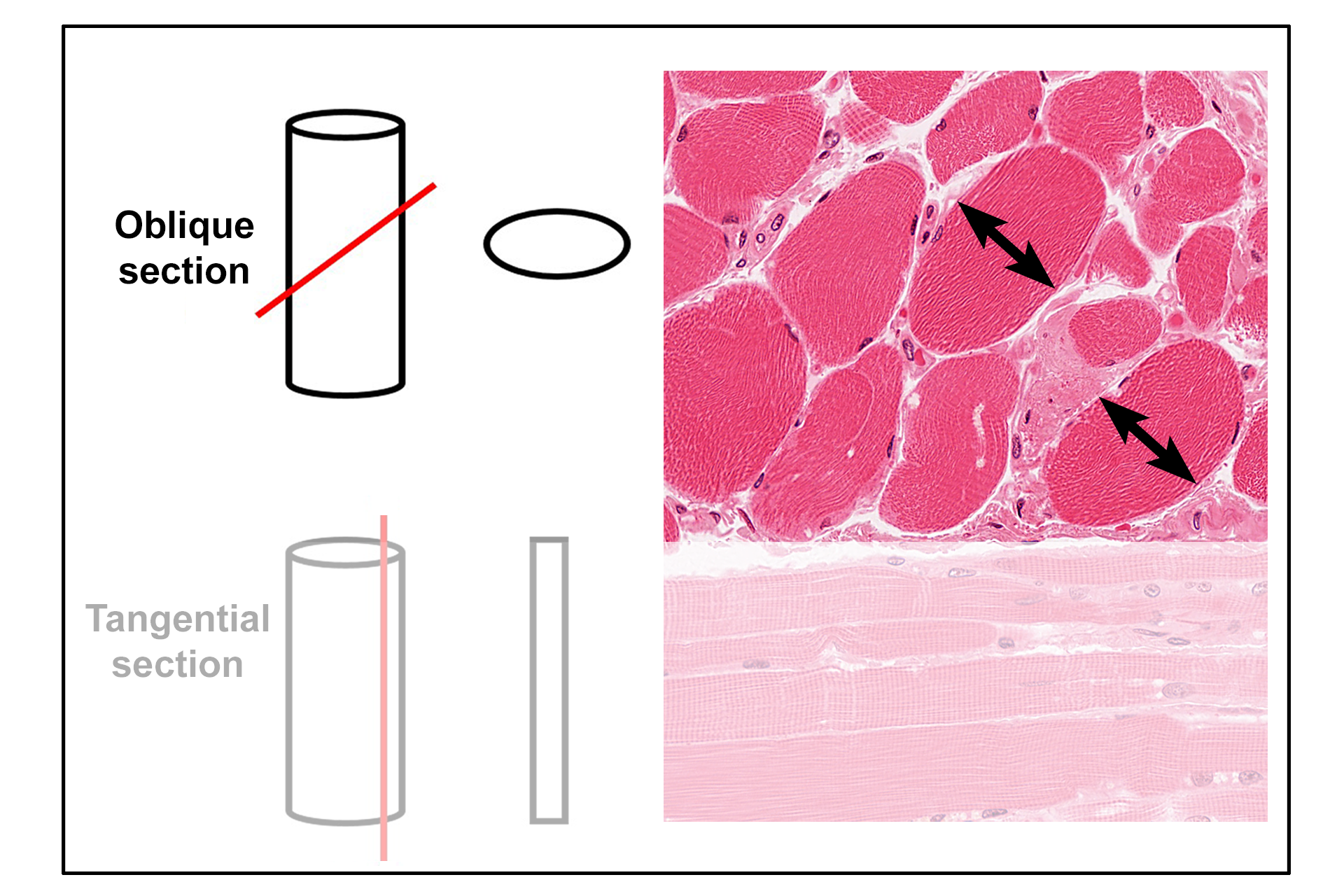
- Oblique section >
An oblique section is a slice through a structure in a plane that is other than parallel or perpendicular to the longest axis of the structure. In this example, a cylindrical structure will appear oval in section. Examples of obliquely-sectioned skeletal muscle fibers are indicated.
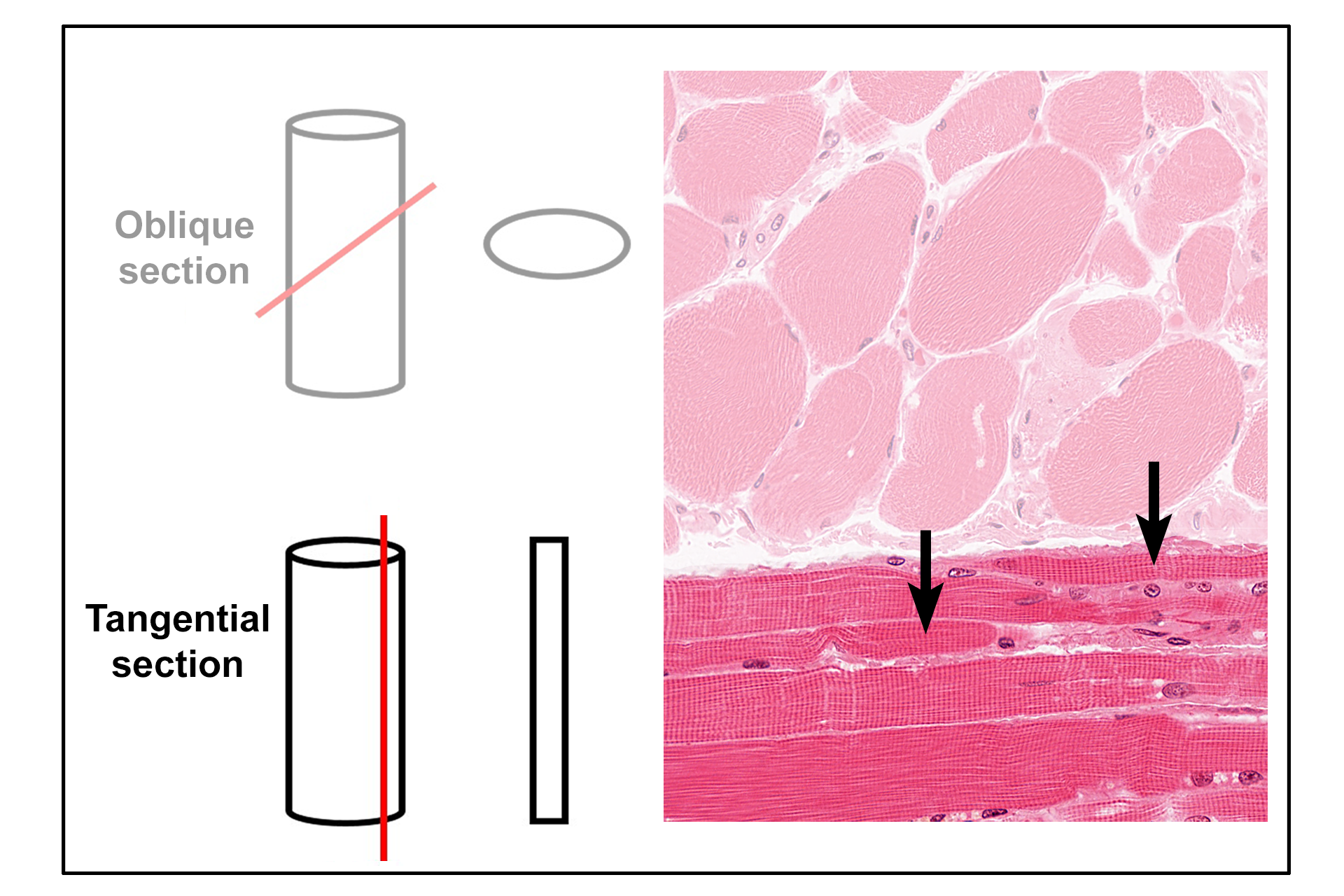
- Tangential section >
A tangential section is a slice that only superficially cuts through the surface of a structure. In this example, a broad cylindrical structure will appear much thinner in section. Examples of tangentially-sectioned skeletal muscle fibers are indicated.