
Overview: Lymphoid organs and tissue
The immune system protects the body against foreign antigens and infectious agents. Primary components of the immune system produce cells that seed secondary lymphoid structures. Secondary lymphoid components filter body fluids and respond by producing antibodies and cells, which will neutralize or inactivate foreign material and destroy foreign microorganisms or cells.
Primary components >
Primary lymphoid components of the immune system consist of the thymus and bone marrow. These components produce T lymphocytes (thymus) and B lymphocytes (bone marrow) that seed secondary lymphoid structures. Primary lymphoid components do not directly participate in the immune response.
- Thymus >
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ and, therefore, is not involved directly with defending against foreign antigens and infectious agents. This organ produces T lymphocytes that migrate from the thymus to seed other lymphoid structures, such as lymph node and spleen. T lymphocytes are involved with cell-mediated immunity by recognizing and responding to foreign antigens.
- Bone marrow >
Bone marrow is the second primary lymphoid tissue. Bone marrow produces B lymphocytes that migrate to other lymphoid structures, such as lymphoid nodules, lymph node and spleen, and are involved with production of humoral antibodies. Bone marrow also produces other types of white blood cells that enter the connective tissues to neutralize and destroy foreign material.
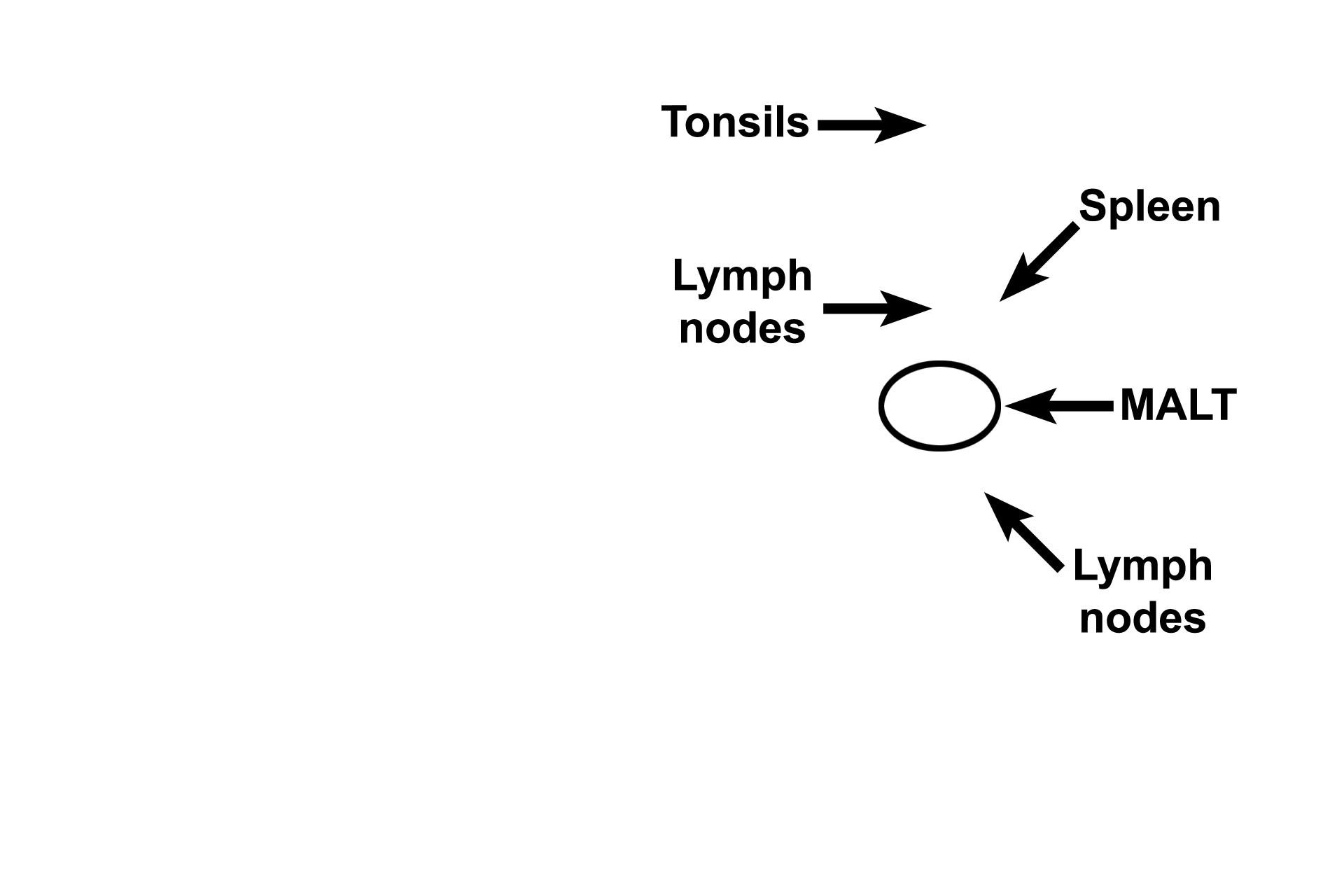
Secondary components >
Secondary lymphoid components of the immune system consist of lymphoid tissue located in the mucosal lamina propria (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, MALT), tonsils, lymph nodes and spleen.

- MALT >
Any organ system opening to the exterior (GI, respiratory, urinary, reproductive) has lymphoid tissue (diffuse lymphoid tissue and lymphoid nodules) in mucosal lamina propria. These tissues, known as mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), filter tissue fluid percolating through lamina propria and respond by initiating an immune response.
-- Tonsils >
The three groups of tonsils (palatine, pharyngeal and lingual) form a ring of lymphoid tissue called “Waldeyer’s ring” around the entrances of the nasal and oral cavities into the pharynx. Tonsils are partially encapsulated aggregations of diffuse and nodular lymphoid tissues located in lamina propria. Tonsils filter tissue fluid and are part of MALT.
- Lymph nodes >
Tissue fluid filtered by MALT structures accumulates as lymph in lymph vessels, accompanied by lymphocytes from MALT. Located along these lymph vessels are lymph nodes that filter lymph and respond to the presence of any foreign agents carried in it.

- Spleen >
Lymph vessels, which drain lymph nodes, empty into the blood vascular system. The spleen, the largest lymphoid organ, filters this blood and reacts to any foreign agents it carries.
