
Skeletal muscle
Prominent cross striations are a distinct feature of skeletal muscle fibers, and are only visible in longitudinal section, shown here. The distinct cross striations result from the precise alignment and overlap of the thin and thick myofilaments. Seen here are the A and I bands and the Z lines. Additionally, a paler region in the center of the A band is the H band. The segment of the myofibril between adjacent Z lines is the sarcomere and represents the contractile unit of striated muscle. 1000x
Muscle fiber
Prominent cross striations are a distinct feature of skeletal muscle fibers, and are only visible in longitudinal section, shown here. The distinct cross striations result from the precise alignment and overlap of the thin and thick myofilaments. Seen here are the A and I bands and the Z lines. Additionally, a paler region in the center of the A band is the H band. The segment of the myofibril between adjacent Z lines is the sarcomere and represents the contractile unit of striated muscle. 1000x

Nuclei
Prominent cross striations are a distinct feature of skeletal muscle fibers, and are only visible in longitudinal section, shown here. The distinct cross striations result from the precise alignment and overlap of the thin and thick myofilaments. Seen here are the A and I bands and the Z lines. Additionally, a paler region in the center of the A band is the H band. The segment of the myofibril between adjacent Z lines is the sarcomere and represents the contractile unit of striated muscle.1000x
A bands >
The dark A band corresponds to the length of the thick filaments. Additionally, the H band appears as a paler region in the center of the A band.
- H band
The dark A band corresponds to the length of the thick filaments. Additionally, the H band appears as a paler region in the center of the A band.

I bands >
The light I band contains thin filaments only and is bisected by the Z line.
- Z lines
The light I band contains thin filaments only and is bisected by the Z line.
Sarcomeres >
The sarcomere is the contractile unit of striated muscles and extends from one Z line to another.
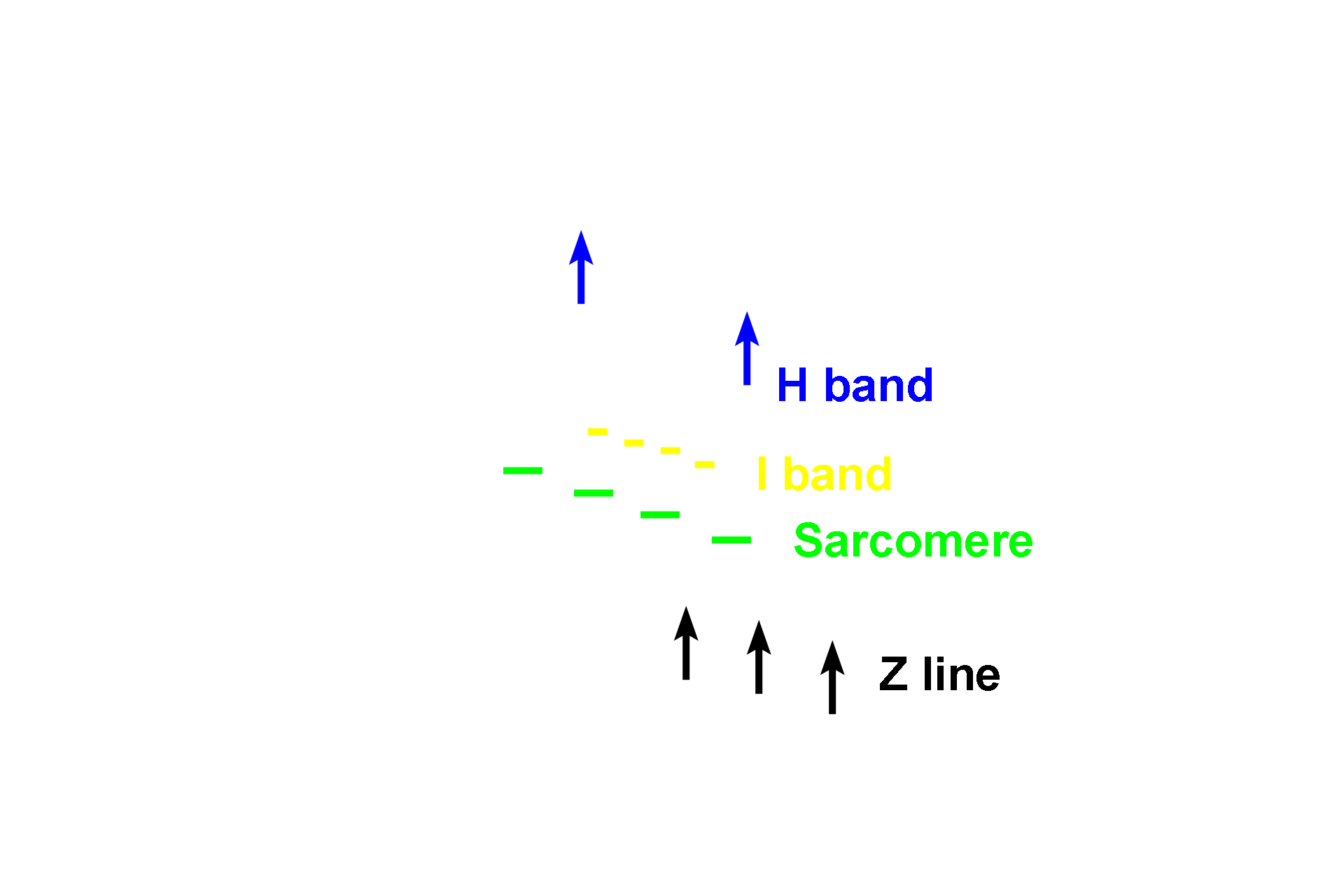
All bands >
The banding pattern of striated muscle results from the very regular overlap of myofilaments within each myofibril. Adjacent myofibrils are arranged in register, such that the banding pattern of individual myofibrils is aligned with adjacent myofibrils across the entire muscle fiber. This organization produces the striated appearance in both skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS