
Intermediate filaments and microtubules
This electron micrograph shows myelinated axons cut in cross section. The hollow microtubules and the intermediate filaments are especially prominent in axons, where they provide intracellular transport and support, respectively. In nerve cells, intermediate filaments are called neurofilaments. Intermediate filaments in a non-neuronal cells are also visible. Brain 50,000x
Intermediate filaments >
In neurons, intermediate filaments are called neurofilaments (red arrows). These filaments are rigid and very stable, providing support, particularly in longer, larger axons. Intermediate filaments are also present in supporting astrocytic glial cells; a group of these filaments is outlined in blue. These filaments, called glial filaments, also provide support.
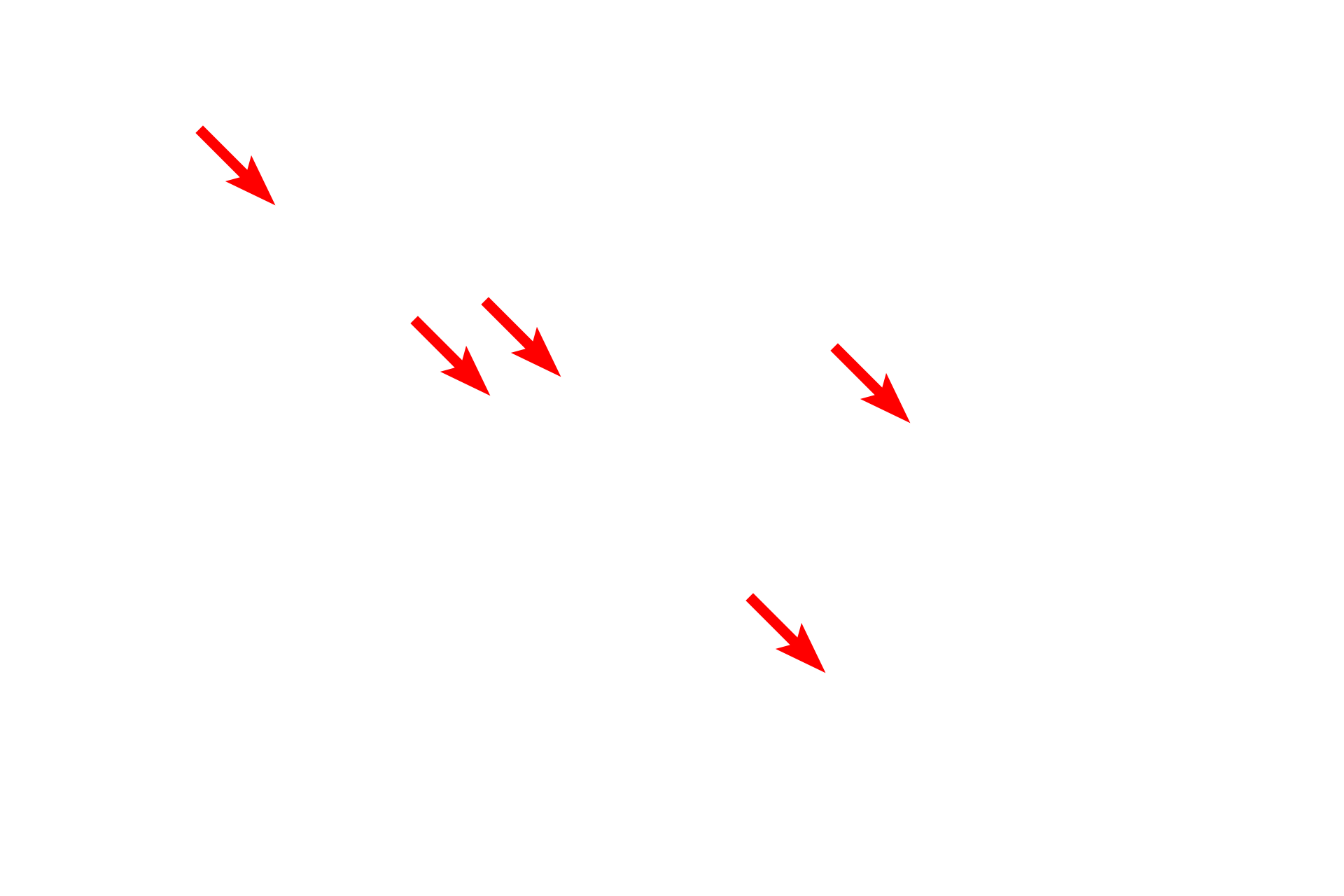

Microtubules
This electron micrograph shows myelinated axons cut in cross section. The hollow microtubules and the intermediate filaments are especially prominent in axons, where they provide intracellular transport and support, respectively. In nerve cells, intermediate filaments are called neurofilaments. Intermediate filaments in a non-neuronal cells are also visible. Brain 50,000x
Axon
This electron micrograph shows myelinated axons cut in cross section. The hollow microtubules and the intermediate filaments are especially prominent in axons, where they provide intracellular transport and support, respectively. In nerve cells, intermediate filaments are called neurofilaments. Intermediate filaments in a non-neuronal cells are also visible. Brain 50,000x
Myelin
This electron micrograph shows myelinated axons cut in cross section. The hollow microtubules and the intermediate filaments are especially prominent in axons, where they provide intracellular transport and support, respectively. In nerve cells, intermediate filaments are called neurofilaments. Intermediate filaments in a non-neuronal cells are also visible. Brain 50,000x
Mitochondria
This electron micrograph shows myelinated axons cut in cross section. The hollow microtubules and the intermediate filaments are especially prominent in axons, where they provide intracellular transport and support, respectively. In nerve cells, intermediate filaments are called neurofilaments. Intermediate filaments in a non-neuronal cells are also visible. Brain 50,000x
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS