
Modes of secretion: holocrine
Holocrine secretion involves the release of entire cells or their fragments from the secretory unit, as shown in this image of a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle. At the periphery of the acinus, cells proliferate and move toward the center, accumulating lipid as they mature, enlarge and degenerate. In this example of a sebaceous gland, lipid-filled cells either rupture their contents, sebum, or are shed as whole cells onto the hair shaft in a hair follicle. 400x

Acini
Holocrine secretion involves the release of entire cells or their fragments from the secretory unit, as shown in this image of a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle. At the periphery of the acinus, cells proliferate and move toward the center, accumulating lipid as they mature, enlarge and degenerate. In this example of a sebaceous gland, lipid-filled cells either rupture their contents, sebum, or are shed as whole cells onto the hair shaft in a hair follicle. 400x
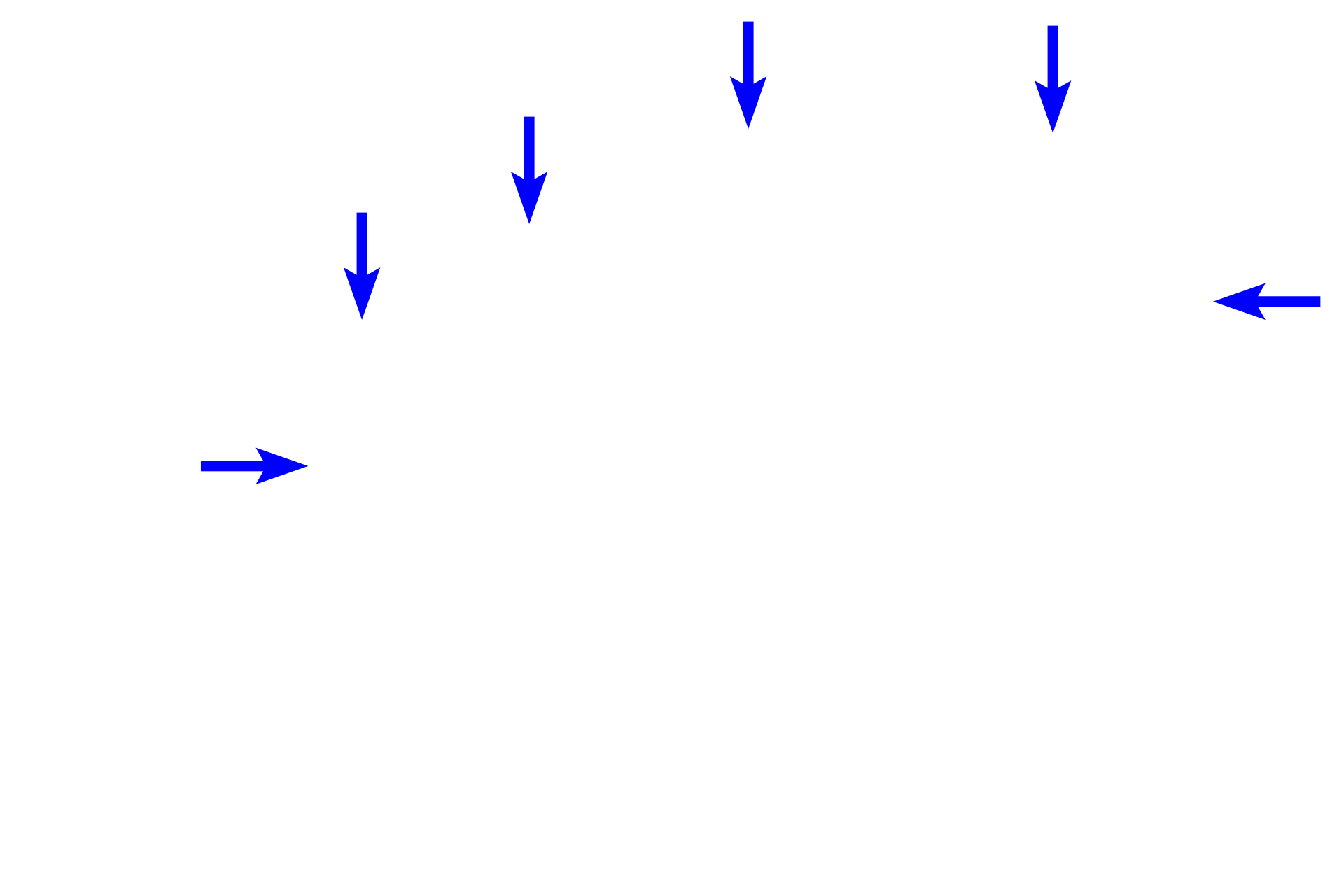
- Proliferating cells
Holocrine secretion involves the release of entire cells or their fragments from the secretory unit, as shown in this image of a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle. At the periphery of the acinus, cells proliferate and move toward the center, accumulating lipid as they mature, enlarge and degenerate. In this example of a sebaceous gland, lipid-filled cells either rupture their contents, sebum, or are shed as whole cells onto the hair shaft in a hair follicle. 400x
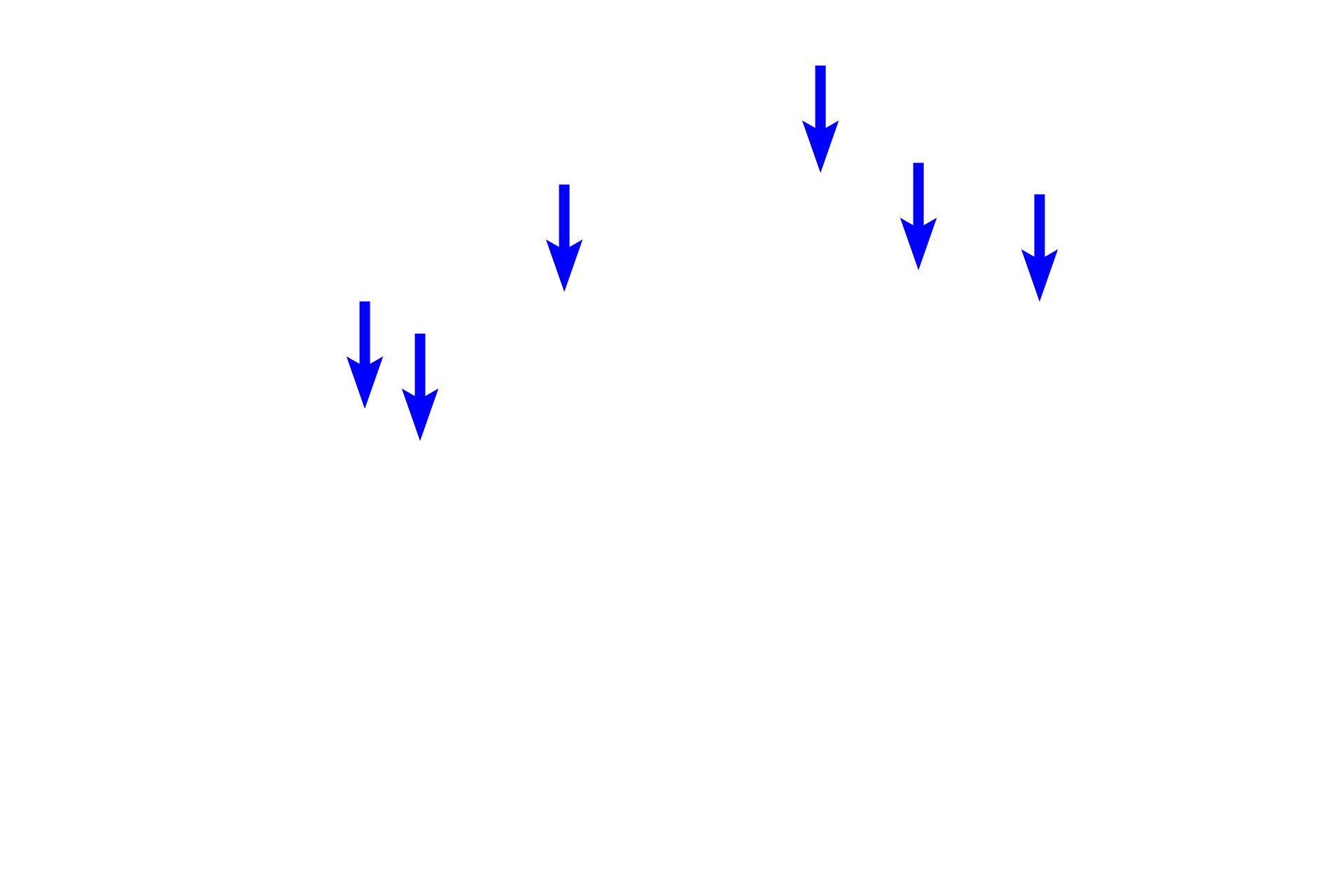
- Cells accumulating lipid
Holocrine secretion involves the release of entire cells or their fragments from the secretory unit, as shown in this image of a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle. At the periphery of the acinus, cells proliferate and move toward the