
Interphase
Interphase accounts for about 95% of the cell cycle. It consists of an initial a period of cell growth (G1), followed by a synthesis phase (S) during which DNA and centriole replication occurs, and lastly by a second growth phase (G2) just prior to mitosis. This diagrammatic illustration of the G1 stage, depicts the chromosomes in the condensed state; they will not actually condense until prophase of mitosis.

Nucleus
Interphase accounts for about 95% of the cell cycle. It consists of an initial a period of cell growth (G1), followed by a synthesis phase (S) during which DNA and centriole replication occurs, and lastly by a second growth phase (G2) just prior to mitosis. This diagrammatic illustration of the G1 stage, depicts the chromosomes in the condensed state; they will not actually condense until prophase of mitosis.

- Nuclear envelope
Interphase accounts for about 95% of the cell cycle. It consists of an initial a period of cell growth (G1), followed by a synthesis phase (S) during which DNA and centriole replication occurs, and lastly by a second growth phase (G2) just prior to mitosis. This diagrammatic illustration of the G1 stage, depicts the chromosomes in the condensed state; they will not actually condense until prophase of mitosis.

- Nucleolus
Interphase accounts for about 95% of the cell cycle. It consists of an initial a period of cell growth (G1), followed by a synthesis phase (S) during which DNA and centriole replication occurs, and lastly by a second growth phase (G2) just prior to mitosis. This diagrammatic illustration of the G1 stage, depicts the chromosomes in the condensed state; they will not actually condense until prophase of mitosis.
- Chromosomes >
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes, XX or XY. The full complement of 23 pairs of chromosomes is designated 2N. In this diagram only a single homologous pair is shown, one in red and the other in blue.
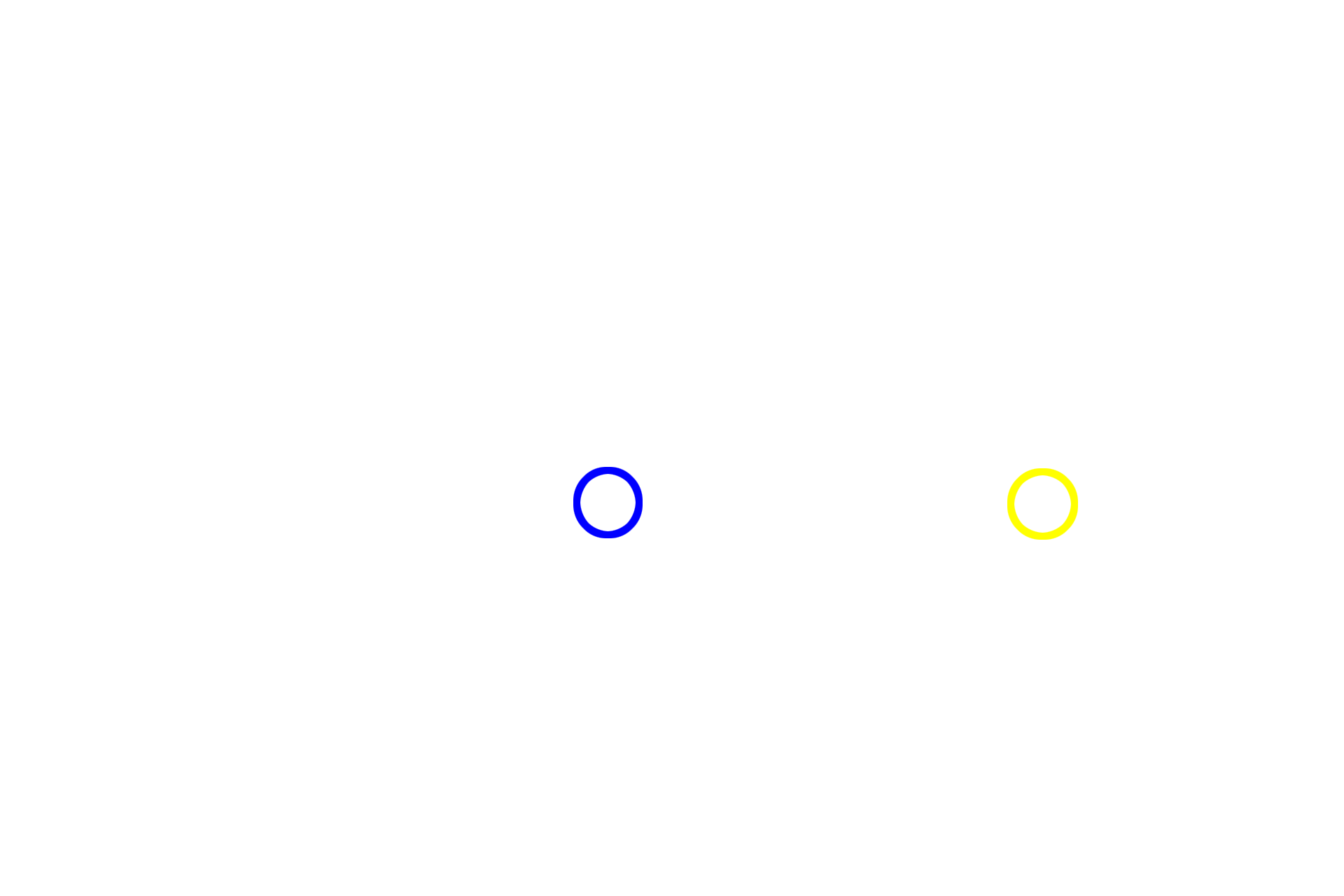
Centrosomes >
The centrosome, the microtubule organizing center of the cell, consists of two centrioles (diplosome) oriented at right angles that are surrounded by the centrosome matrix. During S-phase, the centrosome duplicates; during prophase, each centrosome, with duplicated centrioles, moves to opposite poles of the cell.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS