
Thymus: cortex
Lymphoblasts from the bone marrow migrate to the thymic cortex, where they divide and differentiate to form T lymphocytes. These newly formed, small T lymphocytes (thymocytes) migrate to the medulla, where they enter blood or lymph systems for export to T-dependent areas of other lymphoid organs. 1000x
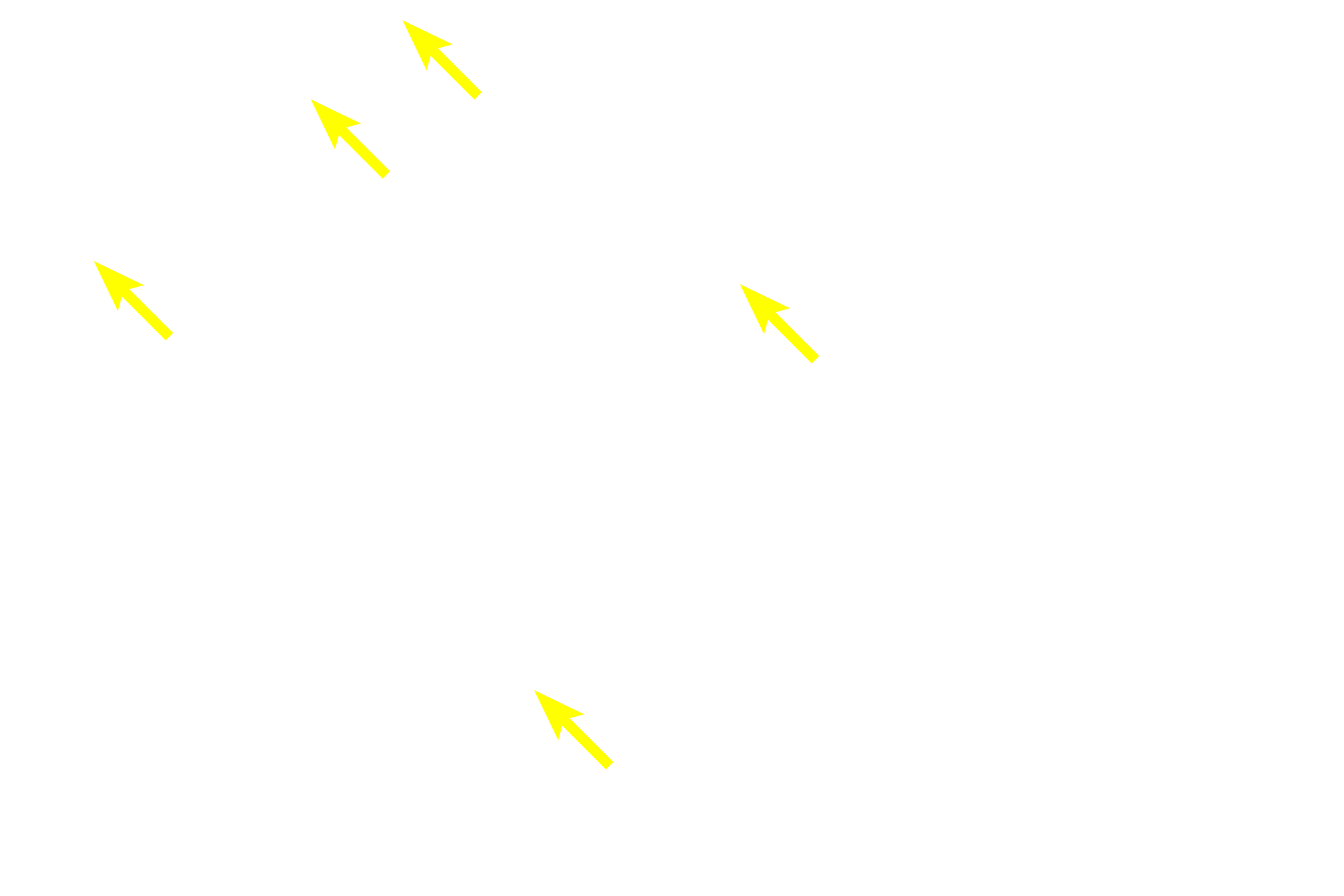
Lymphoblasts >
Lymphoblasts have spherical nuclei that are larger than those of the thymocytes they form. Lymphoblasts are derived from the bone marrow and migrate into the thymus to form T lymphocytes.