center, accumulating lipid as they mature, enlarge and degenerate. In this example of a sebaceous gland, lipid-filled cells either rupture their contents, sebum, or are shed as whole cells onto the hair shaft in a hair follicle. 400x
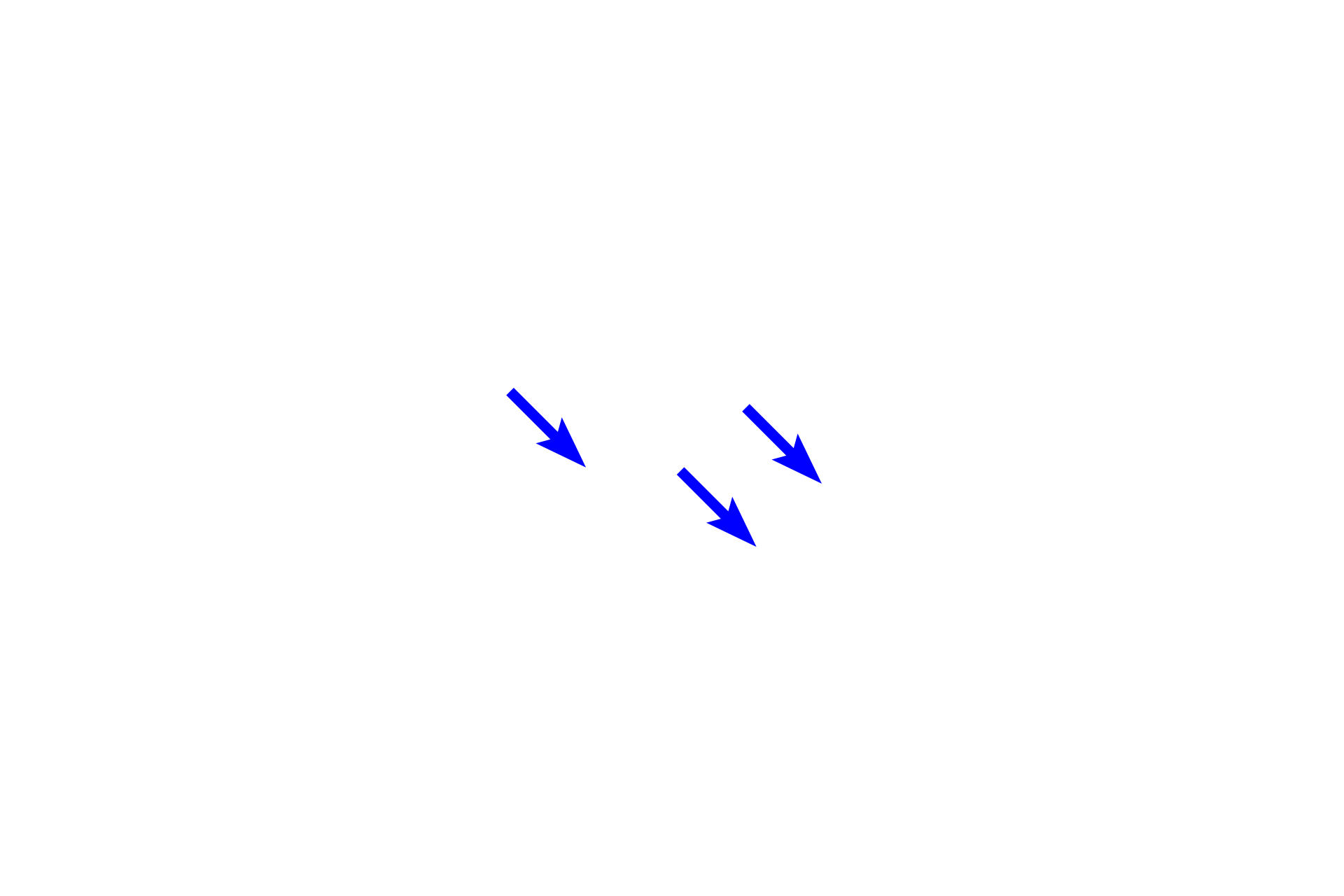
- Lipid-filled, degenerating cells
Holocrine secretion involves the release of entire cells or their fragments from the secretory unit, as shown in this image of a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle. At the periphery of the acinus, cells proliferate and move toward the center, accumulating lipid as they mature, enlarge and degenerate. In this example of a sebaceous gland, lipid-filled cells either rupture their contents, sebum, or are shed as whole cells onto the hair shaft in a hair follicle. 400x
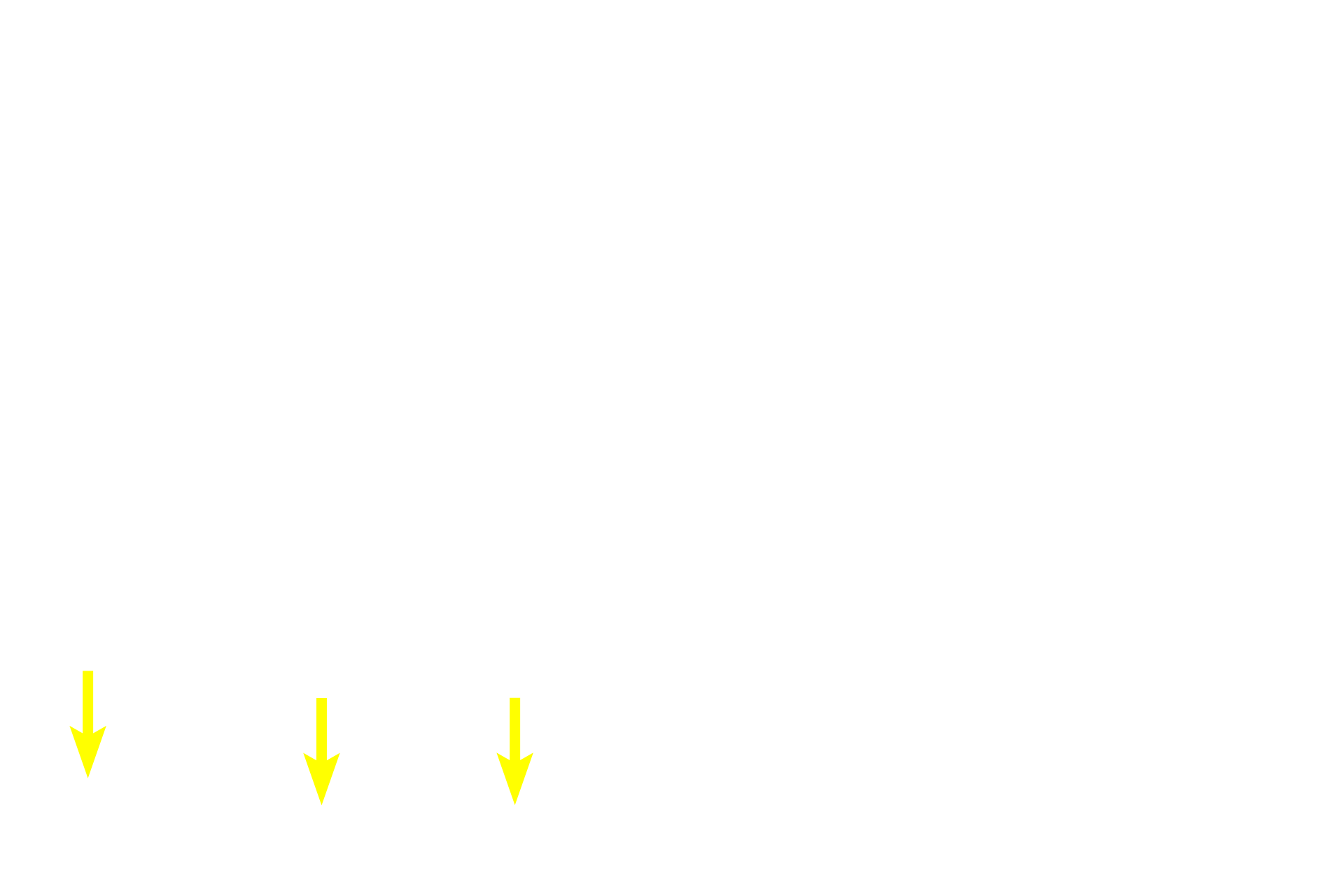
Sebum
Holocrine secretion involves the release of entire cells or their fragments from the secretory unit, as shown in this image of a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle. At the periphery of the acinus, cells proliferate and move toward the center, accumulating lipid as they mature, enlarge and degenerate. In this example of a sebaceous gland, lipid-filled cells either rupture their contents, sebum, or are shed as whole cells onto the hair shaft in a hair follicle. 400x

Hair follicle
Holocrine secretion involves the release of entire cells or their fragments from the secretory unit, as shown in this image of a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle. At the periphery of the acinus, cells proliferate and move toward the center, accumulating lipid as they mature, enlarge and degenerate. In this example of a sebaceous gland, lipid-filled cells either rupture their contents, sebum, or are shed as whole cells onto the hair shaft in a hair follicle. 400x
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS