
Basic tissues
Tissues are groups of cells organized for specific functions. The four tissue types, epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous, differ in composition and appearance, reflecting their various functions. Epithelial, muscle and nervous tissues are composed of closely packed cells with little extracellular material. Connective tissues are unique in their abundant extracellular components along with various cells types. Left: 1000x, 400x; Right: 600x, 600x
Epithelial tissue >
Epithelial tissues consist of closely-spaced cells, arranged in single or multiple layers, that both line or cover all body surfaces as well as form glands. Single-layer epithelia often have surface specializations, like cilia seen here. Individual cells are bound together by junctions that isolate the surface space from the intercellular space, thus providing integrity to the epithelial layer. All epithelia rest on a basement membrane.

Epithelium >
The upper panel shows an epithelium with a single layer of cells with cilia. The epithelium in the lower panel has multiple cell layers. All epithelia have a free surface and rest on a basement membrane.
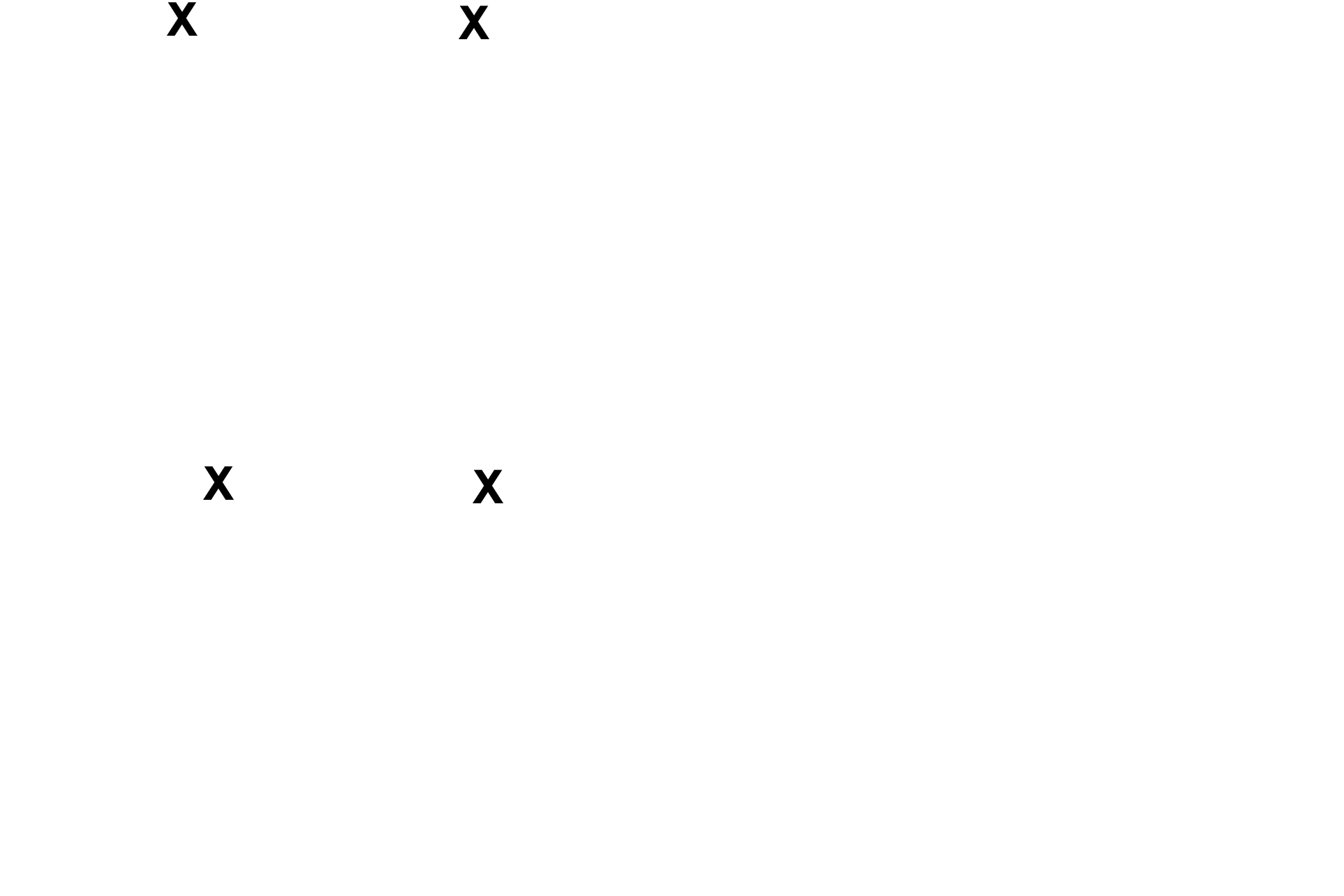
- Free surface
The upper panel shows an epithelium with a single layer of cells with cilia. The epithelium in the lower panel has multiple cell layers. All epithelia have a free surface and rest on a basement membrane.