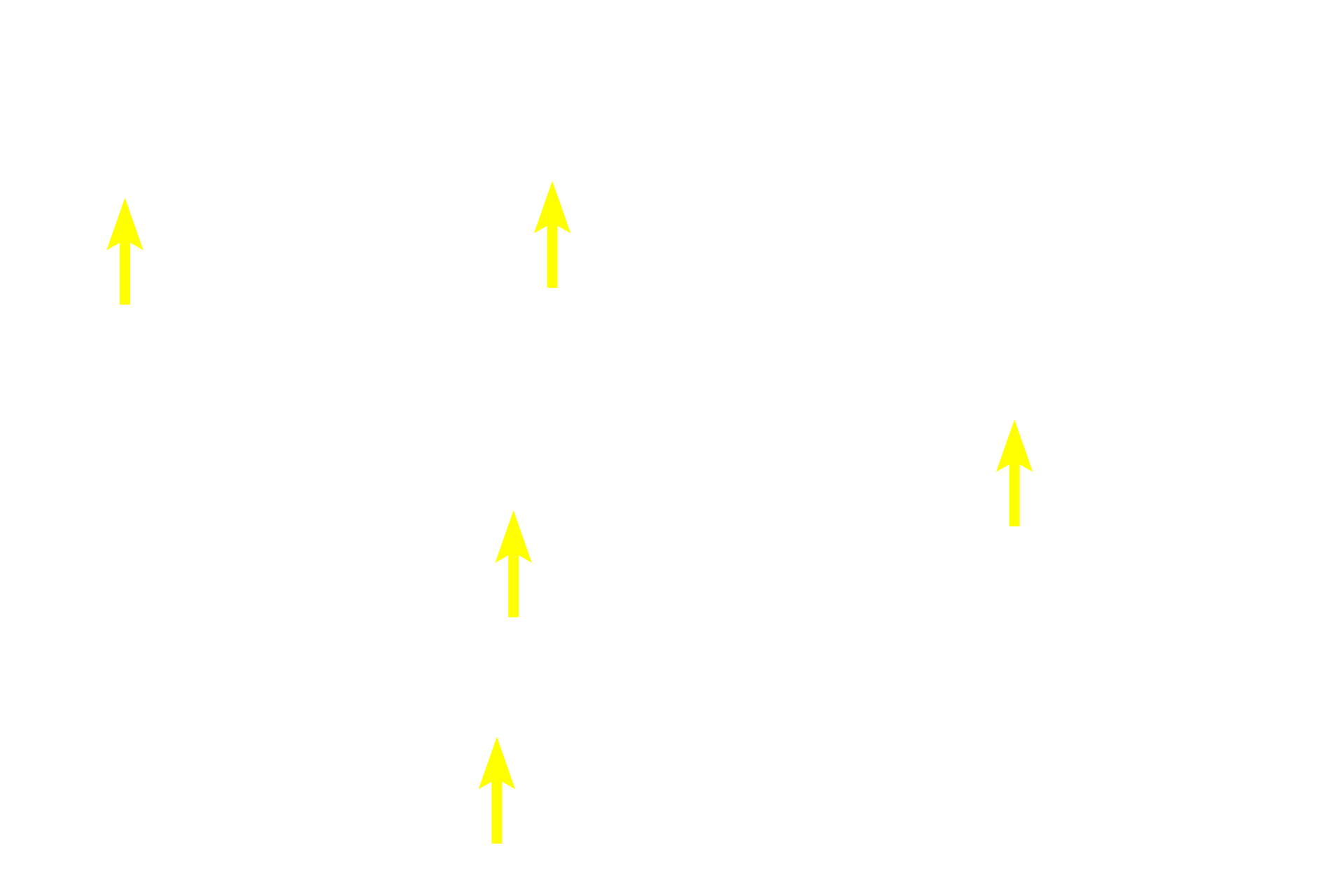
Thymocytes >
Thymic lymphocytes (thymocytes) have small, heterochromatic nuclei and little cytoplasm. The thymic epithelial cells establish mircroenvironments in which T cell maturation and selection occur. They also provide signals for this T cell differentiation.
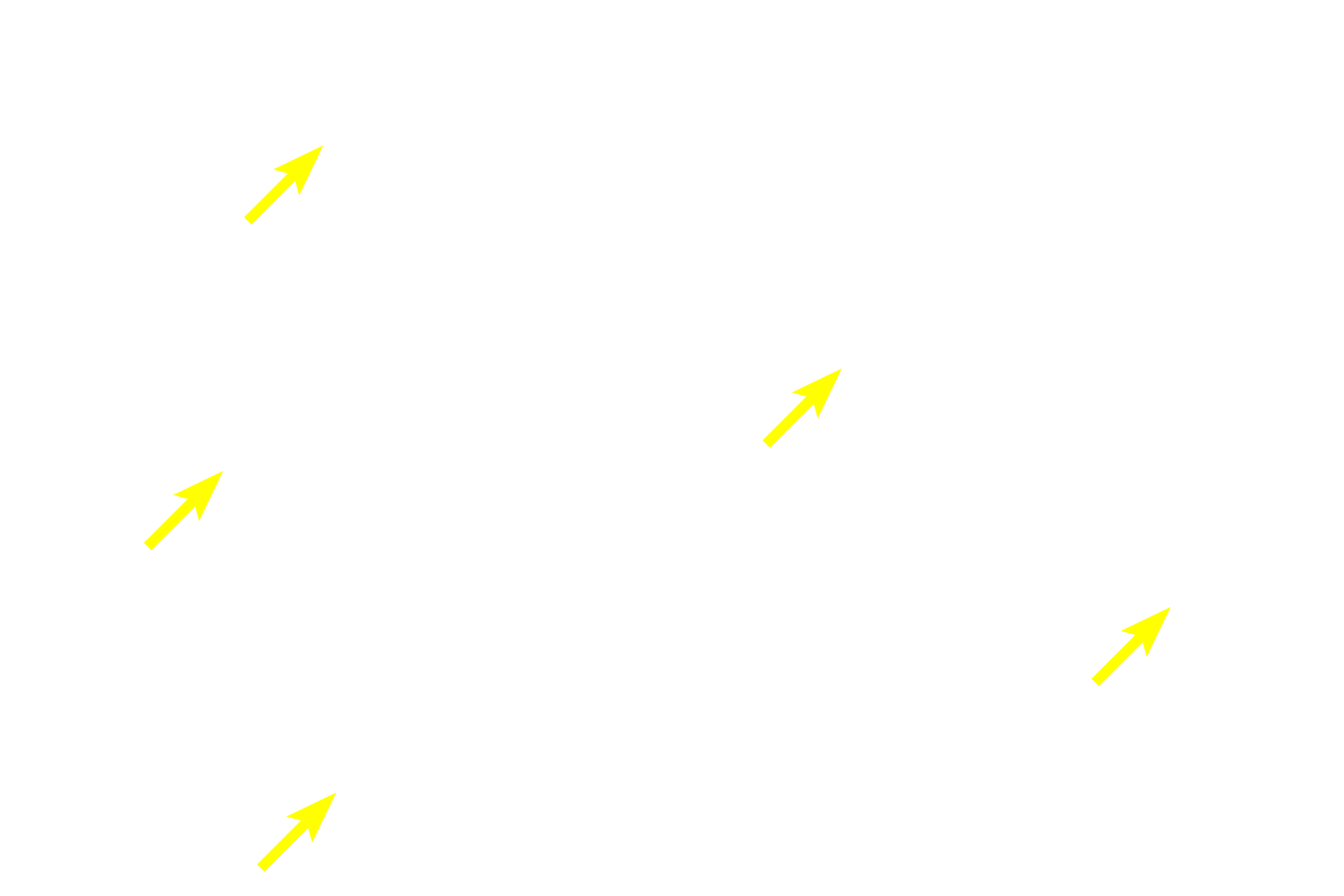
Epithelial reticular cells >
The stromal meshwork supporting the thymus is formed by cells of epithelial, rather than connective tissue origin and, therefore, are called epithelial reticular cells. The nuclei of these cells are large, spherical and euchromatic. No extracellular fibers are present.
