
Centrioles
A centriole is composed of nine triplets of microtubules arranged as a cylinder. Centrioles occur in pairs oriented at right angles to each other near the nucleus. The pair is called a diplosome. Centrioles are the site of origin of microtubules for the mitotic spindle and, in the form of basal bodies, are also located at the bases of cilia and flagella, where they organize the microtubules of these structures.
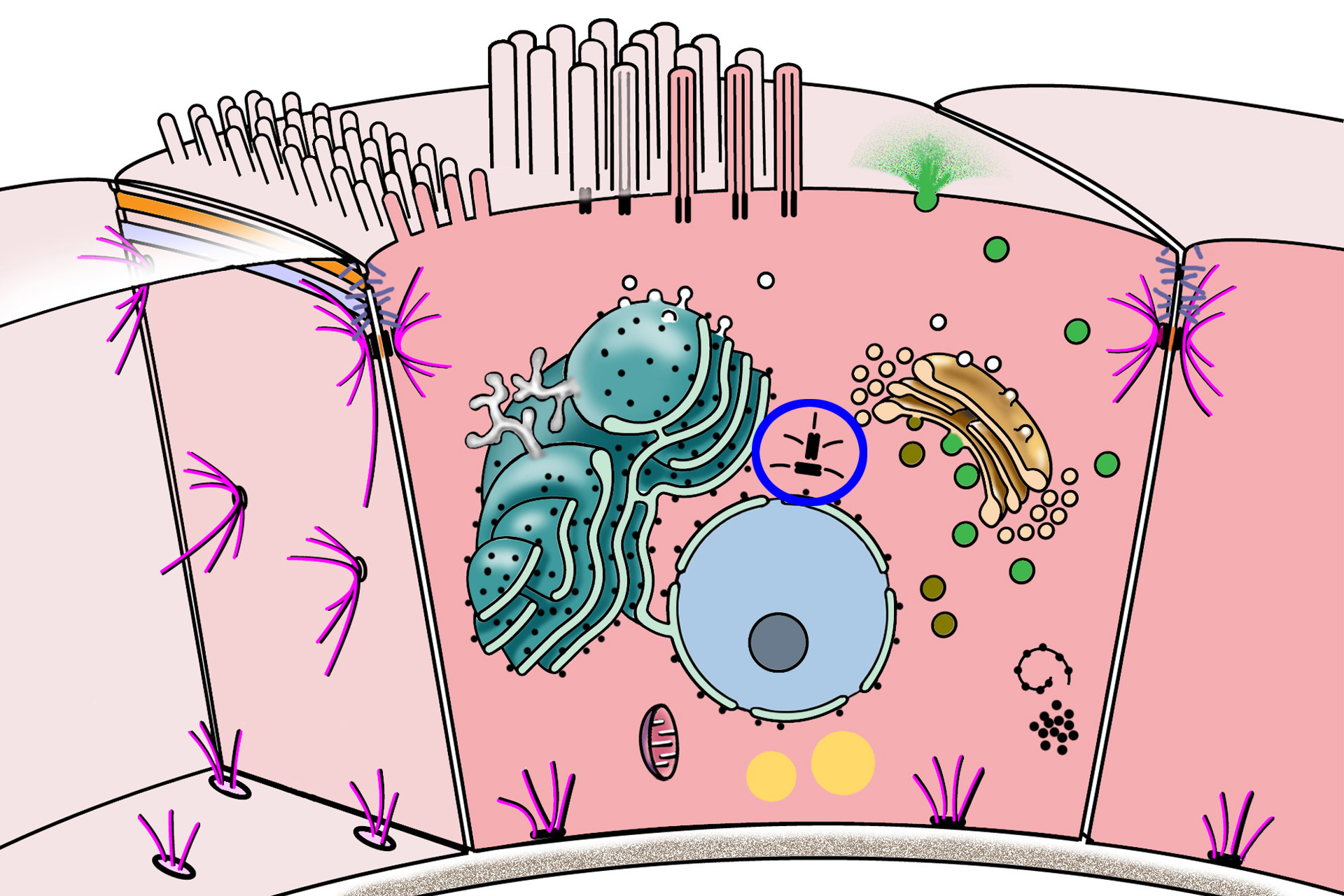
MTOC and diplosome >
The microtuble-organizing center (MTOC), or centrosome, is a region of the cell adjacent to the nucleus that contains the diplosome (paired centrioles) and its surrounding cytoplasm. Microtubules are formed and organized in the MTOC and distributed throughout the cell during interphase.
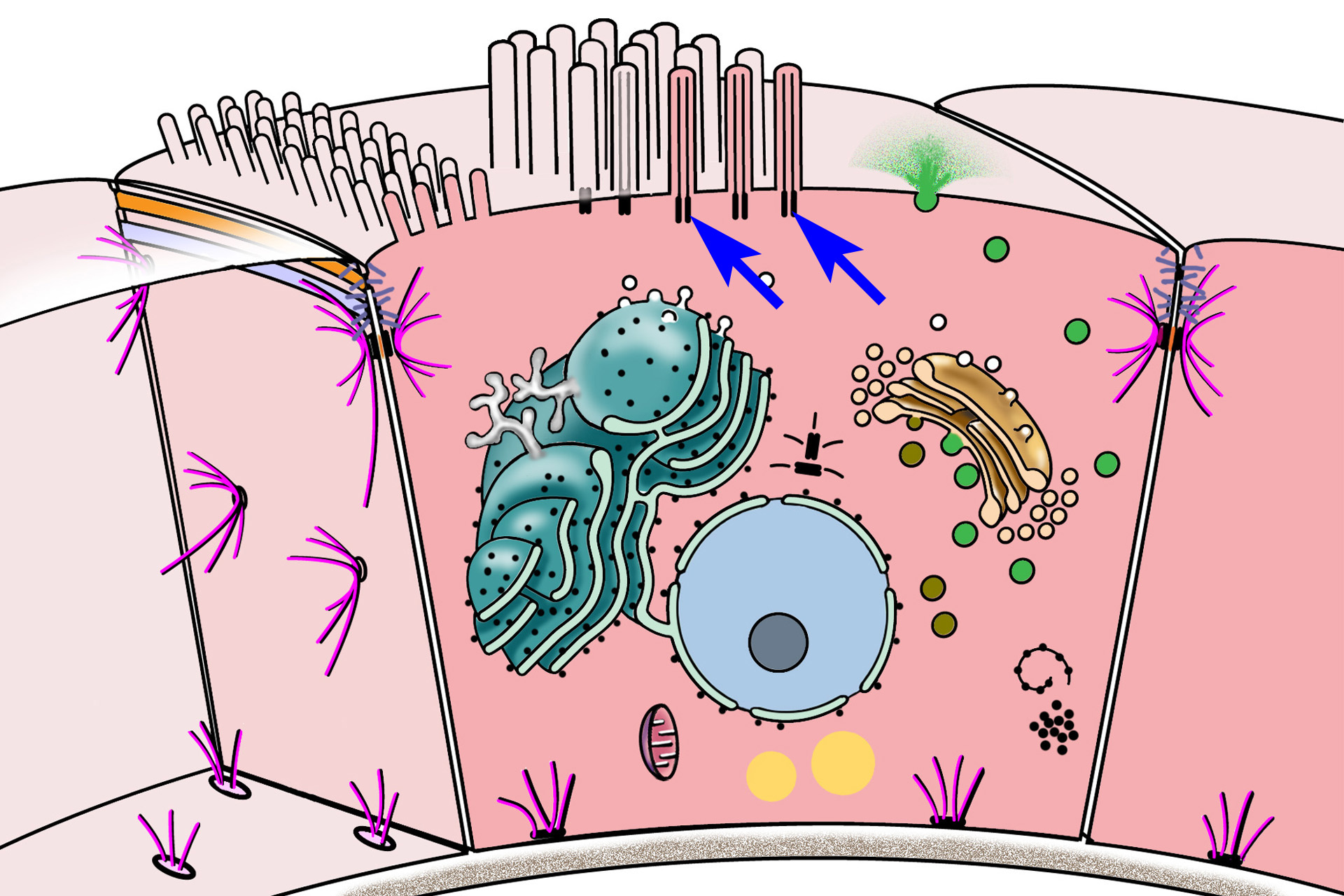
Basal bodies >
Centrioles also form basal bodies, located at the bases of cilia. Basal bodies act as organizing centers for microtubules that extend into each cilium. These microtubules form the core, called the axoneme, of each cilium, which is covered by the plasma membrane.