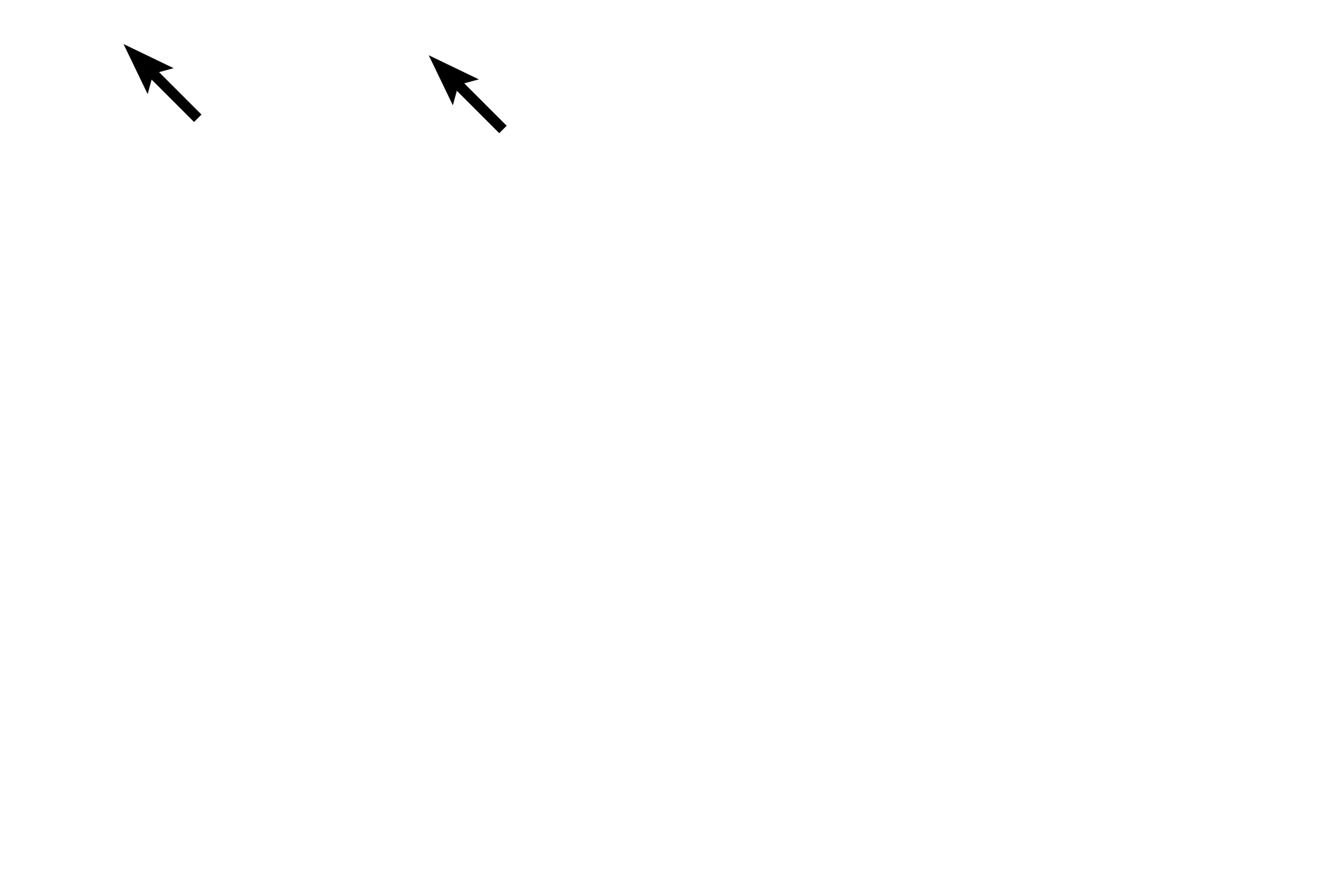
- Cilia
The upper panel shows an epithelium with a single layer of cells with cilia. The epithelium in the lower panel has multiple cell layers. All epithelia have a free surface and rest on a basement membrane.
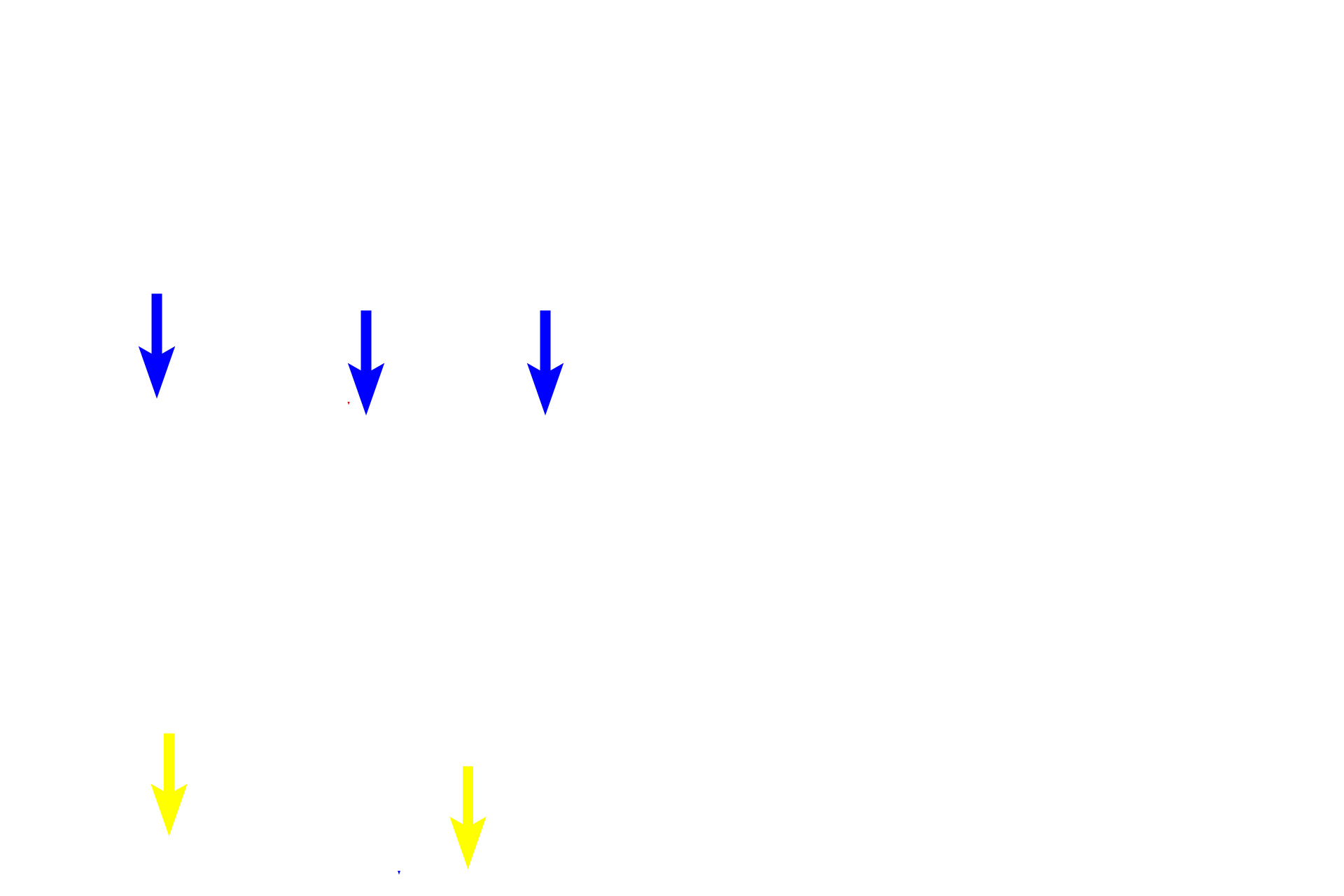
- Basement membrane
The upper panel shows an epithelium with a single layer of cells with cilia. The epithelium in the lower panel has multiple cell layers. All epithelia have a free surface and rest on a basement membrane.
Connective tissue >
Connective tissues possess cells and an abundant extracellular matrix. The matrix, imparting unique functions to this tissue, is composed of ground substance (with the consistency of a liquid, a gel or a flexible rubber) and fibers (providing a framework and strength). Major connective tissue types include blood, connective tissue proper, cartilage and bone.
- Cells
Connective tissues possess cells and an abundant extracellular matrix. The matrix, imparting unique functions to this tissue, is composed of ground substance (with the consistency of a liquid, a gel or a flexible rubber) and fibers (providing a framework and strength). Major connective tissue types include blood, connective tissue proper, cartilage and bone.
- Fibers
Connective tissues possess cells and an abundant extracellular matrix. The matrix, imparting unique functions to this tissue, is composed of ground substance (with the consistency of a liquid, a gel or a flexible rubber) and fibers (providing a framework and strength). Major connective tissue types include blood, connective tissue proper, cartilage and bone.
- Ground substance
Connective tissues possess cells and an abundant extracellular matrix. The matrix, imparting unique functions to this tissue, is composed of ground substance (with the consistency of a liquid, a gel or a flexible rubber) and fibers (providing a framework and strength). Major connective tissue types include blood, connective tissue proper, cartilage and bone.