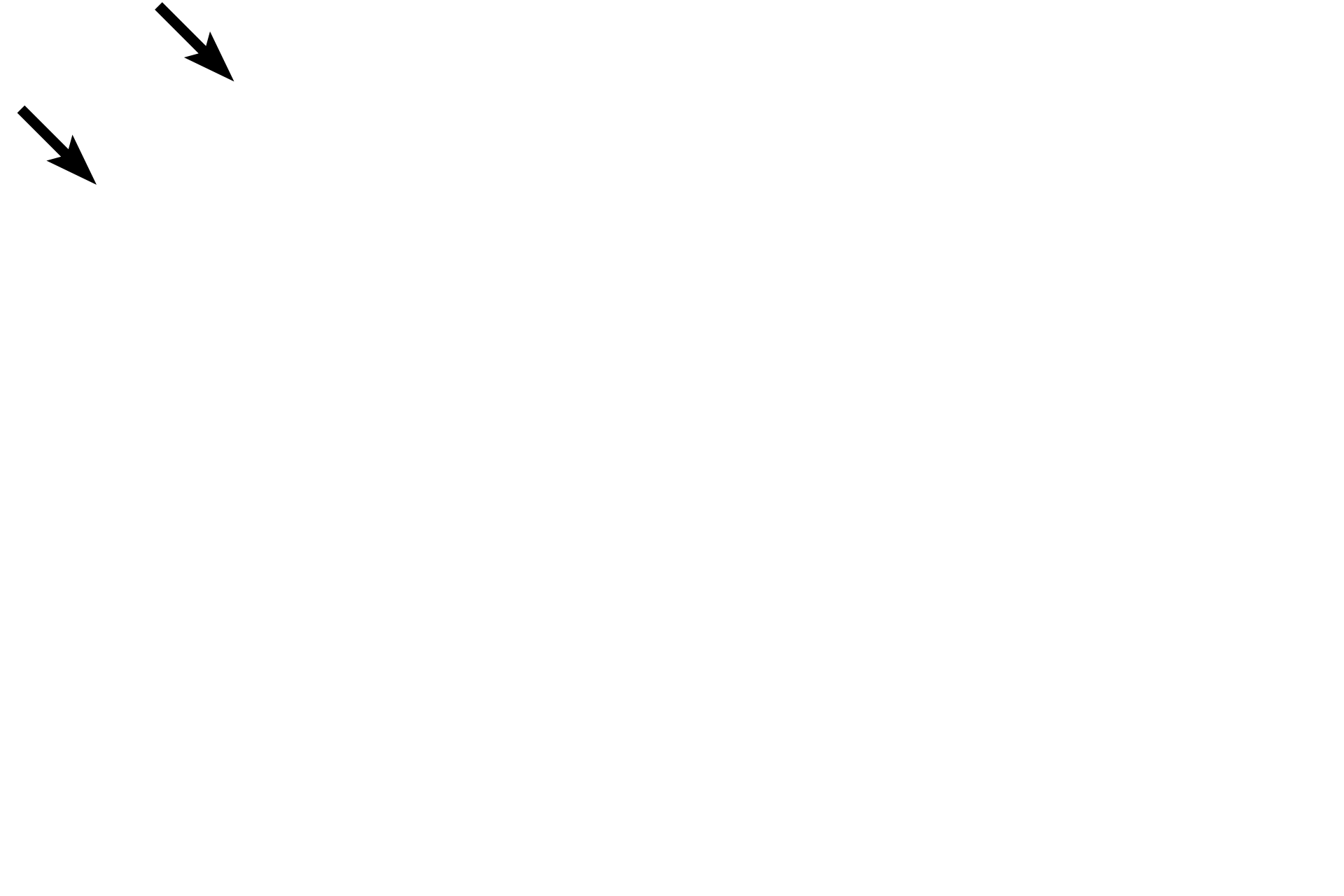
Capsule >
A thin capsule surrounds the thymus.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS